Lab 5 Takehome
... Figure 2 shows the same stars, but here what’s plotted is the apparent brightness of the star as seen from the Earth, instead of the luminosity. The vertical axis is scaled so that 1.0 represe ...
... Figure 2 shows the same stars, but here what’s plotted is the apparent brightness of the star as seen from the Earth, instead of the luminosity. The vertical axis is scaled so that 1.0 represe ...
Photometry
... an object. Often, we will want to know the number of photons at a specific wavelength. When this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an ...
... an object. Often, we will want to know the number of photons at a specific wavelength. When this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an ...
Andromeda Galaxy www.AssignmentPoint.com The Andromeda
... concerning the nature of the Milky Way, spiral nebulae, and the dimensions of the universe. To support his claim of the Great Andromeda Nebula being, in fact, an external galaxy, Curtis also noted the appearance of dark lanes resembling the dust clouds in our own galaxy within Andromeda- the Milky W ...
... concerning the nature of the Milky Way, spiral nebulae, and the dimensions of the universe. To support his claim of the Great Andromeda Nebula being, in fact, an external galaxy, Curtis also noted the appearance of dark lanes resembling the dust clouds in our own galaxy within Andromeda- the Milky W ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... dimmest Note: The eye has a different response to light than mechanical devices. Thus: mV = visual apparent magnitude mB = bolometric apparent magnitude (magnitude including all wavelengths) Relationship between apparent magnitude and apparent brightness What this says is that if I have two stars wi ...
... dimmest Note: The eye has a different response to light than mechanical devices. Thus: mV = visual apparent magnitude mB = bolometric apparent magnitude (magnitude including all wavelengths) Relationship between apparent magnitude and apparent brightness What this says is that if I have two stars wi ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... Milky Way), a bulge (a large clump of stars surrounding the galactic center), and a halo (a larger, spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from dista ...
... Milky Way), a bulge (a large clump of stars surrounding the galactic center), and a halo (a larger, spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from dista ...
1705 chart front
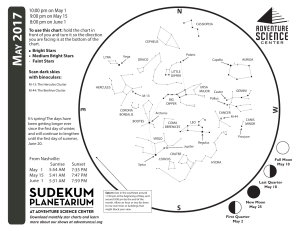
... Stay out past midnight and look toward the east to see three bright stars that make up the Summer Triangle. Low in the southeast you may find the bright red star Antares in Scorpius the Scorpion, and just to its left the even brighter planet Saturn. A backyard telescope will easily reveal the rings ...
... Stay out past midnight and look toward the east to see three bright stars that make up the Summer Triangle. Low in the southeast you may find the bright red star Antares in Scorpius the Scorpion, and just to its left the even brighter planet Saturn. A backyard telescope will easily reveal the rings ...
File
... a fixed relation between period and luminosity. By comparing how bright a variable star appears from Earth, to its actual luminosity, we can calculate the distance. Three Major Classification of Galaxies Galaxy, Elliptical Galaxy, Irregular Galaxy ...
... a fixed relation between period and luminosity. By comparing how bright a variable star appears from Earth, to its actual luminosity, we can calculate the distance. Three Major Classification of Galaxies Galaxy, Elliptical Galaxy, Irregular Galaxy ...
Properties of Stars
... A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of stars and runs diagonally from the upper left to the lower right on the H–R diagram. ...
... A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of stars and runs diagonally from the upper left to the lower right on the H–R diagram. ...
THREE INTRIGUER NEBULAE IN CONSTELLATION CARINA
... (Hopp & Materne 1985, Nakazawa et al. 2000) that is the third nearest galaxy cluster to us, inhabiting the eastern part of this constellation (see picture on first page). Antlia cluster, also known as ACO S 0636, is centered at R.A. 10h 30m 01s Dec. –35° 19´ 35”. With a galactic latitude of 19 degr ...
... (Hopp & Materne 1985, Nakazawa et al. 2000) that is the third nearest galaxy cluster to us, inhabiting the eastern part of this constellation (see picture on first page). Antlia cluster, also known as ACO S 0636, is centered at R.A. 10h 30m 01s Dec. –35° 19´ 35”. With a galactic latitude of 19 degr ...
ppt
... • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of masses and ages! • Conveniently, many stars ar ...
... • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of masses and ages! • Conveniently, many stars ar ...
Sequencing the Stars
... file listing data for each star, one star per line. I culled from the lists any star whose flux was such that the brightest pixels would have saturated the CCD chip. Then I normalized the fluxes to represent what I would have gotten from a 1 second exposure and I combined the three lists into one ma ...
... file listing data for each star, one star per line. I culled from the lists any star whose flux was such that the brightest pixels would have saturated the CCD chip. Then I normalized the fluxes to represent what I would have gotten from a 1 second exposure and I combined the three lists into one ma ...
ASTR2100 - Saint Mary's University | Astronomy & Physics
... function of the age of the stars, there appears to be a net metallicity growth with age amounting to: Δ<[Fe/H]> ≈ 0.5–0.7/1010 years, i.e. an increase of Fe/H by 4 ±1 every 1010 years. The relationship is not zeroed to the Sun, since solar metallicity is calculated to have been reached at an age of ...
