annie jump cannon
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
2 - Lnk2Lrn
... A star is a big ball of gas, with fusion going on at its center, held together by gravity! ...
... A star is a big ball of gas, with fusion going on at its center, held together by gravity! ...
Science Olympiad 2008 Reach for the Stars Division B
... A) location where they are formed B) time they are formed C) luminosity they are formed with D) mass they are formed with E) color they are formed with 111. The spectral sequence sorts stars according to: (choose as many as apply) A) mass B) surface temperature C) luminosity D) core temperature E) r ...
... A) location where they are formed B) time they are formed C) luminosity they are formed with D) mass they are formed with E) color they are formed with 111. The spectral sequence sorts stars according to: (choose as many as apply) A) mass B) surface temperature C) luminosity D) core temperature E) r ...
d = 1 / p
... A quick glance at the night sky will tell you that different stars have different brightnesses. But how much of that effect is due to the fact that some stars are further away, and how much is due to certain stars being intrinsically brighter? If we know the distances from parallax, we can remove th ...
... A quick glance at the night sky will tell you that different stars have different brightnesses. But how much of that effect is due to the fact that some stars are further away, and how much is due to certain stars being intrinsically brighter? If we know the distances from parallax, we can remove th ...
d = 1 / p
... A quick glance at the night sky will tell you that different stars have different brightnesses. But how much of that effect is due to the fact that some stars are further away, and how much is due to certain stars being intrinsically brighter? If we know the distances from parallax, we can remove th ...
... A quick glance at the night sky will tell you that different stars have different brightnesses. But how much of that effect is due to the fact that some stars are further away, and how much is due to certain stars being intrinsically brighter? If we know the distances from parallax, we can remove th ...
Mass and composition determine most of the properties of a star
... The diameters of stars range from as little as 1/10 the Sun’s diameter to hundreds of times larger. The mass of stars can be from less than 1/100 to 20 or more times that of our Sun. Stars over 50 times the Sun’s mass are extremely rare. Our Sun is a medium sized star. ...
... The diameters of stars range from as little as 1/10 the Sun’s diameter to hundreds of times larger. The mass of stars can be from less than 1/100 to 20 or more times that of our Sun. Stars over 50 times the Sun’s mass are extremely rare. Our Sun is a medium sized star. ...
bright - TutorPlus
... • How bright a star appears to us is called its apparent magnitude. • The actual total radiant energy given off by a star is called its luminosity and is sometimes referred to as the absolute magnitude. ...
... • How bright a star appears to us is called its apparent magnitude. • The actual total radiant energy given off by a star is called its luminosity and is sometimes referred to as the absolute magnitude. ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... 5. Circle the group of ten stars above the main sequence. 6. Label these stars as the “red giant stars.” 7. Circle the group of five stars below the main sequence. 8. Label these stars as the “white dwarf stars.” ...
... 5. Circle the group of ten stars above the main sequence. 6. Label these stars as the “red giant stars.” 7. Circle the group of five stars below the main sequence. 8. Label these stars as the “white dwarf stars.” ...
AST 112 – Activity #4 The Stellar Magnitude System
... The stellar magnitude system ranks stars according to their brightnesses. The original idea came from the ancient Greek scientist Hipparchus (c. 130 B.C.), who proclaimed the brightest stars to be of the first “magnitude”, the next brightest of the second magnitude, and so on down to 6th magnitude f ...
... The stellar magnitude system ranks stars according to their brightnesses. The original idea came from the ancient Greek scientist Hipparchus (c. 130 B.C.), who proclaimed the brightest stars to be of the first “magnitude”, the next brightest of the second magnitude, and so on down to 6th magnitude f ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
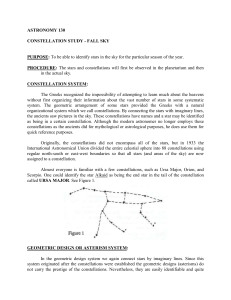
... Deneb (in Cygnus) and Altair (in Aquila). These three constellations make good reference points for the rest of the fall sky. Note in the eastern sky a large area defined roughly by four stars in a great square. This is the body of the constellation of Pegasus, which is connected to Andromeda. Make ...
... Deneb (in Cygnus) and Altair (in Aquila). These three constellations make good reference points for the rest of the fall sky. Note in the eastern sky a large area defined roughly by four stars in a great square. This is the body of the constellation of Pegasus, which is connected to Andromeda. Make ...
The “Life” of Non-living Stars - Etiwanda E
... Size of star changes very little during this stage ...
... Size of star changes very little during this stage ...