SOFIA Science - Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy
... > IR: objects much cooler than normal stars like the Sun for example: stars and planets in the process of forming; > IR: objects embedded in, or behind, opaque ISM dust clouds; SOFIA’s instruments can see into and through those clouds > IR: organic molecules in space, which have many of their spectr ...
... > IR: objects much cooler than normal stars like the Sun for example: stars and planets in the process of forming; > IR: objects embedded in, or behind, opaque ISM dust clouds; SOFIA’s instruments can see into and through those clouds > IR: organic molecules in space, which have many of their spectr ...
Chapter 15, Galaxies
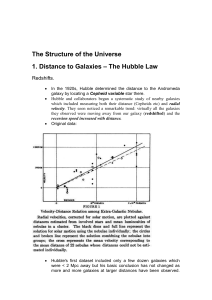
... they much further away from us than the stars? • Before the 1920s, there were no reliable methods of measuring the distance to the galaxies. Many people believed that the galaxies were located within the Milky Way… How do we measure the distance of objects far away in the universe, much farther than ...
... they much further away from us than the stars? • Before the 1920s, there were no reliable methods of measuring the distance to the galaxies. Many people believed that the galaxies were located within the Milky Way… How do we measure the distance of objects far away in the universe, much farther than ...
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL
... their stars formed at the same epoch) vary as the system ages? How is this reflected in the overall photometric properties of the system? (b) A globular cluster has a mass of 106 solar masses and a mass-to-light ratio of 2 (in solar units). Calculate the maximum distance at which the cluster could b ...
... their stars formed at the same epoch) vary as the system ages? How is this reflected in the overall photometric properties of the system? (b) A globular cluster has a mass of 106 solar masses and a mass-to-light ratio of 2 (in solar units). Calculate the maximum distance at which the cluster could b ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... supernova, which is characterised by a spectrum with strong hydrogen lines. (There are also type I supernovae that lack hydrogen lines.) It is expected that a few supernovae will occur per century in the Milky Way, but in practice only four have been observed during the last 1000 years. The reason f ...
... supernova, which is characterised by a spectrum with strong hydrogen lines. (There are also type I supernovae that lack hydrogen lines.) It is expected that a few supernovae will occur per century in the Milky Way, but in practice only four have been observed during the last 1000 years. The reason f ...
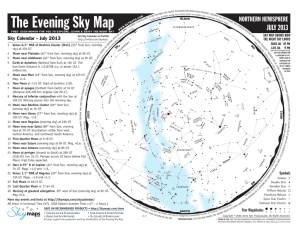
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution
... Ex: Sun = apparent magnitude: -26.7, absolute magnitude: 5 More negative = brighter, more positive = dimmer ...
... Ex: Sun = apparent magnitude: -26.7, absolute magnitude: 5 More negative = brighter, more positive = dimmer ...
Universe 19
... 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, main-sequence, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars? 9. How does our Sun evolve? 10. How can we find the temperature, power, and size of stars from their spectra? ...
... 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, main-sequence, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars? 9. How does our Sun evolve? 10. How can we find the temperature, power, and size of stars from their spectra? ...
TAP 704- 8: The ladder of astronomical distances
... Beyond the distance where individual stars could be seen in galaxies, the only hope was to make further dangerous assumptions, for example that galaxies of the same type are equally bright, or equal in size. Neither method is helped by the fact that galaxies are seen at all angles to the line of sig ...
... Beyond the distance where individual stars could be seen in galaxies, the only hope was to make further dangerous assumptions, for example that galaxies of the same type are equally bright, or equal in size. Neither method is helped by the fact that galaxies are seen at all angles to the line of sig ...
PH607lec08
... significantly similar to young galaxy clusters in the distant, early Universe and that exploring galaxy types and their interactions in nearby Hercules will help unravel the threads of galaxy and cluster evolution. ...
... significantly similar to young galaxy clusters in the distant, early Universe and that exploring galaxy types and their interactions in nearby Hercules will help unravel the threads of galaxy and cluster evolution. ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... denly burn much hotter and brighter. Not only does the disk radiate more light, but it can heat the surface of the companion star, causing it to glow more brightly, too. Some dwarf novae such as U Geminorum can jump from magnitude 15 to 9.5 in just 1-2 days. After an outburst, the star slowly return ...
... denly burn much hotter and brighter. Not only does the disk radiate more light, but it can heat the surface of the companion star, causing it to glow more brightly, too. Some dwarf novae such as U Geminorum can jump from magnitude 15 to 9.5 in just 1-2 days. After an outburst, the star slowly return ...
Activity: Multiwavelength Bingo - Chandra X
... NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope shows various features of this socalled planetary nebula. When a star like the Sun begins to run out of fuel, it becomes a red giant. In X-RAY this phase, a star sheds some of its outer layers, eventually leaving behind a hot core that coll ...
... NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope shows various features of this socalled planetary nebula. When a star like the Sun begins to run out of fuel, it becomes a red giant. In X-RAY this phase, a star sheds some of its outer layers, eventually leaving behind a hot core that coll ...
