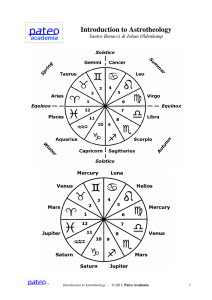
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... fainter than magnitude 3. The spatial relation of the one exception (a magnitude 2.9 star, 7O away) is such that it conceivably could be represented by a cupule on the other side of the crack. (The next nearest bright stars in the sky are in the constellation Scorpius.) Sagittarius does not present ...
... fainter than magnitude 3. The spatial relation of the one exception (a magnitude 2.9 star, 7O away) is such that it conceivably could be represented by a cupule on the other side of the crack. (The next nearest bright stars in the sky are in the constellation Scorpius.) Sagittarius does not present ...
Exploring Stars - Discovery Education
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
Chapter 5 Galaxies and Star Systems
... Our sun is the one star in our solar system. As you move past our solar system, billions of other stars make up our galaxy. Most stars are members of groups of two or more stars, called star systems. Binary stars are pairs of stars. Scientists detect binary stars by observing the brightness and moti ...
... Our sun is the one star in our solar system. As you move past our solar system, billions of other stars make up our galaxy. Most stars are members of groups of two or more stars, called star systems. Binary stars are pairs of stars. Scientists detect binary stars by observing the brightness and moti ...
Analysis of Two Pulsating X-ray Sources
... The acceleration due to gravity (g) on the surface of a star (according to Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation) is given by g = (GM)/R2 where G = 6.67 X 10-11 Nm2/kg2, M=star’s mass and R = star’s radius Centripetal acceleration (ac) of an object on the surface of a star at its equator is given by ...
... The acceleration due to gravity (g) on the surface of a star (according to Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation) is given by g = (GM)/R2 where G = 6.67 X 10-11 Nm2/kg2, M=star’s mass and R = star’s radius Centripetal acceleration (ac) of an object on the surface of a star at its equator is given by ...
E1 Introduction to the universe
... scales of luminosity and/or absolute magnitude, spectral class and/or surface temperature Students should be aware that the scale is not linear. Students should know that the mass of main sequence stars determines their position on the HR diagram. ...
... scales of luminosity and/or absolute magnitude, spectral class and/or surface temperature Students should be aware that the scale is not linear. Students should know that the mass of main sequence stars determines their position on the HR diagram. ...
August Newsletter
... Corona Australis, the Southern Crown is an old constellation and is believed to represent the crown worn by the centaur Sagittarius. It was one of the original 48 constellations named by the astronomer Ptolemy. In ancient times it was pictured as a hand full of arrows held by the centaur, Centaurus. ...
... Corona Australis, the Southern Crown is an old constellation and is believed to represent the crown worn by the centaur Sagittarius. It was one of the original 48 constellations named by the astronomer Ptolemy. In ancient times it was pictured as a hand full of arrows held by the centaur, Centaurus. ...
about Stars
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... Black hole- an object so massive (not always big but having a lot of mass) and dense that even light cannot escape its gravity. Some massive stars produce leftovers too massive to become stable neutron stars. These leftovers contract and the force of the contraction leaves a black hole. Star Groups ...
... Black hole- an object so massive (not always big but having a lot of mass) and dense that even light cannot escape its gravity. Some massive stars produce leftovers too massive to become stable neutron stars. These leftovers contract and the force of the contraction leaves a black hole. Star Groups ...
Friday, April 25 - Otterbein University
... distance ladder out as far as we can see Cepheids – about 50 million ly • In 1920 Hubble used this technique to measure the distance to Andromeda (about 2 million ly) • Works best for periodic variables ...
... distance ladder out as far as we can see Cepheids – about 50 million ly • In 1920 Hubble used this technique to measure the distance to Andromeda (about 2 million ly) • Works best for periodic variables ...
Luminosity - U of L Class Index
... • The light curve of this pulsating variable star shows that its brightness alternately rises and falls over a 50-day period ...
... • The light curve of this pulsating variable star shows that its brightness alternately rises and falls over a 50-day period ...
Interpreting the HR diagram of stellar clusters
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
Astrophysics E1. This question is about stars.
... E2. This question is about cosmology. (a) The diagram below represents a spherical region of space based on Newton’s model of the universe. Earth is at the centre of the region. The dark line represents a very thin spherical shell of space distance R from Earth. With reference to the diagram and New ...
... E2. This question is about cosmology. (a) The diagram below represents a spherical region of space based on Newton’s model of the universe. Earth is at the centre of the region. The dark line represents a very thin spherical shell of space distance R from Earth. With reference to the diagram and New ...
Classifying the Spectra of Stars:
... noticeable. Band heads are very "thick" absorption lines that break up the spectrum. ...
... noticeable. Band heads are very "thick" absorption lines that break up the spectrum. ...
HW #02 Solutions
... 10. If our Sun has a surface temperature of 5840 K, how many times hotter than the Sun is the hottest Otype star? How many times cooler than the Sun is the coolest M-type star? The hottest O-type star has a temperature of about 50,000 K and this is approximately 10 times hotter than the Sun (5,800 K ...
... 10. If our Sun has a surface temperature of 5840 K, how many times hotter than the Sun is the hottest Otype star? How many times cooler than the Sun is the coolest M-type star? The hottest O-type star has a temperature of about 50,000 K and this is approximately 10 times hotter than the Sun (5,800 K ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowing gas that is a galactic twin to the famous ring around the supernova 1987A--see the image of S ...
... disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowing gas that is a galactic twin to the famous ring around the supernova 1987A--see the image of S ...
apparent magnitude - Harding University
... they orbit one another. A visual binary is an orbiting pair of stars that can be resolved (normally with a telescope) as two stars. If one uses large telescopes, about 10% of the stars in the sky are visual binaries. ...
... they orbit one another. A visual binary is an orbiting pair of stars that can be resolved (normally with a telescope) as two stars. If one uses large telescopes, about 10% of the stars in the sky are visual binaries. ...