Lecture - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... Our Universe In 1995, the Hubble Space Telescope pointed at a blank area of the sky near Ursa Major for 10 days. It produced this picture. Almost all the objects in this photograph are galaxies that are located between 5 and 10 billion light years away from Earth. Younger galaxies are blue while ol ...
... Our Universe In 1995, the Hubble Space Telescope pointed at a blank area of the sky near Ursa Major for 10 days. It produced this picture. Almost all the objects in this photograph are galaxies that are located between 5 and 10 billion light years away from Earth. Younger galaxies are blue while ol ...
A Unique Environmental Studies Program
... you look at Alpha Centauri through a telescope you will find that is actually is two stars (a binary star), and they revolve around each other once every 80,000 years. Alpha Centauri is particularly interesting to astronomers because it is the nearest star visible to the naked eye, being 'only' 4.3 ...
... you look at Alpha Centauri through a telescope you will find that is actually is two stars (a binary star), and they revolve around each other once every 80,000 years. Alpha Centauri is particularly interesting to astronomers because it is the nearest star visible to the naked eye, being 'only' 4.3 ...
Star Clusters and their stars
... and angular momentum from the disk will spin it up – this stage is called a Low-Mass X-ray Binary. An extreme case is MXB 1820-30, in the globular cluster NGC 6624. This system has the shortest orbital period known for any astronomical object – only 11.4 minutes. Relative to their mass, globular clu ...
... and angular momentum from the disk will spin it up – this stage is called a Low-Mass X-ray Binary. An extreme case is MXB 1820-30, in the globular cluster NGC 6624. This system has the shortest orbital period known for any astronomical object – only 11.4 minutes. Relative to their mass, globular clu ...
Star_Clusters
... and angular momentum from the disk will spin it up – this stage is called a Low-Mass X-ray Binary. An extreme case is MXB 1820-30, in the globular cluster NGC 6624. This system has the shortest orbital period known for any astronomical object – only 11.4 minutes. Relative to their mass, globular clu ...
... and angular momentum from the disk will spin it up – this stage is called a Low-Mass X-ray Binary. An extreme case is MXB 1820-30, in the globular cluster NGC 6624. This system has the shortest orbital period known for any astronomical object – only 11.4 minutes. Relative to their mass, globular clu ...
Full Press Release - The Open University
... the image have swept out the gas and dust to the periphery of the nebula, creating a hollow shell-like structure. The gas that has been swept out creates the bright filament-like structures seen in the surrounding regions. The dust in the gas is heated by the intense light coming from both the mass ...
... the image have swept out the gas and dust to the periphery of the nebula, creating a hollow shell-like structure. The gas that has been swept out creates the bright filament-like structures seen in the surrounding regions. The dust in the gas is heated by the intense light coming from both the mass ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... star against its spectral type. This works best for a cluster, where you know the stars are all at the same distance. Then apparent brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars only appear in certain parts of the diagram. ...
... star against its spectral type. This works best for a cluster, where you know the stars are all at the same distance. Then apparent brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars only appear in certain parts of the diagram. ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... Hot bright stars are towards the top left of the diagram while cool and dim stars are towards the bottom right. Some stars, like the supergiants are quite cool but because of their enormous size they are in the top right of the diagram. On the other hand white dwarfs are hot small stars and so appea ...
... Hot bright stars are towards the top left of the diagram while cool and dim stars are towards the bottom right. Some stars, like the supergiants are quite cool but because of their enormous size they are in the top right of the diagram. On the other hand white dwarfs are hot small stars and so appea ...
absolute magnitude
... – get the luminosity. This is your y-coordinate. – Then take the spectral type as your x-coordinate, e.g. K5 for Aldebaran. First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
... – get the luminosity. This is your y-coordinate. – Then take the spectral type as your x-coordinate, e.g. K5 for Aldebaran. First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula . • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae faintly visible to the ...
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula . • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae faintly visible to the ...
Black Hole
... It is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. There are three basic types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. A spiral galaxy is a flattened, discus-shaped collection of stars, having a central bulge. Examples include the Milky Way and Andromeda. An elliptical galaxy ranges in sha ...
