Star Life Cycle – Web Activity
... 1. In the age table, what stage of star life corresponds with “Old Age-Death” of a human? 2. Describe what is in the interstellar medium, including specific names of elements present. ...
... 1. In the age table, what stage of star life corresponds with “Old Age-Death” of a human? 2. Describe what is in the interstellar medium, including specific names of elements present. ...
PDF Version
... variation, which is the amount of time before the star’s brightness curve repeats itself, varies with the star’s intrinsic brightness. The star’s apparent brightness, which is the brightness that we can see ourselves, is equal to the intrinsic brightness divided by the square of the distance from us ...
... variation, which is the amount of time before the star’s brightness curve repeats itself, varies with the star’s intrinsic brightness. The star’s apparent brightness, which is the brightness that we can see ourselves, is equal to the intrinsic brightness divided by the square of the distance from us ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... spheroidal galaxies. Both globular clusters and dwarf spheroidal galaxies give rise to tidal streams. Globular clusters appear to contain no dark matter, while dwarf spheroidal galaxies are dominated by dark matter. Stars account for more than half of the ...
... spheroidal galaxies. Both globular clusters and dwarf spheroidal galaxies give rise to tidal streams. Globular clusters appear to contain no dark matter, while dwarf spheroidal galaxies are dominated by dark matter. Stars account for more than half of the ...
Lecture 7
... 4) Galaxies, groups, clusters, walls, and superclusters all formed from gravity acting on matter in the Universe, much as stars form from clumps of gas within galaxies. We will see computer simulations of this later. 5) The density of neighbors around a galaxy is called its environment. These range ...
... 4) Galaxies, groups, clusters, walls, and superclusters all formed from gravity acting on matter in the Universe, much as stars form from clumps of gas within galaxies. We will see computer simulations of this later. 5) The density of neighbors around a galaxy is called its environment. These range ...
The Stars - University of Redlands
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
Binocular Universe: Summer`s Swan Song
... Before shuffling back to Sadr, take a detour northward to the colorful triple star Omicron-1 (ο-1) Cygni. Omicron-1 lies 5° west-northwest of Deneb. Swing your binoculars its way and you’ll find not one, but two suns. Fourth-magnitude Omicron-1 will appear pale orange, while its 5th-magnitude compan ...
... Before shuffling back to Sadr, take a detour northward to the colorful triple star Omicron-1 (ο-1) Cygni. Omicron-1 lies 5° west-northwest of Deneb. Swing your binoculars its way and you’ll find not one, but two suns. Fourth-magnitude Omicron-1 will appear pale orange, while its 5th-magnitude compan ...
Astronomy 102, Spring 2003 Solutions to Review Problems
... have been from a hugely massive star that left behind a black hole rather than a pulsar. Sometimes there’s just no way to know. We observe supernovae now where the type is in doubt; the lightcurve and spectrum are consistent with both types. This is also true of remnants observed from historical sup ...
... have been from a hugely massive star that left behind a black hole rather than a pulsar. Sometimes there’s just no way to know. We observe supernovae now where the type is in doubt; the lightcurve and spectrum are consistent with both types. This is also true of remnants observed from historical sup ...
PowerPoint - Star Life Cycle
... Which of the following best describes the category in which the Sun would be placed? A. blue supergiant stars B. red giant stars C. yellow main sequence stars D. white dwarf stars ...
... Which of the following best describes the category in which the Sun would be placed? A. blue supergiant stars B. red giant stars C. yellow main sequence stars D. white dwarf stars ...
Related Handout - Orange County Astronomers
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
7a Properties of Stars.pptx
... • Luminosity is the measure of the energy output from the surface of a star per second. • This is based on the star’s apparent magnitude and how far away it is. • Sun = 3.85x1026 Wa?s = 3. ...
... • Luminosity is the measure of the energy output from the surface of a star per second. • This is based on the star’s apparent magnitude and how far away it is. • Sun = 3.85x1026 Wa?s = 3. ...
Hall Scorpius constellation (11) Jacob Hall Physics 1040, sec 002
... Dschubba "forehead" marks the middle of the scorpion’s head. It is a multiple star with a hot class B star. It lies about 402 light-years from Earth. Star 7518 theta Scorpii is a yellow giant star approximately 270 light-years distant, whose luminosity is 960 times that of the Sun. It is also known ...
... Dschubba "forehead" marks the middle of the scorpion’s head. It is a multiple star with a hot class B star. It lies about 402 light-years from Earth. Star 7518 theta Scorpii is a yellow giant star approximately 270 light-years distant, whose luminosity is 960 times that of the Sun. It is also known ...
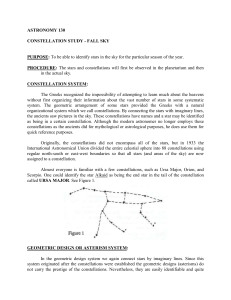
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
The Argonauts, background to the constellation Carina Argo Navis
... through Carina, there are also a large number of open clusters in the constellation. These include the "Southern Pleiades." The most notable object in Carina is Homunculus Nebula (from the Latin meaning Little Man), a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye believed to have been ejected in an enor ...
