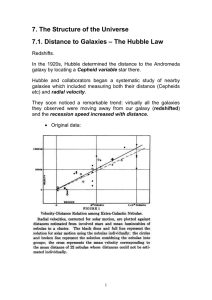
GRB Progenitors and their environments
... • Collapsar Models: Can be produced in single and binary stars. Single star models require high rotation with minimal angular momentum loss in winds (perhaps rotationally-induced mixing can help?). Binary systems are used to i) remove the hydrogen envelope without losing angular momentum, ii) spinni ...
... • Collapsar Models: Can be produced in single and binary stars. Single star models require high rotation with minimal angular momentum loss in winds (perhaps rotationally-induced mixing can help?). Binary systems are used to i) remove the hydrogen envelope without losing angular momentum, ii) spinni ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... Clusters have higher densities than groups, contain a majority of E’s and S0’s while groups are dominated by spirals Nearby clusters cataloged by Abell (1958), extended to southern hemisphere by Abell et al (1989). cataloged 4073 rich clusters Abell also classified clusters as: Regular: ~circula ...
... Clusters have higher densities than groups, contain a majority of E’s and S0’s while groups are dominated by spirals Nearby clusters cataloged by Abell (1958), extended to southern hemisphere by Abell et al (1989). cataloged 4073 rich clusters Abell also classified clusters as: Regular: ~circula ...
Brock physics - Brock University
... 27. White dwarfs dim and eventually become black dwarfs (a) after a few tens of thousands of years. (b) after a few tens of millions of years. (c) after a few hundreds of millions of years. (d) * over a time scale similar to the current age of the universe. 28. A type Ia supernova occurs because of ...
... 27. White dwarfs dim and eventually become black dwarfs (a) after a few tens of thousands of years. (b) after a few tens of millions of years. (c) after a few hundreds of millions of years. (d) * over a time scale similar to the current age of the universe. 28. A type Ia supernova occurs because of ...
The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... light up in ultraviolet because they are filled with hot, newborn stars, objects that pack most of their light into ultraviolet wavelengths. Older galaxies have less star-forming activity and thus give off less ultraviolet light. Both young and old stars radiate visible light, so young and old galax ...
... light up in ultraviolet because they are filled with hot, newborn stars, objects that pack most of their light into ultraviolet wavelengths. Older galaxies have less star-forming activity and thus give off less ultraviolet light. Both young and old stars radiate visible light, so young and old galax ...
The origin, life, and death of stars
... actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core collapses to form a White Dwarf ...
... actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core collapses to form a White Dwarf ...
151 - ESO
... During one of these pulsations the size of the star also changes. The radius of the star can alter with 10-20%. Harvard astronomer Miss Henrietta Leavitt was the first person to determine distances using Cepheids. Therefor in 1912 she made it possible to prove that “spiral-nebulas” (?) are independe ...
... During one of these pulsations the size of the star also changes. The radius of the star can alter with 10-20%. Harvard astronomer Miss Henrietta Leavitt was the first person to determine distances using Cepheids. Therefor in 1912 she made it possible to prove that “spiral-nebulas” (?) are independe ...
star a
... above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and the inverse square law, the star’s luminosity and ...
... above the main sequence, while white dwarfs are below the main sequence. By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a mainsequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf. Using the H-R diagram and the inverse square law, the star’s luminosity and ...
A New Variable Star in Perseus
... robotic telescope operated without filters. A code of Schwarzenberg-Czerny (1989, 1996) was used in order to find the period of variable star. The period of variable star was determined as P=0d.55120.0005 using the first observational point as an initial epoch. Multi-colour observations of GSC 3692 ...
... robotic telescope operated without filters. A code of Schwarzenberg-Czerny (1989, 1996) was used in order to find the period of variable star. The period of variable star was determined as P=0d.55120.0005 using the first observational point as an initial epoch. Multi-colour observations of GSC 3692 ...
Are Gamma-Ray Bursts good Star Formation Indicators?
... recent years, there remains debate about the fraction of star-formation occurring in obscured mode, which is hard to study directly, and uncertainty about the star formation occurring at very high redshifts (z>5). In the latter case, because galaxies (and quasars) are faint and few at high-z, tradit ...
... recent years, there remains debate about the fraction of star-formation occurring in obscured mode, which is hard to study directly, and uncertainty about the star formation occurring at very high redshifts (z>5). In the latter case, because galaxies (and quasars) are faint and few at high-z, tradit ...
Deaths of Stars - Chabot College
... The mystery was solved when a pulsar was discovered in the heart of the Crab Nebula. ...
... The mystery was solved when a pulsar was discovered in the heart of the Crab Nebula. ...
