STAR TYPES
... A white dwarf is a small, very dense, hot star that is made mostly of carbon. These faint stars are what remains after a red giant star loses its outer layers. Their nuclear cores are depleted. They are about the size of the Earth (but tremendously heavier)! They will eventually lose their heat and ...
... A white dwarf is a small, very dense, hot star that is made mostly of carbon. These faint stars are what remains after a red giant star loses its outer layers. Their nuclear cores are depleted. They are about the size of the Earth (but tremendously heavier)! They will eventually lose their heat and ...
Grade Nine Planetarium script
... the bright star near the foot of Perseus' forward leg (the one towards Andromeda) consists of a pair of stars - one much dimmer than the other every 2 days and 21 hours the dimmer star passes right between us and the brighter star over a four-hour period, you can see Algol dim to about a tenth its n ...
... the bright star near the foot of Perseus' forward leg (the one towards Andromeda) consists of a pair of stars - one much dimmer than the other every 2 days and 21 hours the dimmer star passes right between us and the brighter star over a four-hour period, you can see Algol dim to about a tenth its n ...
Background Science - Faulkes Telescope Project
... Radio emission is a different story. Radio waves in a supernova remnant come from high energy electrons which are heated up by the energy released in the explosion and whiz about in the strong magnetic field of the remnant. In this project you will either use observations of one supernova remnant al ...
... Radio emission is a different story. Radio waves in a supernova remnant come from high energy electrons which are heated up by the energy released in the explosion and whiz about in the strong magnetic field of the remnant. In this project you will either use observations of one supernova remnant al ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • The importance of high-mass stars is that they make elements heavier than carbon • You need really hot temperatures which only occur with the weight of a very high-mass star ...
... • The importance of high-mass stars is that they make elements heavier than carbon • You need really hot temperatures which only occur with the weight of a very high-mass star ...
PH607lec12
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
Galaxies
... protogalactic clouds that were able to cool and form stars before gas settled into a disk ...
... protogalactic clouds that were able to cool and form stars before gas settled into a disk ...
Outside the Solar System Outside the Solar System OUTSIDE THE
... of the universe that earlier cultures never could have. However, we are also limited by our current knowledge and technology. As time marches on, humankind will continue to pursue an understanding of the universe and its many amazing features. Someday—perhaps even in students’ lifetimes—we may get a ...
... of the universe that earlier cultures never could have. However, we are also limited by our current knowledge and technology. As time marches on, humankind will continue to pursue an understanding of the universe and its many amazing features. Someday—perhaps even in students’ lifetimes—we may get a ...
• Constellations is a group of visible stars hat form a pattern when
... Constellations is a group of visible stars hat form a pattern when viewed from Earth The sky was divided up into 88 different constellations in 1922. This included 48 ancient constellations listed by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy as well as 40 new constellations. Star maps are made of the brigh ...
... Constellations is a group of visible stars hat form a pattern when viewed from Earth The sky was divided up into 88 different constellations in 1922. This included 48 ancient constellations listed by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy as well as 40 new constellations. Star maps are made of the brigh ...
Explores Angular Size - Chandra X
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
Module 6: “The Message of Starlight Assignment 9: Parallax, stellar
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
charts_set_7
... How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? Main Sequence stars fuse H to He in core. Lifetime depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass of star. Fusion rate is related to luminosity (fusion reactions make the radiation energy). ...
... How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? Main Sequence stars fuse H to He in core. Lifetime depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass of star. Fusion rate is related to luminosity (fusion reactions make the radiation energy). ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... galaxy A has a bright-dim-bright period of 10 days, while the one in galaxy B has a bright-dim-bright period of 30 days. Which of the two galaxies is at a greater distance from us? a) ...
... galaxy A has a bright-dim-bright period of 10 days, while the one in galaxy B has a bright-dim-bright period of 30 days. Which of the two galaxies is at a greater distance from us? a) ...
What is a standard candle?
