(a) Because the core of heavy-mass star never reaches high enough
... (a) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. (b) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing helium into carbon in their cores. (c) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing carbon into iron in their cores. (d) The mass of a star on the main sequence has nothing t ...
... (a) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. (b) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing helium into carbon in their cores. (c) Stars on the main sequence are all fusing carbon into iron in their cores. (d) The mass of a star on the main sequence has nothing t ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
Properties of Stars
... 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun with those of other stars in its group. How are they the same/different? 12. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs away (480 light years) and has a surface temperature of only 3200 K (3473°Celsius). Yet Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars as see ...
... 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun with those of other stars in its group. How are they the same/different? 12. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs away (480 light years) and has a surface temperature of only 3200 K (3473°Celsius). Yet Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars as see ...
The H-R Diagram
... “Planetary Nebula??” • The name can be misleading – it’s a nod to the history of their discovery. • One of the first discovered was the Eskimo Nebula, a little greenish disk that looks remarkably like the planets Uranus and Neptune, in 18th century telescopes (as we’ll see) • Some early discoverers ...
... “Planetary Nebula??” • The name can be misleading – it’s a nod to the history of their discovery. • One of the first discovered was the Eskimo Nebula, a little greenish disk that looks remarkably like the planets Uranus and Neptune, in 18th century telescopes (as we’ll see) • Some early discoverers ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... • The Distribution of stars can reveal part of the disk-like nature of the Milky Way galaxy, but are not “deep” enough probes to fully reveal the structure of the Milky Way. • Open clusters can define the thickness of the Milky Way’s thin disk where star formation is active. • Globular clusters allo ...
... • The Distribution of stars can reveal part of the disk-like nature of the Milky Way galaxy, but are not “deep” enough probes to fully reveal the structure of the Milky Way. • Open clusters can define the thickness of the Milky Way’s thin disk where star formation is active. • Globular clusters allo ...
Fifth - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... wind material up and creates a shells. • When the photosphere of the heating star passes the ~25,000-K mark the swept up shell is ionized and can be seen in forbidden ...
... wind material up and creates a shells. • When the photosphere of the heating star passes the ~25,000-K mark the swept up shell is ionized and can be seen in forbidden ...
Star Classification - University of Louisville
... A star called Betelguese is extremely old, but also extremely big. In fact, it is 500 times wider than the Sun and would, if it was at the center of the Sun's Solar System, be big enough to stretch nearly to Jupiter. This giant star will collapse in a huge explosion called a supernova and will becom ...
... A star called Betelguese is extremely old, but also extremely big. In fact, it is 500 times wider than the Sun and would, if it was at the center of the Sun's Solar System, be big enough to stretch nearly to Jupiter. This giant star will collapse in a huge explosion called a supernova and will becom ...
Chapter 16 - Astronomy
... nucleus, it wasn’t until the development of IR/radio and X-ray/gamma-ray astronomy that we could “look” at the Galactic nucleus. 3. The observed number density of stars increases as we get closer to the Galactic center, down to about 2 pc from the center. For distances closer than 2 pc, observations ...
... nucleus, it wasn’t until the development of IR/radio and X-ray/gamma-ray astronomy that we could “look” at the Galactic nucleus. 3. The observed number density of stars increases as we get closer to the Galactic center, down to about 2 pc from the center. For distances closer than 2 pc, observations ...
Milky Way I
... • The thickness of the disk is only 300pc (1000 light years) on average. • The total detectable mass is 200 billion solar masses. ...
... • The thickness of the disk is only 300pc (1000 light years) on average. • The total detectable mass is 200 billion solar masses. ...
star
... closer to Earth than other stars. In fact, the sun is really a star of only average brightness. Apparent brightness-‐ the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. ...
... closer to Earth than other stars. In fact, the sun is really a star of only average brightness. Apparent brightness-‐ the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. ...
Exercise 4
... (b) C > D > E > A > B (Largest m to smallest m, i.e. dimmest to brightest, i.e. least luminous to most luminous since the objects are at the same distance from the Earth) (c) B > A > E > D > C (Using m–M = 5 log d/10, the largest m-M corresponds the farthest star) ...
... (b) C > D > E > A > B (Largest m to smallest m, i.e. dimmest to brightest, i.e. least luminous to most luminous since the objects are at the same distance from the Earth) (c) B > A > E > D > C (Using m–M = 5 log d/10, the largest m-M corresponds the farthest star) ...