Star - Astrophysics
... luminosity is therefore very small making neutron stars hard to detect. However, in 1967 Jocelyn Bell and Tony Hewish discovered rapidly pulsating radio sources, or pulsars. These are found with periods of a few seconds down to milliseconds. They are incredibly precise ‘clocks’ but slow down slightl ...
... luminosity is therefore very small making neutron stars hard to detect. However, in 1967 Jocelyn Bell and Tony Hewish discovered rapidly pulsating radio sources, or pulsars. These are found with periods of a few seconds down to milliseconds. They are incredibly precise ‘clocks’ but slow down slightl ...
After the ZAMS - Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School
... This is Betelgeuse, as seen recently by the HST. As Betelgeuse is a red supergiant, it will probably explode fairly soon. But as it is 520 light years away, we won’t know for 520 years! ...
... This is Betelgeuse, as seen recently by the HST. As Betelgeuse is a red supergiant, it will probably explode fairly soon. But as it is 520 light years away, we won’t know for 520 years! ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... It is interesting to note that the scale that Hipparchus selected on an intuitive basis, using just the naked eye, is already logarithmic as a result of the way our eyes respond to light. For comparison, the apparent magnitude of the full Moon is about –12.7, the magnitude of Venus can be as high as ...
... It is interesting to note that the scale that Hipparchus selected on an intuitive basis, using just the naked eye, is already logarithmic as a result of the way our eyes respond to light. For comparison, the apparent magnitude of the full Moon is about –12.7, the magnitude of Venus can be as high as ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... Milky Way. The breakthrough came in 1924 when Edwin Hubble was able to measure the distance to the “Great Nebula in Andromeda” (M 31, at right) and found its distance to be much larger than the diameter of the Milky Way. This meant that M 31, and by extension other spiral nebulae, were galaxies in t ...
... Milky Way. The breakthrough came in 1924 when Edwin Hubble was able to measure the distance to the “Great Nebula in Andromeda” (M 31, at right) and found its distance to be much larger than the diameter of the Milky Way. This meant that M 31, and by extension other spiral nebulae, were galaxies in t ...
DTU_9e_ch15
... Young OB associations, H II regions, and molecular clouds in the galactic disk outline huge spiral arms where stars are forming. The Sun is located about 26,000 ly from the galactic nucleus, between the spiral arms. The Sun moves in its orbit at a speed of about 878,000 km/h and takes about 230 mill ...
... Young OB associations, H II regions, and molecular clouds in the galactic disk outline huge spiral arms where stars are forming. The Sun is located about 26,000 ly from the galactic nucleus, between the spiral arms. The Sun moves in its orbit at a speed of about 878,000 km/h and takes about 230 mill ...
Binocular Objects (MS Word)
... This galaxy is one of the brightest and biggest members of the Local Group. The magnitude is 5.5 but its light is spread out over such a large area that it is difficult to see. Although it can be seen with the naked eye on very clear nights, you need a dark sky and binoculars to see a fuzzy glow. Th ...
... This galaxy is one of the brightest and biggest members of the Local Group. The magnitude is 5.5 but its light is spread out over such a large area that it is difficult to see. Although it can be seen with the naked eye on very clear nights, you need a dark sky and binoculars to see a fuzzy glow. Th ...
CCD BVRI and 2MASS Photometry of the Poorly Studied Open
... from 880 to 5000 pc. We can say that no real study has been done for this cluster before Ram Sagar et al. (2001). They presented the first VI CCD photometric study of NGC 6631 and estimated the cluster main parameters by getting the best fit of the theoretical isochrones on V∼(V–I) diagram of the cl ...
... from 880 to 5000 pc. We can say that no real study has been done for this cluster before Ram Sagar et al. (2001). They presented the first VI CCD photometric study of NGC 6631 and estimated the cluster main parameters by getting the best fit of the theoretical isochrones on V∼(V–I) diagram of the cl ...
Study Guide
... Post-Main Sequence Evolution of a High Mass Star • End of the Life of a Massive Star: – Burn H through Si in successive cores – Finally build a massive Iron core ...
... Post-Main Sequence Evolution of a High Mass Star • End of the Life of a Massive Star: – Burn H through Si in successive cores – Finally build a massive Iron core ...
Galaxies have different sizes and shapes.
... Most large galaxies seem to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The mass of a supermassive black hole can be millions or even billions of times greater than that of the Sun. At the center of the Milky Way, for example, is a black hole with a mass about three million times that of the Sun ...
... Most large galaxies seem to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The mass of a supermassive black hole can be millions or even billions of times greater than that of the Sun. At the center of the Milky Way, for example, is a black hole with a mass about three million times that of the Sun ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E3
... Star B has a larger parallax, so it is closer. Hence it appears brighter. ...
... Star B has a larger parallax, so it is closer. Hence it appears brighter. ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.