Astronomy Assignment #1
... This question requires a fairly complete understanding of the celestial coordinate system and the celestial sphere model. According to the last sentence on page 43 “if a star’s declination matches your latitude it will pass over through zenith”. This means that the declination of your zenith is just ...
... This question requires a fairly complete understanding of the celestial coordinate system and the celestial sphere model. According to the last sentence on page 43 “if a star’s declination matches your latitude it will pass over through zenith”. This means that the declination of your zenith is just ...
Using the Heavens to Know Time to Using Time to Know the Heavens
... function of it is. It is a device with which we use to tell the time. The Merriam-Webster dictionary provides a definition of a clock as ‘a device other than a watch for indicating or measuring time commonly by means of hands moving on a dial’ or broadly as ‘any periodic system by which time is meas ...
... function of it is. It is a device with which we use to tell the time. The Merriam-Webster dictionary provides a definition of a clock as ‘a device other than a watch for indicating or measuring time commonly by means of hands moving on a dial’ or broadly as ‘any periodic system by which time is meas ...
FREE Sample Here
... b. Planets reflect light while stars produce their own light. c. Stars move faster in the sky than planets. d. Planets are brighter than stars. ANS: B ...
... b. Planets reflect light while stars produce their own light. c. Stars move faster in the sky than planets. d. Planets are brighter than stars. ANS: B ...
COLEGIO de STO NINO de CABUYAO alma 2006
... As far as we know, man has always been interested in language, in such matters as its origin, its nature, and its various uses, whether in persuasion, poetry, or prayer. Language has been something of a mystery to him, not unlike the mysteries of creation, the origin of the sun, and the coming of fi ...
... As far as we know, man has always been interested in language, in such matters as its origin, its nature, and its various uses, whether in persuasion, poetry, or prayer. Language has been something of a mystery to him, not unlike the mysteries of creation, the origin of the sun, and the coming of fi ...
The Solar System and Beyond
... The Lunar Cycle The phase of the Moon that you see on any given night depends on the relative positions of the Moon, the Sun, and Earth in space. These positions change because the Moon is continually revolving around Earth as Earth revolves around the Sun. It takes the Moon about one month to go th ...
... The Lunar Cycle The phase of the Moon that you see on any given night depends on the relative positions of the Moon, the Sun, and Earth in space. These positions change because the Moon is continually revolving around Earth as Earth revolves around the Sun. It takes the Moon about one month to go th ...
The Sun and Stars
... How our solar A planetary system (like the solar system) forms out of the same system was nebula that creates the star. The protostar that became the sun also formed contained small amounts of other elements such as carbon, nickel, iron, aluminum, and silicon. As the protostar swirled inward on itse ...
... How our solar A planetary system (like the solar system) forms out of the same system was nebula that creates the star. The protostar that became the sun also formed contained small amounts of other elements such as carbon, nickel, iron, aluminum, and silicon. As the protostar swirled inward on itse ...
Level 2 Meteorites, Shooting Stars, and Comets
... There are millions of such particles colliding with the atmosphere every day (I mean day and night). But since you can only see them at night, and you can only look at a small part of the sky at once, when stargazing you can expect to see a shooting star every 10 to 15 minutes. This is on a regular ...
... There are millions of such particles colliding with the atmosphere every day (I mean day and night). But since you can only see them at night, and you can only look at a small part of the sky at once, when stargazing you can expect to see a shooting star every 10 to 15 minutes. This is on a regular ...
spectral lines as distant measurement tools
... The diagram is not filled randomly, but the stellar samples cluster into specific locations. Most lie in a diagonal band called the “main sequence” and a “giant branch” jutting out to the upper right, with a few scattered supergiants and white dwarfs. The star-by-star point density in this HRD corre ...
... The diagram is not filled randomly, but the stellar samples cluster into specific locations. Most lie in a diagonal band called the “main sequence” and a “giant branch” jutting out to the upper right, with a few scattered supergiants and white dwarfs. The star-by-star point density in this HRD corre ...
The Kuiper Belt
... the Spitzer (infrared) Space Telescope and tentatively named Sedna after the Inuit Goddess of the Sea (from which all creatures of the very cold Arctic sea were created), it is currently located around 90 AUs from our Sun, Sol -- an orbital distance that is roughly three times farther out than that ...
