COMETS
... a dust and a plasma tail. The shape and development of the former is governed mainly by Sun’s gravitation and radiation pressure. The interaction between coma and solar wind (and magnetic field it carries along) define the latter. While our knowledge about comets is advancing rapidly there are still ...
... a dust and a plasma tail. The shape and development of the former is governed mainly by Sun’s gravitation and radiation pressure. The interaction between coma and solar wind (and magnetic field it carries along) define the latter. While our knowledge about comets is advancing rapidly there are still ...
UCLA 2004
... •Requires supernova < 10 pc away, ~ 1 Myr before CAIs formed •What are the odds our Solar System “happened” be near supernova? Like case of AGB star: too low. ...
... •Requires supernova < 10 pc away, ~ 1 Myr before CAIs formed •What are the odds our Solar System “happened” be near supernova? Like case of AGB star: too low. ...
Electronic version of lab manual 1-6 ()
... planets/moons/stars is to construct ratios between these celestial bodies so that sizes can be examined in relation to one other. The question could be asked, “How many times larger/smaller is one object than another?” To answer this question requires that we set up a ratio between the two objects. ...
... planets/moons/stars is to construct ratios between these celestial bodies so that sizes can be examined in relation to one other. The question could be asked, “How many times larger/smaller is one object than another?” To answer this question requires that we set up a ratio between the two objects. ...
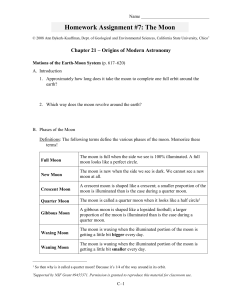
Tilting Into The Seasons
... northern and southern hemispheres. The geographical equator is also the line from which latitudes are measured whereby the latitude of any single point on the equator is 0 degrees. But in astronomy, it is that great circle in which the plane of the equator of the earth intersects the celestial spher ...
... northern and southern hemispheres. The geographical equator is also the line from which latitudes are measured whereby the latitude of any single point on the equator is 0 degrees. But in astronomy, it is that great circle in which the plane of the equator of the earth intersects the celestial spher ...
moon phases and eclipses - Morehead Planetarium and Science
... • Earth’s rotation. It takes 24 hours for the Sun to return to its highest point in the sky (solar day), but only 23 hours and 56 minutes for Earth to rotate when measured relative to the “fixed” stars (sidereal day). Learn more at http:// earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/what-is-sidereal-time ...
... • Earth’s rotation. It takes 24 hours for the Sun to return to its highest point in the sky (solar day), but only 23 hours and 56 minutes for Earth to rotate when measured relative to the “fixed” stars (sidereal day). Learn more at http:// earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/what-is-sidereal-time ...
Microsoft Word
... heavenly bodies were the sun, the moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. The outermost planets (Neptune, Uranus and Pluto) also “wander” but the ancients didn't know about them because you need a telescope to see them (which is a very good thing-can you imagine having 8-day w ...
... heavenly bodies were the sun, the moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. The outermost planets (Neptune, Uranus and Pluto) also “wander” but the ancients didn't know about them because you need a telescope to see them (which is a very good thing-can you imagine having 8-day w ...
Dynamical theory of the solar wind
... energy.* A tightly bound atmosphere traditionally has been considered to be in hydrostatic equilibrium. Escape from the atmosphere is limited to evaporation, or thermionic emission, of the small portion of atoms in the outer layers whose thermal velocity exceeds the escape velocity, as discussed by ...
... energy.* A tightly bound atmosphere traditionally has been considered to be in hydrostatic equilibrium. Escape from the atmosphere is limited to evaporation, or thermionic emission, of the small portion of atoms in the outer layers whose thermal velocity exceeds the escape velocity, as discussed by ...
Accuracy of spectroscopy-based radioactive dating of stars
... obtained by propagating the error in Eq. (5). One may also try to derive an equivalent width for the blended line by subtracting the theoretical equivalent width of the blending components from the total W of the blend. However, in general, this ignores saturation effects, and thus the “corrected” W ...
... obtained by propagating the error in Eq. (5). One may also try to derive an equivalent width for the blended line by subtracting the theoretical equivalent width of the blending components from the total W of the blend. However, in general, this ignores saturation effects, and thus the “corrected” W ...
Read Full Article
... Using a one-degree orb, the progressed Moon will remain in aspect to a planet for nearly two months. When working with the progressed Moon’s aspects, be mindful of its natal aspects. When the progressed Moon contacts a planet that it natally aspects, it may be time to address some of the unconscious ...
... Using a one-degree orb, the progressed Moon will remain in aspect to a planet for nearly two months. When working with the progressed Moon’s aspects, be mindful of its natal aspects. When the progressed Moon contacts a planet that it natally aspects, it may be time to address some of the unconscious ...
Using Star Charts
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
On the Astronomical Meaning of the Day, Year, and Seasons
... Earth’s Orbit of the Sun (construct meaning of “orbital period”) [ST 9] ii. Adding Earth’s Tilt to Identify Winter & Summer [ST 10] iii. Insights on the Reasons for Seasons* (reasons for seasons emphasis: [ST 11 – ST 15]) iv. Finding the Equinoxes and Everyone’s Birthday v. What Does it Mean to “be ...
... Earth’s Orbit of the Sun (construct meaning of “orbital period”) [ST 9] ii. Adding Earth’s Tilt to Identify Winter & Summer [ST 10] iii. Insights on the Reasons for Seasons* (reasons for seasons emphasis: [ST 11 – ST 15]) iv. Finding the Equinoxes and Everyone’s Birthday v. What Does it Mean to “be ...
The Accuracy of the Astronomical Observations of Lewis and Clark*
... did so in the following way. About four hours before noon, one of them measured the sun’s altitude and recorded it along with the watch time. About eight hours later, as the sun was going down toward the horizon, the observer noted the watch reading at the instant the sun came back down to exactly t ...