Star Basics
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... A: The ratio of brightness between two stars with magnitude m1 and m2 is 100(m2-m1)/5. One can easily check this formula with the definition. Now if a star of apparent magnitude m and distance d is moved to 10 pc from us and its new apparent magnitude is M, then the ratio of brightness is 100(M-m)/5 ...
... A: The ratio of brightness between two stars with magnitude m1 and m2 is 100(m2-m1)/5. One can easily check this formula with the definition. Now if a star of apparent magnitude m and distance d is moved to 10 pc from us and its new apparent magnitude is M, then the ratio of brightness is 100(M-m)/5 ...
Finding Your Way In The Sky
... • Latin uses word endings where we often use prepositions (Compare English ‘s) • Possessive form different from normal form • Centaurus but Alpha Centauri • Andromeda but Alpha Andromedae • Gemini – Geminorum • Virgo – Virginis • Orion – Orionis ...
... • Latin uses word endings where we often use prepositions (Compare English ‘s) • Possessive form different from normal form • Centaurus but Alpha Centauri • Andromeda but Alpha Andromedae • Gemini – Geminorum • Virgo – Virginis • Orion – Orionis ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... it for your latitude. Almost any seasonal setting will do. After the students are seated and ready, slowly dim down the side lamps and increase the brightness of the starfield. Begin a discussion of why we see things. (Some students may say because we have eyes, while others will say because of ligh ...
... it for your latitude. Almost any seasonal setting will do. After the students are seated and ready, slowly dim down the side lamps and increase the brightness of the starfield. Begin a discussion of why we see things. (Some students may say because we have eyes, while others will say because of ligh ...
star - TeacherWeb
... A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s Light travels about 9.46 trillion km. per year. The light you see when you look at a star left that star sometime in the past. ...
... A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s Light travels about 9.46 trillion km. per year. The light you see when you look at a star left that star sometime in the past. ...
october 2008 - Mahoning Valley Astronomical Society
... try for the brightest-- go for G1. Also known as Mayall II or Andromeda's Globular, it was discovered in 1953 by the astronomers Nicholas Mayall and Olin J. Eggen. G1 consists of 300,000 to 1 million old stars. It lies about 130,000 light years away from its home galaxy M31. From our perspective thi ...
... try for the brightest-- go for G1. Also known as Mayall II or Andromeda's Globular, it was discovered in 1953 by the astronomers Nicholas Mayall and Olin J. Eggen. G1 consists of 300,000 to 1 million old stars. It lies about 130,000 light years away from its home galaxy M31. From our perspective thi ...
Nebular theory
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
Star Types - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... but shrinks to smaller and smaller sizes. No amount of pressure can stop the collapse, because in those extreme situations, pressure itself contributes more to gravity than it does of opposing it. It forms a singularity – a region in space with the mass of the parent material, but with virtually nul ...
... but shrinks to smaller and smaller sizes. No amount of pressure can stop the collapse, because in those extreme situations, pressure itself contributes more to gravity than it does of opposing it. It forms a singularity – a region in space with the mass of the parent material, but with virtually nul ...
Hitomi Observation of the Highly Obscured High-Mass X-ray
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
Galaxies * Island universes
... disk can overwhelm the light from the rest of the galaxy and a Quasar may even result. Up to 1 solar mass/year infall. • Later, as the galaxy ages, the stuff that CAN fall in, pretty much HAS fallen in, and fueling rate drops. The core fades and instead of looking like a quasar it looks like a Seyfe ...
... disk can overwhelm the light from the rest of the galaxy and a Quasar may even result. Up to 1 solar mass/year infall. • Later, as the galaxy ages, the stuff that CAN fall in, pretty much HAS fallen in, and fueling rate drops. The core fades and instead of looking like a quasar it looks like a Seyfe ...
Star Formation
... They gradually cool off and become dark “clinkers” A protostar must have 0.08 the mass of the Sun (which is 80 times the mass of Jupiter) in order to become dense and hot enough that fusion can begin If the mass of the “failed star” is about 12 Jupiter masses or more, it is luminous when first forme ...
... They gradually cool off and become dark “clinkers” A protostar must have 0.08 the mass of the Sun (which is 80 times the mass of Jupiter) in order to become dense and hot enough that fusion can begin If the mass of the “failed star” is about 12 Jupiter masses or more, it is luminous when first forme ...
Star Types - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... The larger P, the smaller D The smaller P, the larger D ...
... The larger P, the smaller D The smaller P, the larger D ...
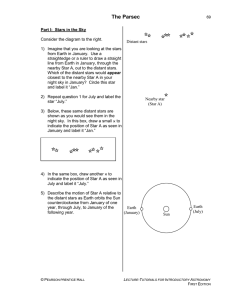
The Parsec
... 7) Starting from Earth in January, draw a line through Star A to the top of the page. 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this an ...
... 7) Starting from Earth in January, draw a line through Star A to the top of the page. 8) There is now a narrow triangle with the Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this an ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.