... galaxy A has a bright-dim-bright period of 10 days, while the one in galaxy B has a bright-dim-bright period of 30 days. Which of the two galaxies is at a greater distance from us? a) ...
... galaxy A has a bright-dim-bright period of 10 days, while the one in galaxy B has a bright-dim-bright period of 30 days. Which of the two galaxies is at a greater distance from us? a) ...
15-1 Notes - westscidept
... 15-1 Notes: Stars Scientists know that the _______ of star indicates the star’s temperature. _____ stars are the coolest, and _______ stars are the hottest. When you look at white light through a prism, you see a rainbow of colors called a ___________. Astronomers use a ________________ to separate ...
... 15-1 Notes: Stars Scientists know that the _______ of star indicates the star’s temperature. _____ stars are the coolest, and _______ stars are the hottest. When you look at white light through a prism, you see a rainbow of colors called a ___________. Astronomers use a ________________ to separate ...
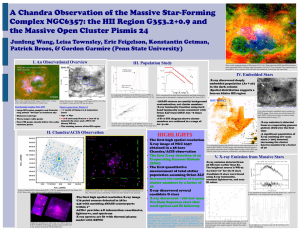
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
Cataclysmic Variable Stars
... Of the 6000 stars visible to the naked eye from the Earth, well over half of two ore more bodies locked in gravitational bound orbits. About half of them consist of interacting binary systems where the two component stars are unable to complete there normal without being influenced by the presence o ...
... Of the 6000 stars visible to the naked eye from the Earth, well over half of two ore more bodies locked in gravitational bound orbits. About half of them consist of interacting binary systems where the two component stars are unable to complete there normal without being influenced by the presence o ...
Powerpoint
... • Sun is a marble, Earth is a grain of sand orbiting 1 m away. • Nearest star is another marble 270 km away. • Solar system extends about 50 m from the Sun; rest of distance to nearest star is basically empty. ...
... • Sun is a marble, Earth is a grain of sand orbiting 1 m away. • Nearest star is another marble 270 km away. • Solar system extends about 50 m from the Sun; rest of distance to nearest star is basically empty. ...
What is a star?
... size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple star systems. The largest object in our solar system is the sun, whi ...
... size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple star systems. The largest object in our solar system is the sun, whi ...
Twitter Feed ITSO Symposium 2017
... mass) and external (environment) processes on the galaxy evolution is difficult because high mass galaxies tend to exist in dense environments. For the past decade, the difference between mass-metallicity relations in the cluster versus field environment has been used to disentangle the effect of in ...
... mass) and external (environment) processes on the galaxy evolution is difficult because high mass galaxies tend to exist in dense environments. For the past decade, the difference between mass-metallicity relations in the cluster versus field environment has been used to disentangle the effect of in ...
cancer, la constelac..
... solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer was the crab sent by Hera to distract Hercules as he fought the Hydra in the marshes at Lerna. Hercules ...
... solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer was the crab sent by Hera to distract Hercules as he fought the Hydra in the marshes at Lerna. Hercules ...
Observing Orion
... UHC filter in front of one objective of the binoculars and closed the other eye. This did help the contrast somewhat, but this is still a low surface brightness object under any conditions. Moving up in aperture to a 4" f/6 RFT refractor shows it as pretty faint, very large and very, very elongated. ...
... UHC filter in front of one objective of the binoculars and closed the other eye. This did help the contrast somewhat, but this is still a low surface brightness object under any conditions. Moving up in aperture to a 4" f/6 RFT refractor shows it as pretty faint, very large and very, very elongated. ...
Stars: some basic characteristics
... Recall that the emission/absorption features can be taken as chemical fingerprints: for instance, if there is a strong Hydrogen absorption feature, then you would expect that there is a lot of hydrogen in the star. ...
... Recall that the emission/absorption features can be taken as chemical fingerprints: for instance, if there is a strong Hydrogen absorption feature, then you would expect that there is a lot of hydrogen in the star. ...
Lecture Notes
... They were discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals, but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. ∼ ...
... They were discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals, but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. ∼ ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.