... did so in the following way. About four hours before noon, one of them measured the sun’s altitude and recorded it along with the watch time. About eight hours later, as the sun was going down toward the horizon, the observer noted the watch reading at the instant the sun came back down to exactly t ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... describe and organize the night sky. Several specialists explain how different cultures named stars and constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video less ...
... describe and organize the night sky. Several specialists explain how different cultures named stars and constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video less ...
Mercury Transits on 9th May-2016
... A date with Mercury over Sun - Mercury Transits on Monday, 9th May 2016 A rare celestial event to explore the inner planet ‘Astronomy teaches us to look upwards.’ It is the study and understanding of the universe beyond the planet Earth. It is impossible for anyone to rival the magnificence of univ ...
... A date with Mercury over Sun - Mercury Transits on Monday, 9th May 2016 A rare celestial event to explore the inner planet ‘Astronomy teaches us to look upwards.’ It is the study and understanding of the universe beyond the planet Earth. It is impossible for anyone to rival the magnificence of univ ...
Avtar Krishen Kaul
... phenomenon of seasons. They are formed when the sun (the earth) during its sojourn through the Ecliptic reaches a point which is at the maximum distance of north from the Equator. The sun has the maximum declination of North (whereas the earth has the maximum declination of South) then and it starts ...
... phenomenon of seasons. They are formed when the sun (the earth) during its sojourn through the Ecliptic reaches a point which is at the maximum distance of north from the Equator. The sun has the maximum declination of North (whereas the earth has the maximum declination of South) then and it starts ...
the solar system and your community
... from the University of Pittsburgh’s Cognitive Studies in Education Program and joined the faculty of the University of Delaware School of Education in 1995. Dr. Smith received the Outstanding Earth Science Teacher Award for Pennsylvania from the National Association of Geoscience Teachers in 1991, s ...
... from the University of Pittsburgh’s Cognitive Studies in Education Program and joined the faculty of the University of Delaware School of Education in 1995. Dr. Smith received the Outstanding Earth Science Teacher Award for Pennsylvania from the National Association of Geoscience Teachers in 1991, s ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved the universe was expanding like a big balloon. In 1930, Einstein visited Wilson Observato ...
... up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved the universe was expanding like a big balloon. In 1930, Einstein visited Wilson Observato ...
A new method to determine the mean density of massive Solar
... Harmony features the structure of the Solar System. This is proved by Kepler’s laws that describe regular geometry of orbits and the ordered coordination of celestial bodies in space and in time. Major planets move in the same direction, in approximately the same plane, and some other celestial obje ...
... Harmony features the structure of the Solar System. This is proved by Kepler’s laws that describe regular geometry of orbits and the ordered coordination of celestial bodies in space and in time. Major planets move in the same direction, in approximately the same plane, and some other celestial obje ...
Overview Orientation of the Night Sky Figure 1:
... The end goal of this project is to see for yourselves if the Moon phase is a consequence of the Moon’s elongation angle (aka the illumination of the Moon given the relative Earth-Moon-Sun geometry). A relationship between the Moon’s elongation and the Moon’s phase can be verified if the data form a ...
... The end goal of this project is to see for yourselves if the Moon phase is a consequence of the Moon’s elongation angle (aka the illumination of the Moon given the relative Earth-Moon-Sun geometry). A relationship between the Moon’s elongation and the Moon’s phase can be verified if the data form a ...
Rotation, activity, and stellar obliquities in a large uniform sample of
... The Kepler mission has provided an unparalleled window into the nature and occurrence rate of planets around other stars (Borucki et al. 2010), with 4,743 planet candidates and 1,042 confirmed exoplanets identified as of this writing. This unprecedented flood of information was enabled by the ...
... The Kepler mission has provided an unparalleled window into the nature and occurrence rate of planets around other stars (Borucki et al. 2010), with 4,743 planet candidates and 1,042 confirmed exoplanets identified as of this writing. This unprecedented flood of information was enabled by the ...
Chapter 16 - Follow “Ironmtn.wordpress.com”
... Difficulty Level: Easy 18. An astronaut standing on Mars and attempting to look at Jupiter might have her view partly blocked by the intervening ...
... Difficulty Level: Easy 18. An astronaut standing on Mars and attempting to look at Jupiter might have her view partly blocked by the intervening ...
PDF format
... • Winter (December) solstice: lowest path; rise and set at most extreme south of due east • Equinoxes: Sun rises precisely due east and sets precisely due west. ...
... • Winter (December) solstice: lowest path; rise and set at most extreme south of due east • Equinoxes: Sun rises precisely due east and sets precisely due west. ...
Constraints on the Birth Aggregate of the Solar System
... to increase the inclination angles beyond ∆θi ≈ 2.4 ≈ 3π/4. As is well known (Shu 1980), the inclination angles for the (present-day) planetary orbits in our solar system show a small spread, only about 3.5 degrees or 0.061 radians. The cross section for the inclination angles to increase to ...
... to increase the inclination angles beyond ∆θi ≈ 2.4 ≈ 3π/4. As is well known (Shu 1980), the inclination angles for the (present-day) planetary orbits in our solar system show a small spread, only about 3.5 degrees or 0.061 radians. The cross section for the inclination angles to increase to ...
M. Sc. Atmospheric Space
... end of fourth semester or thereafter till he/she is eligible to take the examination for that degree. 2) In each Semester, courses offered will be notified by the Head of the Department in consultation with the Faculty of the Department. ...
... end of fourth semester or thereafter till he/she is eligible to take the examination for that degree. 2) In each Semester, courses offered will be notified by the Head of the Department in consultation with the Faculty of the Department. ...