The Life of a Star
... If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a lowmass star becomes a white dwarf, which means it is much small ...
... If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a lowmass star becomes a white dwarf, which means it is much small ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
Stars, Stellar classification, H
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
Stars
... Ancient white dwarf stars shine in the Milky Way galaxy. White dwarfs are stars that have burned up all of the hydrogen and helium they once used as nuclear fuel to elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen ...
... Ancient white dwarf stars shine in the Milky Way galaxy. White dwarfs are stars that have burned up all of the hydrogen and helium they once used as nuclear fuel to elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen ...
dtu7ech11 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • how astronomers analyze starlight to determine a star’s temperature and chemical composition • how the total energy emitted by stars and their surface temperatures are related • the different classes of stars • the variety and importance of binary star systems • how astronomers calculate stellar m ...
... • how astronomers analyze starlight to determine a star’s temperature and chemical composition • how the total energy emitted by stars and their surface temperatures are related • the different classes of stars • the variety and importance of binary star systems • how astronomers calculate stellar m ...
chapter8
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
ASTRONOMY: WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW
... Ionized gasses surrounding a white dwarf seen as the result of slow gas ejected by the red giant being compressed by the fast gases as the red giant collapses into a white dwarf Know the characteristics and lifespan characteristics of white dwarfs. Does not undergo nuclear fusion but rather contains ...
... Ionized gasses surrounding a white dwarf seen as the result of slow gas ejected by the red giant being compressed by the fast gases as the red giant collapses into a white dwarf Know the characteristics and lifespan characteristics of white dwarfs. Does not undergo nuclear fusion but rather contains ...
Stellar Evolution - Harnett County High Schools Wiki
... turning lighthouse. This "pulsing" appearance gives some neutron stars the name pulsars. ...
... turning lighthouse. This "pulsing" appearance gives some neutron stars the name pulsars. ...
Lecture14
... around red supergiant stars. • Radiate in the infrared (cooling mechanism) • Are easily destroyed by collisions ...
... around red supergiant stars. • Radiate in the infrared (cooling mechanism) • Are easily destroyed by collisions ...
HR DIAGRAM ACTIVITY
... Analysis- use pages 627-628 to help you You can check your HR diagram at: http://deskarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/HertzsprungRussell-Diagram.jpg 1. Draw a circle around all the red giants on your graph and label this enclosed area Red Giants. 2. Draw a circle around all the white dwarfs and ...
... Analysis- use pages 627-628 to help you You can check your HR diagram at: http://deskarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/HertzsprungRussell-Diagram.jpg 1. Draw a circle around all the red giants on your graph and label this enclosed area Red Giants. 2. Draw a circle around all the white dwarfs and ...
Life on the Main Sequence + Expansion to Red Giant
... Mmax ~ 100 solar masses a) More massive clouds fragment into smaller pieces during star formation. ...
... Mmax ~ 100 solar masses a) More massive clouds fragment into smaller pieces during star formation. ...
Space The Life of a Star
... If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a low-mass star becomes a white dwarf, which means it is much smal ...
... If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a low-mass star becomes a white dwarf, which means it is much smal ...
More on Cluster HR diagrams - University of Texas Astronomy
... High-mass stars do lose mass, and if they lose enough, their mass at the time the carbon core forms could be small enough to result in a white dwarf. But it is believed that most stars more massive than 8-10 Mo cannot be “saved” as white dwarfs, and instead find themselves with a very different fat ...
... High-mass stars do lose mass, and if they lose enough, their mass at the time the carbon core forms could be small enough to result in a white dwarf. But it is believed that most stars more massive than 8-10 Mo cannot be “saved” as white dwarfs, and instead find themselves with a very different fat ...
and Concept Self-test (1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9)
... need to measure apparent brightness using at few as two frequency measurements. Table at right “V” is measured using “visible” light range (490-590 nm) and “B” blue line sees only “blue” light from 380-480 nm. Star “A”is Rigel, where it is very hot, (30,000 K) so more blue light than yellow. Star (c ...
... need to measure apparent brightness using at few as two frequency measurements. Table at right “V” is measured using “visible” light range (490-590 nm) and “B” blue line sees only “blue” light from 380-480 nm. Star “A”is Rigel, where it is very hot, (30,000 K) so more blue light than yellow. Star (c ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... If the stellar mass is not enough to light new thermonuclear reaction beyond the Helium burning, it ‘dies’ as a white dwarfs of Helium. ...