... the Spitzer (infrared) Space Telescope and tentatively named Sedna after the Inuit Goddess of the Sea (from which all creatures of the very cold Arctic sea were created), it is currently located around 90 AUs from our Sun, Sol -- an orbital distance that is roughly three times farther out than that ...
The Sun and Stars 4.1 Energy formation and layers of the Sun 4.2
... Prominences and Solar Flares. It is important for us to follow the Sunspot cycle to know when there is going to be an increase in Sunspots, because they cause Solar Flares and Prominences. Although the Earth’s magnetic field can deflect or pull in much of the energy that is carried in a solar flare, ...
... Prominences and Solar Flares. It is important for us to follow the Sunspot cycle to know when there is going to be an increase in Sunspots, because they cause Solar Flares and Prominences. Although the Earth’s magnetic field can deflect or pull in much of the energy that is carried in a solar flare, ...
Astronomy Today Charting the Heavens: The Foundations of
... 46) Some type of solar eclipse will happen about: A) every month at new moon. B) every week at full moon. C) every month at full moon. D) about every six months at new moon. E) every year at new moon. Answer: D Section Ref: 1.6 47) The star Wolf 1061 has a parallax of 2.34 arcseconds, while the sta ...
... 46) Some type of solar eclipse will happen about: A) every month at new moon. B) every week at full moon. C) every month at full moon. D) about every six months at new moon. E) every year at new moon. Answer: D Section Ref: 1.6 47) The star Wolf 1061 has a parallax of 2.34 arcseconds, while the sta ...
A COMPREHENSIVE COMPARISON OF THE SUN TO
... studies as both typical and atypical. In an effort to reduce this ambiguity and quantify how typical the Sun is, we identify 11 maximally independent properties that have plausible correlations with habitability and that have been observed by, or can be derived from, sufficiently large, currently av ...
... studies as both typical and atypical. In an effort to reduce this ambiguity and quantify how typical the Sun is, we identify 11 maximally independent properties that have plausible correlations with habitability and that have been observed by, or can be derived from, sufficiently large, currently av ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... 1960, I was pleased to accept the invitation to review evidence of neutron repulsion and its implications for the evolution of life. It will be shown that life [1] and atomic nuclei have evolved together on opposite sides of the Sun’s opaque photosphere. My conclusions do not support Fowler's concer ...
... 1960, I was pleased to accept the invitation to review evidence of neutron repulsion and its implications for the evolution of life. It will be shown that life [1] and atomic nuclei have evolved together on opposite sides of the Sun’s opaque photosphere. My conclusions do not support Fowler's concer ...
File - South Sevier High School
... traveling at the same speed and moving across the sky would appear to be going nearly a hundred million times more slowly than the plane overhead. The stars (other than the Sun) are all more than 40 trillion kilometers (25 trillion miles) from us. Therefore, although the patterns of stars in the sky ...
... traveling at the same speed and moving across the sky would appear to be going nearly a hundred million times more slowly than the plane overhead. The stars (other than the Sun) are all more than 40 trillion kilometers (25 trillion miles) from us. Therefore, although the patterns of stars in the sky ...
Module3: Life of a Star
... The Solar System is made up of the Sun and everything that orbits around it: the Earth, the planets, asteroids and comets. The Sun makes up 99.9% of all the mass in our Solar System. The Earth orbits around 150 million kilometres from the Sun, although due to the elliptical shape of Earth’s orbit th ...
... The Solar System is made up of the Sun and everything that orbits around it: the Earth, the planets, asteroids and comets. The Sun makes up 99.9% of all the mass in our Solar System. The Earth orbits around 150 million kilometres from the Sun, although due to the elliptical shape of Earth’s orbit th ...
I. Early History of Astronomy
... Tycho Brahe (1546–1601) 4. Great instrument maker Cassiopeia…1572 Tycho’s Supernova ...
... Tycho Brahe (1546–1601) 4. Great instrument maker Cassiopeia…1572 Tycho’s Supernova ...
The Sun`s journey through the local interstellar medium: the
... stars near the Sun, indicates that sometime in the late Quaternary the Sun, which has been moving through the very low density region known as the Local Bubble, encountered the cluster of local interstellar clouds (CLIC) flowing away from the direction of the Scorpius-Centaurus Association (Frisch, ...
