(HR) Diagrams
... 5. How many sub-types are there in each spectral class? a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circ ...
... 5. How many sub-types are there in each spectral class? a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circ ...
White Dwarf Stars Near The Earth
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
Life Cycle of a Star - CullenScience
... As the temperature in the shell of the star increases, the outer layers of the star expand. 2. What is a Red Giant? ...
... As the temperature in the shell of the star increases, the outer layers of the star expand. 2. What is a Red Giant? ...
Name
... Explain the life cycle of a massive star staring with its formation to its death. Be sure to use the following terms and give all possible endings: nebula, black hole, supernova, red supergiant, main sequence, interstellar medium, pulsar ...
... Explain the life cycle of a massive star staring with its formation to its death. Be sure to use the following terms and give all possible endings: nebula, black hole, supernova, red supergiant, main sequence, interstellar medium, pulsar ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Star Life Cycles
... light a star gives off determines the star’s brightness. Stars close to Earth can appear bright, even if they do not give off much light. Additionally, very bright stars may appear faint if they are far away. Parallax – the apparent shift in position of an object when ...
... light a star gives off determines the star’s brightness. Stars close to Earth can appear bright, even if they do not give off much light. Additionally, very bright stars may appear faint if they are far away. Parallax – the apparent shift in position of an object when ...
What is the net result of the proton-proton chain? a. 2 protons make
... a. All stars in the cluster are the same size and luminosity b. Their combined light makes them much easier to spot from a distance c. Stars in cluster have the same age, similar compositions, and are essentially at the same distance d. Stars in clusters are all relatively young and therefore shine ...
... a. All stars in the cluster are the same size and luminosity b. Their combined light makes them much easier to spot from a distance c. Stars in cluster have the same age, similar compositions, and are essentially at the same distance d. Stars in clusters are all relatively young and therefore shine ...
FRIENDS OF THE PLANETARIUM NEWSLETTER April2002
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
Interstellar clouds
... • White dwarfs have immense gravity, some with the mass of sun and a volume of the earth. ...
... • White dwarfs have immense gravity, some with the mass of sun and a volume of the earth. ...
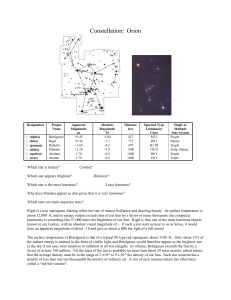
Orion
... Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of many thousands; the computed luminosity is something like 57,000 ...
... Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of many thousands; the computed luminosity is something like 57,000 ...
star map looking north january-march
... Our nearest large galaxy – Andromeda – can be seen in the Andromeda constellation. It appears to us as an elongated fuzzy blob. The Andromeda galaxy is so far away that its light takes over two million years to reach us. ...
... Our nearest large galaxy – Andromeda – can be seen in the Andromeda constellation. It appears to us as an elongated fuzzy blob. The Andromeda galaxy is so far away that its light takes over two million years to reach us. ...
Document
... Notice that the X axis is spaced unevenly, and the number of Kelvins (degrees) between each line is not constant. This because it is a logarithmic scale. For example: each line between 2,000 and 3,000 represents 100 degrees; but each line between 6,000 and 7,000 represents 200 degrees; and differe ...
... Notice that the X axis is spaced unevenly, and the number of Kelvins (degrees) between each line is not constant. This because it is a logarithmic scale. For example: each line between 2,000 and 3,000 represents 100 degrees; but each line between 6,000 and 7,000 represents 200 degrees; and differe ...
Notes: 3.5 STAR EVOLUTION Name: ______ Star
... Once the star runs out of fuel for good it will be destroyed. Ø A PLANETARY NEBULA is when a Giant star begins to fall apart and the outer layer of gas float out into space. Ø A supernova is big EXPLOSION that happens when a Supergiant runs out of fuel 6. End of Stars Life. (White Dwarf, Neutron S ...
... Once the star runs out of fuel for good it will be destroyed. Ø A PLANETARY NEBULA is when a Giant star begins to fall apart and the outer layer of gas float out into space. Ø A supernova is big EXPLOSION that happens when a Supergiant runs out of fuel 6. End of Stars Life. (White Dwarf, Neutron S ...
Life of a star - bahringcarthnoians
... A star’s life begins when clumps of gas and dust come together from it’s own gravity. Gravity pushes these clumps together to make more pressure. Small amounts of gas and dust fizzle out. If the clump is big enough, the centre of the forming star boosts over 10 million degrees Celsius. A nuclear re ...
... A star’s life begins when clumps of gas and dust come together from it’s own gravity. Gravity pushes these clumps together to make more pressure. Small amounts of gas and dust fizzle out. If the clump is big enough, the centre of the forming star boosts over 10 million degrees Celsius. A nuclear re ...










![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)