... If the stellar mass is not enough to light new thermonuclear reaction beyond the Helium burning, it ‘dies’ as a white dwarfs of Helium. ...
The Size and Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
... Dark Matter: A Major Problem for Contemporary Physics and Astronomy • Stars are a small fraction of the mass of major galaxies • The dark matter problem becomes more pronounced as you go out in the universe • The form of the dark matter is unknown; probably not what you studied in chemistry • Possi ...
... Dark Matter: A Major Problem for Contemporary Physics and Astronomy • Stars are a small fraction of the mass of major galaxies • The dark matter problem becomes more pronounced as you go out in the universe • The form of the dark matter is unknown; probably not what you studied in chemistry • Possi ...
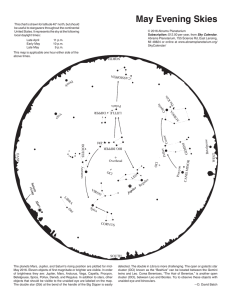
March
... Bright planets are low in the east and west at the beginning of the month. Venus (not shown on the chart) might be seen from places with a low western skyline, setting 40 minutes after the Sun at the start of the month. It sets steadily earlier, disappearing by mid-March. Golden Jupiter rises in the ...
... Bright planets are low in the east and west at the beginning of the month. Venus (not shown on the chart) might be seen from places with a low western skyline, setting 40 minutes after the Sun at the start of the month. It sets steadily earlier, disappearing by mid-March. Golden Jupiter rises in the ...
The First Star at Night
... I was asked recently which star is the first one to be visible at night. It is a question I hear often, and it is a quite interesting one because together with the question is usually another: 'is that the one called the evening star?' There is some confusion surrounding this topic. Indeed, I recall ...
... I was asked recently which star is the first one to be visible at night. It is a question I hear often, and it is a quite interesting one because together with the question is usually another: 'is that the one called the evening star?' There is some confusion surrounding this topic. Indeed, I recall ...
May 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive galaxy or cluster of galaxies bends the light emitted from a more distant galaxy, forming a highly magnified, though much distorted, image. In this particular case, the galaxy known as SDP.81 and an intervening galaxy line up so perfectly that the light f ...
... Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive galaxy or cluster of galaxies bends the light emitted from a more distant galaxy, forming a highly magnified, though much distorted, image. In this particular case, the galaxy known as SDP.81 and an intervening galaxy line up so perfectly that the light f ...
Star Cycle2013
... Nuclear fusion • Fusion makes LOTS of energy • E = mc2 What do E and M symbolize? E = Energy and m = mass ….and “c”….? c = the speed of light (300,000,000 m/s) ...
... Nuclear fusion • Fusion makes LOTS of energy • E = mc2 What do E and M symbolize? E = Energy and m = mass ….and “c”….? c = the speed of light (300,000,000 m/s) ...
Schedule for Spring 2013 SCI 103 Introductory Astronomy
... Full HR diagram with main sequence masses Sample Problems ...
... Full HR diagram with main sequence masses Sample Problems ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • The value of 6 solar masses per solar luminosity tells us that most of the matter is dimmer than the Sun out to the Sun’s orbit • Mass-to-Light ratio of our Sun is 1 solar mass per solar luminosity • So most matter is dimmer than the Sun ...
... • The value of 6 solar masses per solar luminosity tells us that most of the matter is dimmer than the Sun out to the Sun’s orbit • Mass-to-Light ratio of our Sun is 1 solar mass per solar luminosity • So most matter is dimmer than the Sun ...
The Missing Mass
... • Many of the stars will be faint, red main sequence stars, but some will be bright blue O and B stars. These stars will continue to drift through the region. • The O and B stars don’t go far before they go supernova. The brightest (and bluest) of a galaxy’s stars will never be far from the spiral a ...
... • Many of the stars will be faint, red main sequence stars, but some will be bright blue O and B stars. These stars will continue to drift through the region. • The O and B stars don’t go far before they go supernova. The brightest (and bluest) of a galaxy’s stars will never be far from the spiral a ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.