... stars near the Sun, indicates that sometime in the late Quaternary the Sun, which has been moving through the very low density region known as the Local Bubble, encountered the cluster of local interstellar clouds (CLIC) flowing away from the direction of the Scorpius-Centaurus Association (Frisch, ...
IAU 29th General Assembly
... Focus Meetings of the 29th IAU GA included: •FM 1 – Dynamical Problems in Extrasolar Planets Science •FM 2 – Astronomical Heritage: Progressing the UNESCO–IAU Initiative •FM 3 – Scholarly Publication in Astronomy: Evolution or Revolution? •FM 4 – Planetary Nebulae as Probes of Galactic Structure an ...
... Focus Meetings of the 29th IAU GA included: •FM 1 – Dynamical Problems in Extrasolar Planets Science •FM 2 – Astronomical Heritage: Progressing the UNESCO–IAU Initiative •FM 3 – Scholarly Publication in Astronomy: Evolution or Revolution? •FM 4 – Planetary Nebulae as Probes of Galactic Structure an ...
EQUINOCTIAL vLOBE ·
... globe 1800,=1925::: (by table) 26� 52' 1] \25, or 27° nearly= difference oflongitude of 1J Sirius at the time of Hipparchus and the present. Bring the pole of the ecliptic under 66°t and 8 under N. keep the poles P. p of the ecliptic fixed, turn the globe contrary to the order of the signs 27°, arid ...
... globe 1800,=1925::: (by table) 26� 52' 1] \25, or 27° nearly= difference oflongitude of 1J Sirius at the time of Hipparchus and the present. Bring the pole of the ecliptic under 66°t and 8 under N. keep the poles P. p of the ecliptic fixed, turn the globe contrary to the order of the signs 27°, arid ...
Astronomy
... – We understand the physics of this very well indeed • We can create fusion reactions on Earth! • We can measure the sun’s energy output • We know the processes causing this • We know how much fuel the sun has • Detailed calculations give ~10B yrs lifespan • Simulations agree © Colin Frayn, 2008 www ...
... – We understand the physics of this very well indeed • We can create fusion reactions on Earth! • We can measure the sun’s energy output • We know the processes causing this • We know how much fuel the sun has • Detailed calculations give ~10B yrs lifespan • Simulations agree © Colin Frayn, 2008 www ...
PHYS_3380_091905_bw - in a secure place with other
... precise measurements of stellar and planetary positions - compiled best set of naked-eye observation ever made - to within 1 arcminute (thickness of a fingernail at arm’s length) - observed supernova of 1572 - proved it was farther away than the Sun - called it a nova (“new star”) - observed comet - ...
... precise measurements of stellar and planetary positions - compiled best set of naked-eye observation ever made - to within 1 arcminute (thickness of a fingernail at arm’s length) - observed supernova of 1572 - proved it was farther away than the Sun - called it a nova (“new star”) - observed comet - ...
Calculations of tithis
... discussed above. To this, an additional correction (term ‘b’) is added to correct for the ...
... discussed above. To this, an additional correction (term ‘b’) is added to correct for the ...
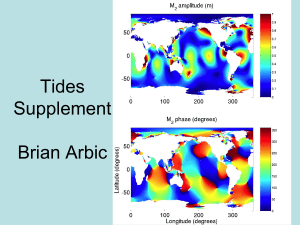
Tides Supplement
... – When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are all in a line, the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon reinforce, and the ocean experiences spring tides (very high high tides, very low low tides). When the Moon is in the first- or third-quarter, the tidal bulges produced by the Sun are at right angles to those gen ...
... – When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are all in a line, the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon reinforce, and the ocean experiences spring tides (very high high tides, very low low tides). When the Moon is in the first- or third-quarter, the tidal bulges produced by the Sun are at right angles to those gen ...
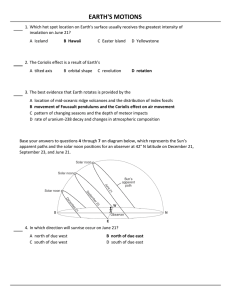
Practice Regents Questions Key
... The duration of insolation will decrease and the temperature will decrease. The duration of insolation will decrease and the temperature will increase. The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will decrease. The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increa ...
... The duration of insolation will decrease and the temperature will decrease. The duration of insolation will decrease and the temperature will increase. The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will decrease. The duration of insolation will increase and the temperature will increa ...