2 Kepler`s Laws
... Compromise Theory: The Sun orbits the Earth, but the remaining planets orbit the Sun. Brahe passed along his observations to Johannes Kepler, his assistant. ...
... Compromise Theory: The Sun orbits the Earth, but the remaining planets orbit the Sun. Brahe passed along his observations to Johannes Kepler, his assistant. ...
Ancient Mathematics 450 B.C. 400 B.C. 350 B.C. 300 B.C. 250 B.C.
... Created a system of latitude and longitude, calculated the circumference of the earth and tilt of earth’s axis, attempted to calculate the distance to the Moon and Sun. ...
... Created a system of latitude and longitude, calculated the circumference of the earth and tilt of earth’s axis, attempted to calculate the distance to the Moon and Sun. ...
Topic 9/10
... Celestial sphere- sphere with reference points to outer space Celestial object- any object outside or above Earth’s atmosphere Terrestrial- Earth-like Constellation- group of stars forming a pattern in the sky Geocentric- Earth centered model of the solar system Heliocentric model- Sun centered mode ...
... Celestial sphere- sphere with reference points to outer space Celestial object- any object outside or above Earth’s atmosphere Terrestrial- Earth-like Constellation- group of stars forming a pattern in the sky Geocentric- Earth centered model of the solar system Heliocentric model- Sun centered mode ...
Solar System Bead Distance Activity
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
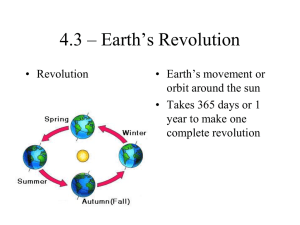
4.3 – Earth`s Revolution
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...
... • Evidence the Earth is revolving around the sun • Stars seem to change position throughout the course of the year – look closer or father away • ACTUALLY!! Earth is moving – not the star ...
The Earth in Space
... We are about 93,000,000 miles from the sun (it takes 8 minutes for sunlight to reach us!) ...
... We are about 93,000,000 miles from the sun (it takes 8 minutes for sunlight to reach us!) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2003
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
1 PS 3.9 Grade 9 Review
... Doppler effect solar eclipse lunar eclipse risks of space travel benefits of space travel technology in space types of galaxies neutron star big bang theory galaxy dwarf star hydrogen & helium aurora borealis solar wind ...
... Doppler effect solar eclipse lunar eclipse risks of space travel benefits of space travel technology in space types of galaxies neutron star big bang theory galaxy dwarf star hydrogen & helium aurora borealis solar wind ...
Mon May 27, 2013 THE VENERABLE BEDE FEAST DAY On May
... Sixty years ago, on May 28th, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay of Nepal, became the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, the highest mountain on earth. This great peak is over 29,000 feet above sea level – that’s almost five and a half miles up, the highest poi ...
... Sixty years ago, on May 28th, 1953, Edmund Hillary of New Zealand and Tenzing Norgay of Nepal, became the first explorers to reach the summit of Mount Everest, the highest mountain on earth. This great peak is over 29,000 feet above sea level – that’s almost five and a half miles up, the highest poi ...
Our Sun is a Star:
... What are the dark spots on this picture? (Hint: they are not sunspots.) ___ Coronal Holes ___ Plumes ___ Active Regions ...
... What are the dark spots on this picture? (Hint: they are not sunspots.) ___ Coronal Holes ___ Plumes ___ Active Regions ...
Earth, Space and all that jazz… A long time ago, in the second
... Earth, Space and all that jazz… A long time ago, in the second century, There was a Greek astronomer called Claudius Ptolemy. Who came up with a theory called the geocentric model, Which made the Earth the focal point and centre of it all. Centuries went past before some began to doubt. ‘We simply d ...
... Earth, Space and all that jazz… A long time ago, in the second century, There was a Greek astronomer called Claudius Ptolemy. Who came up with a theory called the geocentric model, Which made the Earth the focal point and centre of it all. Centuries went past before some began to doubt. ‘We simply d ...
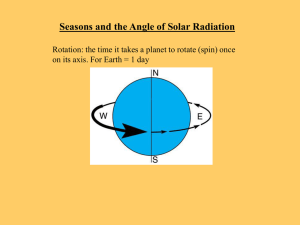
Sidereal and Solar Time
... Sidereal and Solar Time We measure time according to the position of the Sun in the sky. o Our day is the time from Noon to Noon and is exactly 24 hours long. This time period is called a ``Solar Day''. It takes the Earth 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds to complete a rotation. o This time pe ...
... Sidereal and Solar Time We measure time according to the position of the Sun in the sky. o Our day is the time from Noon to Noon and is exactly 24 hours long. This time period is called a ``Solar Day''. It takes the Earth 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds to complete a rotation. o This time pe ...
5th Grade Solar System - Mrs. Kellogg`s 5th Grade Class
... L.O. I will describe what is in our solar system. ...
... L.O. I will describe what is in our solar system. ...
Coordinate System Notes 3 - School District of La Crosse
... A. year- the time necessary for one complete revolution about the sun 365.25 mean solar days. B.Types of years 1. sidereal year- The time necessary for the sun to return to the same position with repect to the stars. 2. solar year( tropical) is the intreval between the passage of the sun through the ...
... A. year- the time necessary for one complete revolution about the sun 365.25 mean solar days. B.Types of years 1. sidereal year- The time necessary for the sun to return to the same position with repect to the stars. 2. solar year( tropical) is the intreval between the passage of the sun through the ...
Review-Sheet-sun-solar-system-galaxies-and-cosmology-fall
... 1. What are the three layers of the sun’s interior? What part is responsible for fusion? 2. What are the three layers of the Sun’s atmosphere? Be able to describe them briefly, such as lowest layer, the visible surface, etc… 3. What is the solar wind? What happens when the solar wind gets trapped in ...
... 1. What are the three layers of the sun’s interior? What part is responsible for fusion? 2. What are the three layers of the Sun’s atmosphere? Be able to describe them briefly, such as lowest layer, the visible surface, etc… 3. What is the solar wind? What happens when the solar wind gets trapped in ...
Seasons
... Solstice is when the Sun rises or sets as far North or South of the equator as it can (days are longest or shortest) Equinox is when the Sun crosses the equator, so the days and nights are equal in time ...
... Solstice is when the Sun rises or sets as far North or South of the equator as it can (days are longest or shortest) Equinox is when the Sun crosses the equator, so the days and nights are equal in time ...
Document
... from a star is shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum? The star is moving towards the observer. ...
... from a star is shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum? The star is moving towards the observer. ...
(Lecture 3). The Solar System in the Night Sky (cont)
... count 365 days, and exactly 365 mean solar days later, as the Sun crosses the Meridian, we celebrate the start of the new year. The trouble is, the Sun has not returned to the same place relative to the stars. It is still 0.25 days away from that point. After the next year, it is half a day, and the ...
... count 365 days, and exactly 365 mean solar days later, as the Sun crosses the Meridian, we celebrate the start of the new year. The trouble is, the Sun has not returned to the same place relative to the stars. It is still 0.25 days away from that point. After the next year, it is half a day, and the ...
The Sun as We See It Lecture 10, September 17, 2003
... The Sun has a “heartbeat”; its properties change on a period of 11 years ...
... The Sun has a “heartbeat”; its properties change on a period of 11 years ...
3observing3s
... Can measure distance on the sky in degrees (360 degrees = complete circle) Horizon -Zenith -Meridian -- line running from north to south through zenith ...
... Can measure distance on the sky in degrees (360 degrees = complete circle) Horizon -Zenith -Meridian -- line running from north to south through zenith ...