PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 1
... If the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters away, how far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? ...
... If the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters away, how far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? ...
Section 25.2 Stellar Evolution
... Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same ...
... Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse into a white dwarf. Death of Medium-Mass Stars Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same ...
Stars
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
stars
... • Closest star to our planet Earth. • Our sun is a medium-sized star. • It is about 333,000 times the mass of the Earth. • The Sun will burn fuel for about 5 billion more years (middle-aged star) • It’s surface temperature is 11,000°F ...
... • Closest star to our planet Earth. • Our sun is a medium-sized star. • It is about 333,000 times the mass of the Earth. • The Sun will burn fuel for about 5 billion more years (middle-aged star) • It’s surface temperature is 11,000°F ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Galaxies Reading Guide
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
solution
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
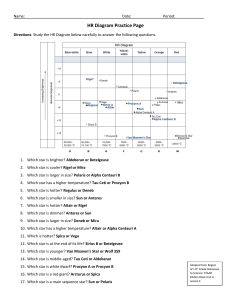
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
Section 3: Evolution of Stars pages 114-119
... A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts. Are classified by: ____________________________________________________ Protostar __________________ pulls huge nebulas of hydrogen gas and dust into a single spinning cloud. As the particles cras ...
... A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts. Are classified by: ____________________________________________________ Protostar __________________ pulls huge nebulas of hydrogen gas and dust into a single spinning cloud. As the particles cras ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
Stars
... Life Cycle of Stars Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years ...
... Life Cycle of Stars Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years ...
Unit 6--Astronomy
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
Characteristics of Stars
... wire in a light bulb glow? Which color is hotter? Is Betelgeuse a cool or hot star? What color is Betelgeuse? What color is Rigel? Is Rigel a hot or cold star? 7. The brightness of a star depends on what two characteristics? What is a star’s apparent magnitude? What is absolute magnitude? What two t ...
... wire in a light bulb glow? Which color is hotter? Is Betelgeuse a cool or hot star? What color is Betelgeuse? What color is Rigel? Is Rigel a hot or cold star? 7. The brightness of a star depends on what two characteristics? What is a star’s apparent magnitude? What is absolute magnitude? What two t ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
Stellar Evolution
... •Most stars appear on the Main Sequence, where stars appear to obey a Mass-Luminosity relation: L M3.5 •For example, if the mass of a star is doubled, its luminosity increases by a factor 23.5 ~ 11. •Thus, stars like Sirius that are about twice as massive as the Sun are about 11 times as luminous. ...
... •Most stars appear on the Main Sequence, where stars appear to obey a Mass-Luminosity relation: L M3.5 •For example, if the mass of a star is doubled, its luminosity increases by a factor 23.5 ~ 11. •Thus, stars like Sirius that are about twice as massive as the Sun are about 11 times as luminous. ...
star brightness
... Even the faintest stars are not the same brightness as each other, when zooming in on the ‘Jewel Box’ in the Southern Cross (Hubble Space Telescope). Credit: ESO. ...
... Even the faintest stars are not the same brightness as each other, when zooming in on the ‘Jewel Box’ in the Southern Cross (Hubble Space Telescope). Credit: ESO. ...
Slide 1
... Magnitude is the degree of brightness of a star. In 1856, British astronomer Norman Pogson proposed a quantitative scale of stellar magnitudes, which was adopted by the astronomical community. Each increment in magnitude corresponds to an increase in the amount of energy by 2.512, approximately. A f ...
... Magnitude is the degree of brightness of a star. In 1856, British astronomer Norman Pogson proposed a quantitative scale of stellar magnitudes, which was adopted by the astronomical community. Each increment in magnitude corresponds to an increase in the amount of energy by 2.512, approximately. A f ...