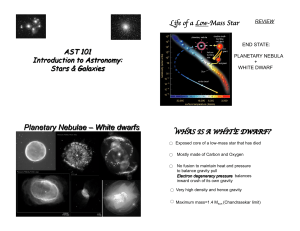
ASTRONOMY
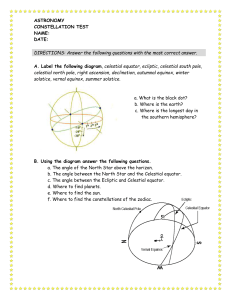
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
Binary Star Systems - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... • In a telescope, an optical double looks like a binary star system, 2 stars that are in orbit around a common center of mass. • However, they’re really far apart from each other. They just happen to be in the same part of the sky. • Mizar and Alcor are an optical double pair. ...
... • In a telescope, an optical double looks like a binary star system, 2 stars that are in orbit around a common center of mass. • However, they’re really far apart from each other. They just happen to be in the same part of the sky. • Mizar and Alcor are an optical double pair. ...
Lecture 10 Advanced Variable Star Stuff March 18 2003 8:00 PM
... A white dwarf is the remnant that is left after a star similar to our Sun dies. It blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we add a bunch of fuel, w ...
... A white dwarf is the remnant that is left after a star similar to our Sun dies. It blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we add a bunch of fuel, w ...
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
... galaxies were moving away from us, at rather large speeds. In the 1920’s, Edwin Hubble measured the distances to many galaxies, and determined an interesting relationship: the farther away the galaxy, the faster it appears to be moving away from us. If the motions of galaxies are purely do to random ...
... galaxies were moving away from us, at rather large speeds. In the 1920’s, Edwin Hubble measured the distances to many galaxies, and determined an interesting relationship: the farther away the galaxy, the faster it appears to be moving away from us. If the motions of galaxies are purely do to random ...
Stars - RSM Home
... • When a neutron star is rapidly spinning, it is called PULSAR. It emits rapid pulses of radio waves and optical energy. • This is Pulsar B1509. It is spinning so rapidly(7 rotations/sec), 12 miles wide, it creates a hand-shaped nebula ...
... • When a neutron star is rapidly spinning, it is called PULSAR. It emits rapid pulses of radio waves and optical energy. • This is Pulsar B1509. It is spinning so rapidly(7 rotations/sec), 12 miles wide, it creates a hand-shaped nebula ...
No Slide Title
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
Chapter 19. Mapping the Universe from Herschel to Sloan
... (Andromeda Galaxy) and M33, but the star were too faint to obtain spectra which could be classified. Therefore, we did not know if these stars were ordinary main sequence objects in a rather nearby cluster of stars, within the boundaries of the Milky Way Galaxy or whether they were supergiants in a ...
... (Andromeda Galaxy) and M33, but the star were too faint to obtain spectra which could be classified. Therefore, we did not know if these stars were ordinary main sequence objects in a rather nearby cluster of stars, within the boundaries of the Milky Way Galaxy or whether they were supergiants in a ...
Our Star - the Sun
... A spectrum binary appears to be a single star but has a spectrum with the absorption lines for two distinctly different spectral types A spectroscopic binary has spectral lines that shift back and forth in wavelength This is caused by the Doppler effect, as the orbits of the stars carry them first t ...
... A spectrum binary appears to be a single star but has a spectrum with the absorption lines for two distinctly different spectral types A spectroscopic binary has spectral lines that shift back and forth in wavelength This is caused by the Doppler effect, as the orbits of the stars carry them first t ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: 11.1 Properties of Stars
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times ...
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times ...
Slide 1 - Personal.psu.edu
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the Main Sequence. ...
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the Main Sequence. ...
Prep/Review Questions - Faculty Web Sites at the University
... (T/F) An important catalog of extended objects related to stellar evolution (e.g. clusters and nebulae) was compiled by comet hunter Charles Messier. What are the Pleiades and the Hyades? Why are they, and objects like them, important to deciphering the evolution of stars? Why would you expect that ...