... through Carina, there are also a large number of open clusters in the constellation. These include the "Southern Pleiades." The most notable object in Carina is Homunculus Nebula (from the Latin meaning Little Man), a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye believed to have been ejected in an enor ...
Assignment 10
... d. this black hole contains only dark matter, and we know dark matter is concentrated toward the center of our Galaxy; none of it can be found near the outer regions of the Milky Way e. no one can think of a way to make a black hole this massive; that's why most astronomers are skeptical about the ...
... d. this black hole contains only dark matter, and we know dark matter is concentrated toward the center of our Galaxy; none of it can be found near the outer regions of the Milky Way e. no one can think of a way to make a black hole this massive; that's why most astronomers are skeptical about the ...
Chapter 20 Stellar Evolution (20.1-20.3)
... The envelope is called a planetary nebula, even though it has nothing to do with planets—early astronomers viewing the fuzzy envelope thought it resembled a planetary system. Planetary nebulae can have many shapes: As the dead core of the star cools, the nebula continues to expand and dissipates int ...
... The envelope is called a planetary nebula, even though it has nothing to do with planets—early astronomers viewing the fuzzy envelope thought it resembled a planetary system. Planetary nebulae can have many shapes: As the dead core of the star cools, the nebula continues to expand and dissipates int ...
08 September: How far away are the closest stars?
... of the Sun • The 34 stars are contained in 25 star systems • Those visible to the naked eye are Alpha Centauri (A & B), Sirius, Epsilon Eridani, Epsilon Indi, Tau Ceti, and Procyon • We won’t see any of them tonight! ...
... of the Sun • The 34 stars are contained in 25 star systems • Those visible to the naked eye are Alpha Centauri (A & B), Sirius, Epsilon Eridani, Epsilon Indi, Tau Ceti, and Procyon • We won’t see any of them tonight! ...
Lecture notes -- pdf file - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... The distances to the stars are truly enormous • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
... The distances to the stars are truly enormous • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
Week 11
... FUSION: small nuclei combine together IF they collide fast enough • example: hydrogen ...
... FUSION: small nuclei combine together IF they collide fast enough • example: hydrogen ...
AST121 Introduction to Astronomy
... • Local space-time is curved by the presence of mass – light (and everything else) travels in a curved space-time. – objects left to themselves travel in straight lines – a straight-line on a curved surface is a geodesic, or great circle ...
... • Local space-time is curved by the presence of mass – light (and everything else) travels in a curved space-time. – objects left to themselves travel in straight lines – a straight-line on a curved surface is a geodesic, or great circle ...
How Far To That Star?
... The Standard Candle Method compares Apparent magnitude to Absolute Magnitude to find the distance to more distant stars and even other galaxies It uses the Inverse Square Law. ...
... The Standard Candle Method compares Apparent magnitude to Absolute Magnitude to find the distance to more distant stars and even other galaxies It uses the Inverse Square Law. ...
Lecture5 - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Also Sun • “Spiral Nebulae” are outside our Galaxy • “Spiral Nebulae” are systems of stars, i.e., other galaxies • Slipher’s spectroscopic measurements high radial velocities • Showed photos of spiral nebulae – with absorbing bands ...
... Also Sun • “Spiral Nebulae” are outside our Galaxy • “Spiral Nebulae” are systems of stars, i.e., other galaxies • Slipher’s spectroscopic measurements high radial velocities • Showed photos of spiral nebulae – with absorbing bands ...
Parallax - High Point University
... • Local space-time is curved by the presence of mass – light (and everything else) travels in a curved space-time. – objects left to themselves travel in straight lines – a straight-line on a curved surface is a geodesic, or great circle ...
... • Local space-time is curved by the presence of mass – light (and everything else) travels in a curved space-time. – objects left to themselves travel in straight lines – a straight-line on a curved surface is a geodesic, or great circle ...
Hypervelocity Globular: A beacon of merging clusters Oleg Gnedin with Alexey Vikhlinin
... While measuring radial velocities of globular clusters around M87 in Virgo Cluster, Caldwell et al. (2014) found an outlier… A triple interaction with a binary black hole (slingshot) can lead to a very high ejection velocity. ...
... While measuring radial velocities of globular clusters around M87 in Virgo Cluster, Caldwell et al. (2014) found an outlier… A triple interaction with a binary black hole (slingshot) can lead to a very high ejection velocity. ...
Chapter19
... the cycle begins anew. AGB stars have thick, cool dust shells around them that absorb their visible light and re-emit it in the infrared. The gas in the planetary nebula was shed from the star while it was an AGB star. The star must be hot in order to produce ultraviolet radiation, which can ionize ...
... the cycle begins anew. AGB stars have thick, cool dust shells around them that absorb their visible light and re-emit it in the infrared. The gas in the planetary nebula was shed from the star while it was an AGB star. The star must be hot in order to produce ultraviolet radiation, which can ionize ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.