Relativity
... constant velocity. You will notice during this time that the laws of motion will appear different in the room. The billiard balls on the table will roll backward on their own, as if acted upon by an unseen force. You may even have trouble walking because of the sensation of a force acting on you. Al ...
... constant velocity. You will notice during this time that the laws of motion will appear different in the room. The billiard balls on the table will roll backward on their own, as if acted upon by an unseen force. You may even have trouble walking because of the sensation of a force acting on you. Al ...
pdf - at www.arxiv.org.
... about Euler and his laws concerning rigid bodies, let us consider an important fact. We are used to define the angular momentum of a particle as a cross product of its position vector and its linear momentum. However, Euler, like Newton, did not use vectors in physics. They, of course, considered ve ...
... about Euler and his laws concerning rigid bodies, let us consider an important fact. We are used to define the angular momentum of a particle as a cross product of its position vector and its linear momentum. However, Euler, like Newton, did not use vectors in physics. They, of course, considered ve ...
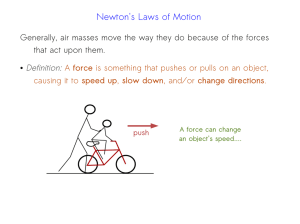
force
... is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame. We can cons ...
... is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame. We can cons ...
Physical Meaning of Hydrostatic Equilibrium of Celestial
... force which decreases the water weight in the last branch by the unit. He found by calculation that if the Earth has a uniform mass of matter and has no any motion and the ratio of its axis PQ to the diameter £¥ is 100:101, then the gravity force of the Earth at the point Q relates to the gravity fo ...
... force which decreases the water weight in the last branch by the unit. He found by calculation that if the Earth has a uniform mass of matter and has no any motion and the ratio of its axis PQ to the diameter £¥ is 100:101, then the gravity force of the Earth at the point Q relates to the gravity fo ...
10-1 Note 10 Rotational Motion I
... about an axis perpendicular to its plane passing through a point O. In the coordinate system of the figure, this axis can be thought of as the z-axis. We assume that the object is a rigid, extended body. By this we mean it cannot be modelled as a single particle. It can, however, be modelled (approx ...
... about an axis perpendicular to its plane passing through a point O. In the coordinate system of the figure, this axis can be thought of as the z-axis. We assume that the object is a rigid, extended body. By this we mean it cannot be modelled as a single particle. It can, however, be modelled (approx ...
CHAPTER 4
... 4.1 Forces and Motion 1. The space probe has a constant velocity in the +x direction when suddenly an engine exerts a force on the probe in the +x direction. 2. The space probe has a constant velocity in the +x direction when suddenly an engine exerts a force on the probe in the -x direction. 3. The ...
... 4.1 Forces and Motion 1. The space probe has a constant velocity in the +x direction when suddenly an engine exerts a force on the probe in the +x direction. 2. The space probe has a constant velocity in the +x direction when suddenly an engine exerts a force on the probe in the -x direction. 3. The ...
Dynamics: Newton’s Laws of Motion
... of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
C-Circular-Kinematics-Dynamics-Unit
... By the end of the unit, students will be able to… 1. distinguish between circular (“translational;” “tangential”) and rotational motion. 2. perform measurements and calculations involving period and frequency of rotating objects and objects moving in circular motion. 3. analyze the angular displacem ...
... By the end of the unit, students will be able to… 1. distinguish between circular (“translational;” “tangential”) and rotational motion. 2. perform measurements and calculations involving period and frequency of rotating objects and objects moving in circular motion. 3. analyze the angular displacem ...
Note
... If the path of a particle has been described in the polar or cylindrical co-ordinate system it is easy to obtain the force components in the r, , and z directions. If the normal and tangential components are required, de…ne the angle between the extended radial line, and the tangent to the path. ...
... If the path of a particle has been described in the polar or cylindrical co-ordinate system it is easy to obtain the force components in the r, , and z directions. If the normal and tangential components are required, de…ne the angle between the extended radial line, and the tangent to the path. ...
The Physical Forces of Everyday Life, 3, 10
... To prepare us for the statement of the last basic Rule for Forces, we need, first, to introduce the concept of torque or the moment of force. This concept provides a measure of the turning tendency or twisting strength of a force. That turning tendency depends not only on the strength and direction ...
... To prepare us for the statement of the last basic Rule for Forces, we need, first, to introduce the concept of torque or the moment of force. This concept provides a measure of the turning tendency or twisting strength of a force. That turning tendency depends not only on the strength and direction ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... rotate with the turntable, which way will the object go? ω Ans. It will follow the straight path along which the velocity vr ...
... rotate with the turntable, which way will the object go? ω Ans. It will follow the straight path along which the velocity vr ...
Class Notes - St. Bonaventure University
... Now, the amount of a physical quantity remains the same, no matter what system of units is used to obtain a numerical measure of that quantity. For instance, we might measure the length of an (American) football field with a meter stick and a yard stick. We’d get two different numerical values, but ...
... Now, the amount of a physical quantity remains the same, no matter what system of units is used to obtain a numerical measure of that quantity. For instance, we might measure the length of an (American) football field with a meter stick and a yard stick. We’d get two different numerical values, but ...
angular motion - Craigie High School
... Torque is a vector quantity. The direction of the torque vector is at right angles to the plane containing both r and F and lies along the axis of rotation. (In the example shown in the diagram torque, T, points out of the page). A force acting on the rim of an object will cause the object to rotate ...
... Torque is a vector quantity. The direction of the torque vector is at right angles to the plane containing both r and F and lies along the axis of rotation. (In the example shown in the diagram torque, T, points out of the page). A force acting on the rim of an object will cause the object to rotate ...