doc - Pocket Stars
... chart if currently visible and Done is chosen. An image of the object is displayed if available. Choose "Info" to show a text description of the object. Messier and Caldwell images can be downloaded automatically if you have an internet connection to your Smartphone (either phone network or ActiveSy ...
... chart if currently visible and Done is chosen. An image of the object is displayed if available. Choose "Info" to show a text description of the object. Messier and Caldwell images can be downloaded automatically if you have an internet connection to your Smartphone (either phone network or ActiveSy ...
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
... space slightly larger than the solar system. D) They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
... space slightly larger than the solar system. D) They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
The galactic metallicity gradient Martín Hernández, Nieves Leticia
... is, the more rapidly it exhausts its hydrogen supply. For instance , the expected lifetime of a star ten times more massive than the Sun is about ten million (10 000 000) years, compared to the ten thousand million (10 000 000 000) years that a star like the Sun lives. Thus, high-mass stars burn hot ...
... is, the more rapidly it exhausts its hydrogen supply. For instance , the expected lifetime of a star ten times more massive than the Sun is about ten million (10 000 000) years, compared to the ten thousand million (10 000 000 000) years that a star like the Sun lives. Thus, high-mass stars burn hot ...
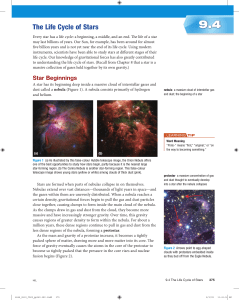
The Life Cycle of Stars
... protostar to form (Figure 3). The new star, buried inside the nebula, emits radiation in the form of heat, light, X-rays, gamma rays, and other energetic particles. Energy generated at the core makes its way to the surface and is radiated away at the photosphere. This radiation causes gases surround ...
... protostar to form (Figure 3). The new star, buried inside the nebula, emits radiation in the form of heat, light, X-rays, gamma rays, and other energetic particles. Energy generated at the core makes its way to the surface and is radiated away at the photosphere. This radiation causes gases surround ...
July 2014 BRAS Newsletter - The Baton Rouge Astronomical Society
... NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, launched into an Earth-trailing orbit in 2009, stared at some 156,000 stars in the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more plan ...
... NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, launched into an Earth-trailing orbit in 2009, stared at some 156,000 stars in the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more plan ...
Camelopardalis-Better-Know-A-Constellation
... reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one in 1954 (SN 1954J) with the others, a half a century later in 2002 (SN 2002kg) and in 2004 (SN 2004DJ). ...
... reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one in 1954 (SN 1954J) with the others, a half a century later in 2002 (SN 2002kg) and in 2004 (SN 2004DJ). ...
January 2015 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... packed, has a radius of 17.6 light years and the cluster's tidal radius has a radius of 33 light years. However, about one-third of confirmed member stars have been observed to be well outside this boundary in the cluster's extended halo. These stars are probably in the process of escaping from the ...
... packed, has a radius of 17.6 light years and the cluster's tidal radius has a radius of 33 light years. However, about one-third of confirmed member stars have been observed to be well outside this boundary in the cluster's extended halo. These stars are probably in the process of escaping from the ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
HR DIAGRAM (Page 1) - McDonald Observatory
... Looking up into the night sky, you see thousands of stars at varying distances from Earth. The luminosity and temperature of each star varies as well. These are the reasons behind the wide range of apparent magnitudes of stars. Imagine being able to magically pull or push each star (including the su ...
... Looking up into the night sky, you see thousands of stars at varying distances from Earth. The luminosity and temperature of each star varies as well. These are the reasons behind the wide range of apparent magnitudes of stars. Imagine being able to magically pull or push each star (including the su ...
File
... *Their cores contract and fuse helium first in the core and then in a shell, producing a carbon–oxygen core. ...
... *Their cores contract and fuse helium first in the core and then in a shell, producing a carbon–oxygen core. ...
Section 4
... the positions of the bright star in Algol, its dim companion star, and Earth when Algol appears less bright? (The companion star would be passing between the bright star and Earth.) Apply Ask: How might life on Earth be different if our sun were part of a binary system? (Possible answers: there woul ...
... the positions of the bright star in Algol, its dim companion star, and Earth when Algol appears less bright? (The companion star would be passing between the bright star and Earth.) Apply Ask: How might life on Earth be different if our sun were part of a binary system? (Possible answers: there woul ...
Lecture6
... • Since all protostars of all mass range are born at roughly ~ 3000 K, with different luminosities, they all lie along the Hayashi Track on the HR Diagram. See Fig. II-56. (See class notes for the details.) • As the protostar keeps contracting and heats up, it moves on the H-R Diagram from the Haya ...
... • Since all protostars of all mass range are born at roughly ~ 3000 K, with different luminosities, they all lie along the Hayashi Track on the HR Diagram. See Fig. II-56. (See class notes for the details.) • As the protostar keeps contracting and heats up, it moves on the H-R Diagram from the Haya ...
star
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... but well below the stellar regime. Considerable radiation comes from the disk atmosphere, which will typically have a density less than 10^15 cm^-3 but well above the molecular cloud core value. The innermost regions of an accretion disk can be very hot. ...
... but well below the stellar regime. Considerable radiation comes from the disk atmosphere, which will typically have a density less than 10^15 cm^-3 but well above the molecular cloud core value. The innermost regions of an accretion disk can be very hot. ...
Rotation in the ZAMS: Be and Bn stars
... Figure 3a shows the apparent V=7 magnitude limited counts of dwarf Be stars relative to dwarf B stars. There is an apparent lack of dwarf Be stars cooler than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to f ...
... Figure 3a shows the apparent V=7 magnitude limited counts of dwarf Be stars relative to dwarf B stars. There is an apparent lack of dwarf Be stars cooler than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to f ...
Chapter 11
... Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...
... Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...