Lesson 4 - Scientist in Residence Program
... 1. Students will be able to recognize that stars have different colours 2. Students will be able to correlate star colour with star brightness 3. Students will be able to correlate star brightness with star size Background Information Stars like humans come in different sizes and colours. However, u ...
... 1. Students will be able to recognize that stars have different colours 2. Students will be able to correlate star colour with star brightness 3. Students will be able to correlate star brightness with star size Background Information Stars like humans come in different sizes and colours. However, u ...
May 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... However, when it is a thin crescent, during the few days after or before a New Moon, a faint illumination of the dark part of the Moon can be seen soon after sunset. This is caused by light from the setting Sun being reflected from the Earth. The winter months, when the Sun is setting early and towa ...
... However, when it is a thin crescent, during the few days after or before a New Moon, a faint illumination of the dark part of the Moon can be seen soon after sunset. This is caused by light from the setting Sun being reflected from the Earth. The winter months, when the Sun is setting early and towa ...
Origin of the Earth and of the Solar System
... years ago within the protosolar cloud (with an uncertainty of just 2 million years). Right: Ca/Al-rich inclusion within Allende-Meteorite with a diameter of ~1 cm (the oldest material, which could be dated so far). The first „Planetary-Embryos“ formed within just about 100 000 years. Roughly 10 mill ...
... years ago within the protosolar cloud (with an uncertainty of just 2 million years). Right: Ca/Al-rich inclusion within Allende-Meteorite with a diameter of ~1 cm (the oldest material, which could be dated so far). The first „Planetary-Embryos“ formed within just about 100 000 years. Roughly 10 mill ...
here
... small the gravitational force between the two objects can cause the orbiting planet’s period of rotation to become equal to its period of revolution. • This is referred to as tidal locking. The result is that only one side of the planet faces the star and is always illuminated, the other side never ...
... small the gravitational force between the two objects can cause the orbiting planet’s period of rotation to become equal to its period of revolution. • This is referred to as tidal locking. The result is that only one side of the planet faces the star and is always illuminated, the other side never ...
Mark Rubin
... • At “modest” redshifts (z<11) where Lyman α emission appears in the J-band, one of the best environments to discover Pop III dwarf galaxies may be the chemically unevolved surroundings of a large galaxy or proto-cluster of galaxies. • The central sources are likely to have ionized a local “bubble” ...
... • At “modest” redshifts (z<11) where Lyman α emission appears in the J-band, one of the best environments to discover Pop III dwarf galaxies may be the chemically unevolved surroundings of a large galaxy or proto-cluster of galaxies. • The central sources are likely to have ionized a local “bubble” ...
Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Exercises 2
... when they appear to have been first produced at the central powerhouse, and are subsequently observed to move apparently outward in opposite directions from the centre of the quasar image. Fourteen years after the quasar actually emitted the clouds, they are in reality twelve ly. closer to us than t ...
... when they appear to have been first produced at the central powerhouse, and are subsequently observed to move apparently outward in opposite directions from the centre of the quasar image. Fourteen years after the quasar actually emitted the clouds, they are in reality twelve ly. closer to us than t ...
Astrophysics - Mr Priest`s Physics Notes
... Angle is the angle between the rays coming from different points on the distant object (for example, the edges of the Moon) as they enter the telescope objective lens or the unaided eye. Angle is the angle between the same rays as they enter the eye after passing through the telescope. Angular m ...
... Angle is the angle between the rays coming from different points on the distant object (for example, the edges of the Moon) as they enter the telescope objective lens or the unaided eye. Angle is the angle between the same rays as they enter the eye after passing through the telescope. Angular m ...
Day-26
... We can take images and directly see the planets. We can detect radio signals from life on the planets. A star’s light could be affected by its planet. ...
... We can take images and directly see the planets. We can detect radio signals from life on the planets. A star’s light could be affected by its planet. ...
Stars - WhatisOutThere
... brighter than the faint glow coming from the stars. If you were standing on the moon for example, you would be able to see the stars both day and night. This is because there is no atmosphere on the moon, meaning that it is always dark. Therefore you can see the stars. ...
