What causes the moon to change in appearance
... moon is changing its shape in the sky. This is because as the moon changes its position, the amount of sunlight reflected back to Earth also changes. The moon sometimes appears fully lit and sometimes completely dark. Most of the time we see it partially lit. The North and South Poles mark Earth’s a ...
... moon is changing its shape in the sky. This is because as the moon changes its position, the amount of sunlight reflected back to Earth also changes. The moon sometimes appears fully lit and sometimes completely dark. Most of the time we see it partially lit. The North and South Poles mark Earth’s a ...
Shouting in the Jungle: the SETI Transmission Debate
... greater than this]. The pc is defined as the distance at which an object displays a parallax of 1 second of arc across a baseline of 1 astronomical unit (which is, of course, the radius of the Earth’s orbit). By symmetry, the Earth, as viewed from that star, will thus appear to be separated from the ...
... greater than this]. The pc is defined as the distance at which an object displays a parallax of 1 second of arc across a baseline of 1 astronomical unit (which is, of course, the radius of the Earth’s orbit). By symmetry, the Earth, as viewed from that star, will thus appear to be separated from the ...
The evolution of the Sun`s birth cluster and the search for the solar
... The Galactic bar The central bar is modelled with a Ferrers potential (Ferrers 1877) which describes the potential associated to an elliptical distribution of mass. In an inertial frame located at the Galactic centre, the bar rotates with a constant pattern speed of 40–70 km s−1 kpc−1 (Martı́nez-Bar ...
... The Galactic bar The central bar is modelled with a Ferrers potential (Ferrers 1877) which describes the potential associated to an elliptical distribution of mass. In an inertial frame located at the Galactic centre, the bar rotates with a constant pattern speed of 40–70 km s−1 kpc−1 (Martı́nez-Bar ...
Galaxy / Cluster Ecosystem Ming Sun (University of Alabama in Huntsville)
... embedded in the 6.7 keV ICM. A sharp edge 0.8 kpc south of the nucleus. Galaxy’svelocity vs.Perseus’s: + 2170 km/s --Mach number of ~ 3 --- a Bullet galaxy ! Soft X-ray Radio Optical Sun, Jerius & Jones 2005 ...
... embedded in the 6.7 keV ICM. A sharp edge 0.8 kpc south of the nucleus. Galaxy’svelocity vs.Perseus’s: + 2170 km/s --Mach number of ~ 3 --- a Bullet galaxy ! Soft X-ray Radio Optical Sun, Jerius & Jones 2005 ...
GEK 1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy
... Men have always been conscious of the passing of time, constantly seeking to invent instruments to tell time accurately. As people in the past started following the Sun’s movement in a day, they observed its motion across the sky as it rises in the East, climbs to its highest point in the sky (due S ...
... Men have always been conscious of the passing of time, constantly seeking to invent instruments to tell time accurately. As people in the past started following the Sun’s movement in a day, they observed its motion across the sky as it rises in the East, climbs to its highest point in the sky (due S ...
Venus Retrograde 2015: Love, Lust and War
... Mercury and Venus (which are inferior planets since they lie closer to the Sun than the Earth) will always form an inferior conjunction with the Sun (i.e., between the Sun and the Earth) midway through their retrograde cycle. Conjunctions of Sun with either Mercury or Venus alternate their conjunct ...
... Mercury and Venus (which are inferior planets since they lie closer to the Sun than the Earth) will always form an inferior conjunction with the Sun (i.e., between the Sun and the Earth) midway through their retrograde cycle. Conjunctions of Sun with either Mercury or Venus alternate their conjunct ...
STELLAR CLASSIFICATIONS: TYPE “O” STARS
... worth knowing. These are “sub-stellar” objects, commonly called red and brown dwarfs. What distinguishes these objects from real stars is that dwarfs do not undergo stellar fusion. Their cores never quite reach a high enough temperature to turn hydrogen into helium. So why do we not just call them p ...
... worth knowing. These are “sub-stellar” objects, commonly called red and brown dwarfs. What distinguishes these objects from real stars is that dwarfs do not undergo stellar fusion. Their cores never quite reach a high enough temperature to turn hydrogen into helium. So why do we not just call them p ...