... function of the age of the stars, there appears to be a net metallicity growth with age amounting to: Δ<[Fe/H]> ≈ 0.5–0.7/1010 years, i.e. an increase of Fe/H by 4 ±1 every 1010 years. The relationship is not zeroed to the Sun, since solar metallicity is calculated to have been reached at an age of ...
E8B6_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_Final
... information which can be observed in the photo EXCEPT A. more stars exist within the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy than are above or below it. B. the Milky Way Galaxy contains a range of stars from high temperature to low temperature. C. the Milky Way Galaxy is a barred-spiral galaxy which has severa ...
... information which can be observed in the photo EXCEPT A. more stars exist within the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy than are above or below it. B. the Milky Way Galaxy contains a range of stars from high temperature to low temperature. C. the Milky Way Galaxy is a barred-spiral galaxy which has severa ...
Investigate Stars and Galaxies - American Museum of Natural History
... (Answer: They don’t have enough mass to produce the temperatures and densities in their core that lead to nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion causes stars to shine.) ...
... (Answer: They don’t have enough mass to produce the temperatures and densities in their core that lead to nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion causes stars to shine.) ...
Pallavicini - IASF Milano
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
Sizing Up The Universe
... know that, on average, for every million parsecs (a megaparsec) farther away a galaxy is from us, it will be going away from us an additional 71 kilometers per second faster. A galaxy that is 10 megaparsecs away from us will have a recessional velocity of 710 kilometers per second, and one that is 1 ...
... know that, on average, for every million parsecs (a megaparsec) farther away a galaxy is from us, it will be going away from us an additional 71 kilometers per second faster. A galaxy that is 10 megaparsecs away from us will have a recessional velocity of 710 kilometers per second, and one that is 1 ...
Stars: radius and mass
... We have been assuming that we see the binary system face on when imaging the orbit and edge-on when measuring the velocity. In general, the orbit is tilted relative to our line of sight. The tilt, or inclination i, will affect the observed orbit trajectory and the observed velocities. In general, on ...
... We have been assuming that we see the binary system face on when imaging the orbit and edge-on when measuring the velocity. In general, the orbit is tilted relative to our line of sight. The tilt, or inclination i, will affect the observed orbit trajectory and the observed velocities. In general, on ...
Supernovae – the biggest bangs since the Big Bang
... Sun, it will make a huge explosion. The entire white dwarf will explode with the energy of four billion Suns. This is called a “white dwarf supernova” (also known as a “Type Ia supernova”). Imagine you made a series of bombs, each with the same amount of the same material. The bombs would all hav ...
... Sun, it will make a huge explosion. The entire white dwarf will explode with the energy of four billion Suns. This is called a “white dwarf supernova” (also known as a “Type Ia supernova”). Imagine you made a series of bombs, each with the same amount of the same material. The bombs would all hav ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
Today`s Class: Measuring temperatures of stars Astronomer`s
... View looking south from the historic mountain top Pic du Midi Observatory combines moonlit domes, a winter night sky, and the snowy peaks of the French Pyrenees. Encroaching on the night, lights from the La Mongie ski resort illuminate the mountain slopes. The night sky features stars of the constel ...
... View looking south from the historic mountain top Pic du Midi Observatory combines moonlit domes, a winter night sky, and the snowy peaks of the French Pyrenees. Encroaching on the night, lights from the La Mongie ski resort illuminate the mountain slopes. The night sky features stars of the constel ...
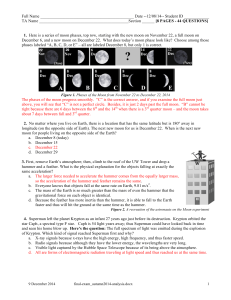
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
TYPES OF STARS
... the locations (energies) at which absorption or emission lines occur can be used to “fingerprint” the star’s composition. The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines ( ...
... the locations (energies) at which absorption or emission lines occur can be used to “fingerprint” the star’s composition. The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines ( ...
canopus e.g procyon
... Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about ...
... Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years from the Earth (now) and about 0.24 light years from Alpha-Centauri A and B. • Alpha-Centauri A and B – a double star system with a period of about ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... depending on its size. • If the star is of low mass, it expands its outer layers, creating nebulae and a white dwarf forms from the core. • If it is of high mass, death occurs in a massive explosion known as a supernova, the remaining core then transforms into a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... depending on its size. • If the star is of low mass, it expands its outer layers, creating nebulae and a white dwarf forms from the core. • If it is of high mass, death occurs in a massive explosion known as a supernova, the remaining core then transforms into a neutron star or a black hole. ...
HW #4 (due March 27)
... the locations (energies) at which absorption or emission lines occur can be used to “fingerprint” the star’s composition. The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines ( ...
... the locations (energies) at which absorption or emission lines occur can be used to “fingerprint” the star’s composition. The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines ( ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.