Chapter 18 Study Guide
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
Read
... Spectral type – Indicates the color of the star, which is related to its surface temperature. From the hottest to coolest, also from blue to red color, the types are: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. A second number is added for finer classification, like G0, G1, G2, …, G9. A blue star is hotter than a yellow s ...
... Spectral type – Indicates the color of the star, which is related to its surface temperature. From the hottest to coolest, also from blue to red color, the types are: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. A second number is added for finer classification, like G0, G1, G2, …, G9. A blue star is hotter than a yellow s ...
The Life Cycle of a star
... • A supernova can light up the sky for weeks. • The temperature in one can reach 1,000,000,000 °C. • The supernova then either becomes a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... • A supernova can light up the sky for weeks. • The temperature in one can reach 1,000,000,000 °C. • The supernova then either becomes a neutron star or a black hole. ...
File
... Supergiants are the largest and brightest stars in the galaxy. Red supergiants are larger than blue ones, but less hot. When a large star runs out of hydrogen to fuse, it expands to become a red giant. When it reaches the stage of burning helium to carbon, it expands and become a red supergiant. Thr ...
... Supergiants are the largest and brightest stars in the galaxy. Red supergiants are larger than blue ones, but less hot. When a large star runs out of hydrogen to fuse, it expands to become a red giant. When it reaches the stage of burning helium to carbon, it expands and become a red supergiant. Thr ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
... Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? Which has the largest radius (_8_)? Which is most like our sun (_9_)? Approximatel ...
... Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? Which has the largest radius (_8_)? Which is most like our sun (_9_)? Approximatel ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
Questions for this book (Word format)
... Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydrogen fusion to occur ...
... Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydrogen fusion to occur ...
2009 Assessment Schedule (90764)
... less luminous than the sun, and spectral type of B – F. (The Sun is a main sequence star / other stars are not main sequence stars so are at different stages in their life cycles) (a) ...
... less luminous than the sun, and spectral type of B – F. (The Sun is a main sequence star / other stars are not main sequence stars so are at different stages in their life cycles) (a) ...
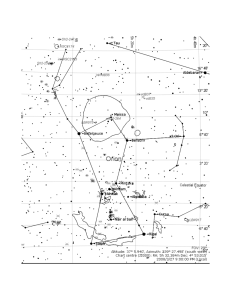
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... Cassiopeia was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda. It is a constellation in the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due ...
... Cassiopeia was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda. It is a constellation in the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due ...