SECTION28.1 Formation of the Solar System
... • Within the rotating disk surrounding the young Sun, the temperature varied greatly with location. This resulted in different elements and compounds condensing, depending on their distance from the Sun, and affected the distribution of elements in the forming planets. ...
... • Within the rotating disk surrounding the young Sun, the temperature varied greatly with location. This resulted in different elements and compounds condensing, depending on their distance from the Sun, and affected the distribution of elements in the forming planets. ...
Brightness and Flux Density
... we distinguish between the brightness of the Sun, which does not depend on distance, and the apparent flux, which does. Note also that the number of photons per unit area hitting the film is proportional to cos Ò if the normal to the film is tilted by an angle Ò from the ray direction. This is just ...
... we distinguish between the brightness of the Sun, which does not depend on distance, and the apparent flux, which does. Note also that the number of photons per unit area hitting the film is proportional to cos Ò if the normal to the film is tilted by an angle Ò from the ray direction. This is just ...
PDF format
... c) No, the celestial sphere is so far away that, even moving at close to the speed of light, it would take tens of thousands of years to reach. d) No, the celestial sphere moves away from us at the speed of light so we can never catch up with it. e) This statement doesn't make sense because the c ...
... c) No, the celestial sphere is so far away that, even moving at close to the speed of light, it would take tens of thousands of years to reach. d) No, the celestial sphere moves away from us at the speed of light so we can never catch up with it. e) This statement doesn't make sense because the c ...
Solar System
... Due to their higher boiling points, only metals and silicates could exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very small fraction of the solar n ...
... Due to their higher boiling points, only metals and silicates could exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very small fraction of the solar n ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 1. How do the positions of the celestial equator depend on the latitude of the observer? The position of the celestial equator has depends on the observer’s latitude in the following manner. The points where the celestial equator intersect the horizon are 90° azimuth (due East) and 270° azimuth (due ...
... 1. How do the positions of the celestial equator depend on the latitude of the observer? The position of the celestial equator has depends on the observer’s latitude in the following manner. The points where the celestial equator intersect the horizon are 90° azimuth (due East) and 270° azimuth (due ...
Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem
... The three principal coordinate systems in the sky are described in Sec. II; they are based on the local horizon, on the equator, and on the ecliptic. The relations between these coordinate systems are fundamental for understanding the process of observing and interpreting the results of the observat ...
... The three principal coordinate systems in the sky are described in Sec. II; they are based on the local horizon, on the equator, and on the ecliptic. The relations between these coordinate systems are fundamental for understanding the process of observing and interpreting the results of the observat ...
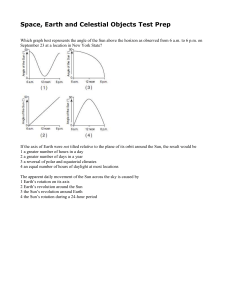
Space, Earth and Celestial Objects Test Prep
... and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupiter or Mars. The closest known near-Earth collision was in 1994, when asteroid 1994 XL1 came within the Moon’s orb ...
... and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupiter or Mars. The closest known near-Earth collision was in 1994, when asteroid 1994 XL1 came within the Moon’s orb ...
Solar system formation by accretion has no observational evidence
... there had been no nebula. On the other hand, observations of debris formation are common in astronomy, especially in cases of stellar instability discussed below. The cosmos seems to be undergoing dissolution rather than evolving. This is why theorists have been unable to explain how the solar nebul ...
... there had been no nebula. On the other hand, observations of debris formation are common in astronomy, especially in cases of stellar instability discussed below. The cosmos seems to be undergoing dissolution rather than evolving. This is why theorists have been unable to explain how the solar nebul ...
PHYS_3380_082615_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - in some regions, not much differentiation between the seasons. - different constellations visible at different times of the year - can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summer. - many of the myths associated wit ...
... - in some regions, not much differentiation between the seasons. - different constellations visible at different times of the year - can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summer. - many of the myths associated wit ...