... brighter than the faint glow coming from the stars. If you were standing on the moon for example, you would be able to see the stars both day and night. This is because there is no atmosphere on the moon, meaning that it is always dark. Therefore you can see the stars. ...
Document
... Possible solutions to the Fermi paradox 2. Low probability of intelligent life • Life seems to appear quite easily in favorable conditions • But maybe it needs very special conditions for intelligence to emerge (= to become an asset in natural selection) • On Earth, it took more than 2 billion years ...
... Possible solutions to the Fermi paradox 2. Low probability of intelligent life • Life seems to appear quite easily in favorable conditions • But maybe it needs very special conditions for intelligence to emerge (= to become an asset in natural selection) • On Earth, it took more than 2 billion years ...
The Sun and other Stars
... Stars begin as interstellar clouds – A mix of gas. When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
... Stars begin as interstellar clouds – A mix of gas. When stars like the Sun begin to fuse H to He they fall into the Main sequence stars. The Sun will remain a main sequence star until uses about 90% of its fuel in the core. This is the beginning of the End ...
1. - TeacherWeb
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
Solutions
... left the main sequence (since all the stars formed at once), they are only a little bit more massive, in contrast to the difference in Problem 1). 4. Chapter 15, Question 9: In Latin, Nova means new. Novae, as we now know, are not “new” stars. Explain how novae might have gotten their name. On a goo ...
... left the main sequence (since all the stars formed at once), they are only a little bit more massive, in contrast to the difference in Problem 1). 4. Chapter 15, Question 9: In Latin, Nova means new. Novae, as we now know, are not “new” stars. Explain how novae might have gotten their name. On a goo ...
Slide 1 - Arif Solmaz
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
celestial sphere
... PURPOSE: To compare the horizon and equatorial coordinate systems and to learn how to determine sidereal time. To make use of a celestial globe in understanding the basic coordinate systems. PROCEDURE: Making use of the celestial globe, answer the questions in this lab pertaining to the horizon and ...
... PURPOSE: To compare the horizon and equatorial coordinate systems and to learn how to determine sidereal time. To make use of a celestial globe in understanding the basic coordinate systems. PROCEDURE: Making use of the celestial globe, answer the questions in this lab pertaining to the horizon and ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Research in observational
... main-sequence like structure, except slightly smaller, hotter and more luminous. • We call these core-helium burning stars “Horizontal Branch (HB) stars” or even “clump stars”. • The HB lasts about 100 million years. ...
... main-sequence like structure, except slightly smaller, hotter and more luminous. • We call these core-helium burning stars “Horizontal Branch (HB) stars” or even “clump stars”. • The HB lasts about 100 million years. ...
Solutions Assignment #3
... g. Alpha Centauri A is most similar to the Sun because it has the same spectral type and luminosity class, G2 V. h. Antares is a red supergiant; its spectral type M means it is red, and its luminosity class I indicates a supergiant. i. Antares has the largest radius because it is the only supergiant ...
... g. Alpha Centauri A is most similar to the Sun because it has the same spectral type and luminosity class, G2 V. h. Antares is a red supergiant; its spectral type M means it is red, and its luminosity class I indicates a supergiant. i. Antares has the largest radius because it is the only supergiant ...
Lecture 16
... B. They create new elements and blow them out into space, and a new generation of stars can be made from them. C. They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. ...
... B. They create new elements and blow them out into space, and a new generation of stars can be made from them. C. They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. ...
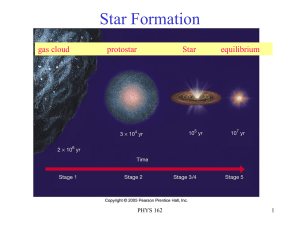
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
... about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
PPTX
... HST 2009 image in F547M (WFPC2/PC). Panel is 8″.7 wide. Bandpass is dominated by stellar C IV emission & shows slightly non-stellar bright spot. This is probably the central star, seen through substantial dust extinction. ...
... HST 2009 image in F547M (WFPC2/PC). Panel is 8″.7 wide. Bandpass is dominated by stellar C IV emission & shows slightly non-stellar bright spot. This is probably the central star, seen through substantial dust extinction. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.