... It is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. There are three basic types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. A spiral galaxy is a flattened, discus-shaped collection of stars, having a central bulge. Examples include the Milky Way and Andromeda. An elliptical galaxy ranges in sha ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... The largest stars are in the upper right corner of the HR Diagram. Note that Absolute Magnitude is a measure of the Luminosity of the Star Apparent visual Magnitude is a measure of the Apparent Brightness (or Intensity) of the starlight reaching the observer. ...
... The largest stars are in the upper right corner of the HR Diagram. Note that Absolute Magnitude is a measure of the Luminosity of the Star Apparent visual Magnitude is a measure of the Apparent Brightness (or Intensity) of the starlight reaching the observer. ...
Stars and Constellations
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. The distances to more remote stars are ...
... to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. The distances to more remote stars are ...
Slides from Dr. Frank`s Lecture17
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
HR Diagram and Stellar Fusion
... • Millions of miles of un-fused hydrogen, helium, carbon and other elements catastrophically collapse down onto the beyond white hot, hot iron core. • In real time that lasts only a matter of Earth hours, a massive star’s outer layers suddenly ignite in the most incredible nuclear display in the Uni ...
... • Millions of miles of un-fused hydrogen, helium, carbon and other elements catastrophically collapse down onto the beyond white hot, hot iron core. • In real time that lasts only a matter of Earth hours, a massive star’s outer layers suddenly ignite in the most incredible nuclear display in the Uni ...
Spectrum Analysis Activity File
... From right to left, weave “pull tab out” down slit A and back up slit B, down through slit C and back up slit D, then down through slit E. Always keep the “reference lines” aligned. Each element has this reference line for purposes of alignment. Match spectral lines of the known elements with the un ...
... From right to left, weave “pull tab out” down slit A and back up slit B, down through slit C and back up slit D, then down through slit E. Always keep the “reference lines” aligned. Each element has this reference line for purposes of alignment. Match spectral lines of the known elements with the un ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... began improving on the system that Fleming had developed while also recording more stellar spectra and classifying them by eye. Cannon discovered a new sequence that simplified the lettering to O B A F G K M. This is the system ...
... began improving on the system that Fleming had developed while also recording more stellar spectra and classifying them by eye. Cannon discovered a new sequence that simplified the lettering to O B A F G K M. This is the system ...
Answer to question 1 - Northwestern University
... expands and “over shoots the point where the internal heat (and light) pressure will hold up the envelope. •The result is that the envelope then comes ...
... expands and “over shoots the point where the internal heat (and light) pressure will hold up the envelope. •The result is that the envelope then comes ...
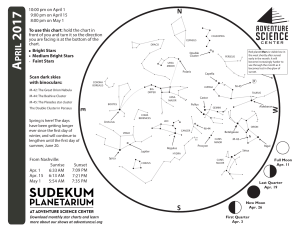
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
AS 60 - Astronomy of the Americas
... Astronomy 4 - Introduction to Astronomy Module 8 Quiz 1. If you take a spectrum of a galaxy, what type of spectrum will you observe? a. b. c. d. ...
... Astronomy 4 - Introduction to Astronomy Module 8 Quiz 1. If you take a spectrum of a galaxy, what type of spectrum will you observe? a. b. c. d. ...
Astronomy 10B List of Concepts– by Chapter
... • Stars form in clusters because … • The stages of star formation • Why does a disk form? • Why do jets form? • Differences between a proto-star and a main sequence star • Definition of Zero-Age Main Sequence star • Stellar mass and the rate of star formation (and evolution) • The H-R diagram and st ...
... • Stars form in clusters because … • The stages of star formation • Why does a disk form? • Why do jets form? • Differences between a proto-star and a main sequence star • Definition of Zero-Age Main Sequence star • Stellar mass and the rate of star formation (and evolution) • The H-R diagram and st ...
12.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun
... It can be seen from this H-R diagram that stars more massive than the Sun follow very different paths when leaving the Main Sequence: ...
... It can be seen from this H-R diagram that stars more massive than the Sun follow very different paths when leaving the Main Sequence: ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.