THE MATHEMATICS OF ASTROLOGY
... fire, earth, air and water. The division according to the squares are the cardinal signs, the fixed signs, and the mutable signs. The geometrical group formed by the inscribed hexagon are either positive or negative signs. The positives signs are supposed to be masculine, while the negative signs ar ...
... fire, earth, air and water. The division according to the squares are the cardinal signs, the fixed signs, and the mutable signs. The geometrical group formed by the inscribed hexagon are either positive or negative signs. The positives signs are supposed to be masculine, while the negative signs ar ...
Chapter2.1
... What have we learned? • What causes the seasons? – The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes sunlight to hit different parts of the Earth more directly during the summer and less directly during the winter. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and ...
... What have we learned? • What causes the seasons? – The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes sunlight to hit different parts of the Earth more directly during the summer and less directly during the winter. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and ...
SUPREME WISDOM 99 ACTUAL FACTS
... 82) The Black Man has 7 ½ Ounces of Original Brain. 83) The White Man has 6 Ounces of Grafted Brain. 84) The Black Man has 14 Billion Brain Cells. 85) Thought Travels at the Rate of 24 Billion Miles (Per Second) 86) The Black Man’s Brain CAN contain 360 Degrees of Knowledge. 87) The White Man’s Brai ...
... 82) The Black Man has 7 ½ Ounces of Original Brain. 83) The White Man has 6 Ounces of Grafted Brain. 84) The Black Man has 14 Billion Brain Cells. 85) Thought Travels at the Rate of 24 Billion Miles (Per Second) 86) The Black Man’s Brain CAN contain 360 Degrees of Knowledge. 87) The White Man’s Brai ...
Johannes Kepler`s on the More Certain
... mundane task of predicting terrestrial events. Nevertheless, both disciplines have in common a concern with the heavens, and both have a rational basis for their operation. Ptolemy states: Of the means of prediction through [celestial observations] . . . two are the most importantand valid. One, whi ...
... mundane task of predicting terrestrial events. Nevertheless, both disciplines have in common a concern with the heavens, and both have a rational basis for their operation. Ptolemy states: Of the means of prediction through [celestial observations] . . . two are the most importantand valid. One, whi ...
Document
... separations, plus the largest and smallest superior conjunction separations. [Example: Earth’s total variation is about 3 percent, or 1.5 percent plus or minus from the average of 1 AU. Thus, the minimum is 0.985 AU. For Mars the change is about 10 percent either way, so its minimum is 1.52 AU *1.1 ...
... separations, plus the largest and smallest superior conjunction separations. [Example: Earth’s total variation is about 3 percent, or 1.5 percent plus or minus from the average of 1 AU. Thus, the minimum is 0.985 AU. For Mars the change is about 10 percent either way, so its minimum is 1.52 AU *1.1 ...
Your Astrology Defense Kit
... The Precession of the Earth: Are You Reading the Wrong Horoscope? Our Earth moves through space in a variety of ways. In addition to rotating on its axis (giving us our day) and orbiting the Sun (giving us our year), Earth has another — more gradual — motion that few people know about. Our planet’s ...
... The Precession of the Earth: Are You Reading the Wrong Horoscope? Our Earth moves through space in a variety of ways. In addition to rotating on its axis (giving us our day) and orbiting the Sun (giving us our year), Earth has another — more gradual — motion that few people know about. Our planet’s ...
Geometry of orbits - Harpursville Middle School
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
Chapter2 - Discovering the Universe for yourself-pptx
... set at most extreme north of due east Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most extreme south of due east Equinoxes: Sun rises precisely due east and sets precisely due west. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... set at most extreme north of due east Winter solstice: Lowest path, rise and set at most extreme south of due east Equinoxes: Sun rises precisely due east and sets precisely due west. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
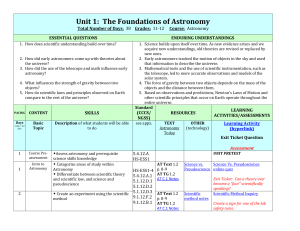
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...