... (T/F) An important catalog of extended objects related to stellar evolution (e.g. clusters and nebulae) was compiled by comet hunter Charles Messier. What are the Pleiades and the Hyades? Why are they, and objects like them, important to deciphering the evolution of stars? Why would you expect that ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 3 Stars, Galaxies, and the
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
September 3 and 5 slides
... Curtis noted that many of the spirals had dark, thick bands of obscuring material and gave 3 big “ifs”: (1) if the MW has such a band, (2) if we are located in the mid-plane of the band, and (3) if the spirals are located outside the MW, then the Zone of Avoidance is caused by the obscuring material ...
... Curtis noted that many of the spirals had dark, thick bands of obscuring material and gave 3 big “ifs”: (1) if the MW has such a band, (2) if we are located in the mid-plane of the band, and (3) if the spirals are located outside the MW, then the Zone of Avoidance is caused by the obscuring material ...
The universe is faster, colder, and wackier than anything we can
... somehow come together in an isolated region of space such that they can move without being affected by larger galaxies, they can reach out with their feeble gravity and take up a fragile orbit around each other. Of the many binary pairs of small galaxies we know of, the pair that is bound together mo ...
... somehow come together in an isolated region of space such that they can move without being affected by larger galaxies, they can reach out with their feeble gravity and take up a fragile orbit around each other. Of the many binary pairs of small galaxies we know of, the pair that is bound together mo ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... Hottest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Coolest Or, all have the same temperature ______________ Page 1 ! of !4 ...
... Hottest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Coolest Or, all have the same temperature ______________ Page 1 ! of !4 ...
How the universe works – Answer Key Star dust is the building
... sun. All life begins with stars. In our galaxy there are over 100 billion stars and in the universe there are over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on earth. Every star can create the basic matter for everything in the universe, including us. Stars are balls o ...
... sun. All life begins with stars. In our galaxy there are over 100 billion stars and in the universe there are over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on earth. Every star can create the basic matter for everything in the universe, including us. Stars are balls o ...
File
... •A star is a huge ball of hot glowing gases, called plasma. •Stars twinkle because the light is distorted by Earth’s atmosphere. •All stars have one thing in common, the way they produce energy. •The energy comes from nuclear reactions that change hydrogen into helium. It is as if millions of atomi ...
... •A star is a huge ball of hot glowing gases, called plasma. •Stars twinkle because the light is distorted by Earth’s atmosphere. •All stars have one thing in common, the way they produce energy. •The energy comes from nuclear reactions that change hydrogen into helium. It is as if millions of atomi ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a galaxy. When you look up into the night sky, most of the stars appear to be about the same size. However, in real ...
... atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a galaxy. When you look up into the night sky, most of the stars appear to be about the same size. However, in real ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
Physics - Content by Unit
... complex, distant objects, it is not surprising that astronomers did not immediately begin to worry about "the dark matter problem." By the early 1970s, technology, astronomy, and particle physics had advanced enough that the dark matter problem seemed more tractable. General relativity and nuclear p ...
... complex, distant objects, it is not surprising that astronomers did not immediately begin to worry about "the dark matter problem." By the early 1970s, technology, astronomy, and particle physics had advanced enough that the dark matter problem seemed more tractable. General relativity and nuclear p ...
Chapter13
... (> 8 Msun), leading to the formation of an iron core, happen extremely rapidly: Si burning lasts only for ~ 1 day. ...
... (> 8 Msun), leading to the formation of an iron core, happen extremely rapidly: Si burning lasts only for ~ 1 day. ...
parallax in arc seconds
... System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
... System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... A. __________ gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the ______ _____. 2. _______ _______ - spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar 3. _______ ...
... A. __________ gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the ______ _____. 2. _______ _______ - spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar 3. _______ ...
Slide 1
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.