Stars and Galaxies
... • Mass of massive stars 6x that of sun • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the heavy element ...
... • Mass of massive stars 6x that of sun • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the heavy element ...
Why Aren`t All Galaxies Barred?
... Although the initial disk of stars in Fig. 3 was in equilibrium, the equilibrium is about as unstable as a pencil balanced on its point. Just as a tiny disturbance will cause the pencil to fall, so a slight clumping of stars will attract more, making the attraction stronger and so dragging in yet m ...
... Although the initial disk of stars in Fig. 3 was in equilibrium, the equilibrium is about as unstable as a pencil balanced on its point. Just as a tiny disturbance will cause the pencil to fall, so a slight clumping of stars will attract more, making the attraction stronger and so dragging in yet m ...
A glance at the beginning of the Universe
... and the period of Cepheids (variable stars). Using this relation it is possible to measure the distance to galaxies with Cepheids. ...
... and the period of Cepheids (variable stars). Using this relation it is possible to measure the distance to galaxies with Cepheids. ...
Galactic Structure
... Enrichment is then a Poisson process Each fragment assumed to be well-mixed Model parameter is the mean number of enrichment events per region – changes shape. Adopted value of 3 here. ...
... Enrichment is then a Poisson process Each fragment assumed to be well-mixed Model parameter is the mean number of enrichment events per region – changes shape. Adopted value of 3 here. ...
What We Know About Stars So Far
... •Scientists also figured out that the color of the star told us something about their temperature •Red-colored stars are cooler in temperature compared to bluecolored stars. ...
... •Scientists also figured out that the color of the star told us something about their temperature •Red-colored stars are cooler in temperature compared to bluecolored stars. ...
Name - MIT
... 33) The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram has ________________. (the horizontal axis is the x-axis and the vertical axis is the y-axis) A) surface temperature (or spectral type) on its horizontal axis and apparent brightness on its vertical axis B) age on its horizontal axis and diameter on its vertical a ...
... 33) The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram has ________________. (the horizontal axis is the x-axis and the vertical axis is the y-axis) A) surface temperature (or spectral type) on its horizontal axis and apparent brightness on its vertical axis B) age on its horizontal axis and diameter on its vertical a ...
Physical Science Laboratory: Skyglobe
... automatically increments the time. Time progression can be reversed by pressing Shift-A. ...
... automatically increments the time. Time progression can be reversed by pressing Shift-A. ...
NAME_______________________________________
... For questions 5 - 10, Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
... For questions 5 - 10, Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
2017 Div. C (High School) Astronomy Help Session
... our sun: Mass ~0.5 to ~4+x mass of sun (Msun) the progenitor stars are not massive enough to generate neutron stars or black holes when they die. • White dwarfs do not generate any energy – they are just cooling off and will follow a well defined “cooling” curve on the H-R diagram. • Maximum mass ...
... our sun: Mass ~0.5 to ~4+x mass of sun (Msun) the progenitor stars are not massive enough to generate neutron stars or black holes when they die. • White dwarfs do not generate any energy – they are just cooling off and will follow a well defined “cooling” curve on the H-R diagram. • Maximum mass ...
intergalactic move
... to a different part of our Galaxy? Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is so big that it would take 100.000 years to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of ...
... to a different part of our Galaxy? Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is so big that it would take 100.000 years to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of ...
Basic properties of stars
... parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as good as +/- 1 arc minute, but he could measure no parallaxes. This implied either that the stars were more than 3000 Astronomical Units away, or that the Earth was ...
... parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as good as +/- 1 arc minute, but he could measure no parallaxes. This implied either that the stars were more than 3000 Astronomical Units away, or that the Earth was ...
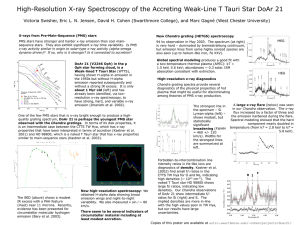
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... high densities (~ 1013 cm-3). The naked T Tauri star HD 98800 shows large f/i ratios, indicating low densities. Our Chandra observations of DoAr 21 show intermediate f/i ratios for Si (right) and S. The implied densities are more in-line with the high values seen in TW Hya, but our results have larg ...
... high densities (~ 1013 cm-3). The naked T Tauri star HD 98800 shows large f/i ratios, indicating low densities. Our Chandra observations of DoAr 21 show intermediate f/i ratios for Si (right) and S. The implied densities are more in-line with the high values seen in TW Hya, but our results have larg ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.