death_high_mass
... 3. The universe isn’t old enough to have cooler white dwarfs 4. WD come into temperature equilibrium with the universe and remain that temperature ...
... 3. The universe isn’t old enough to have cooler white dwarfs 4. WD come into temperature equilibrium with the universe and remain that temperature ...
Accretion Disk
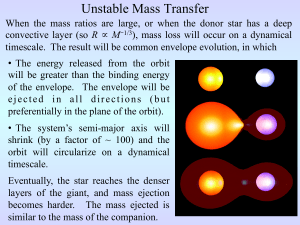
... § The binary will have a very small separation, less than the radius of the Sun. § Since the separation is so small, the remains of the main sequence companion may/will overflow its Roche Lobe. It will then transfer mass onto the white dwarf on a thermal or nuclear timescale. This matter will form ...
... § The binary will have a very small separation, less than the radius of the Sun. § Since the separation is so small, the remains of the main sequence companion may/will overflow its Roche Lobe. It will then transfer mass onto the white dwarf on a thermal or nuclear timescale. This matter will form ...
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
... Sun, is the solar system’s source of heat and light as well as its central mass, a gravitational anchor holding everything together as we travel around the galaxy. Its warmth naturally divides the planetary system into two zones of disparate size: one hot, bright, and compact, and the other cold, da ...
... Sun, is the solar system’s source of heat and light as well as its central mass, a gravitational anchor holding everything together as we travel around the galaxy. Its warmth naturally divides the planetary system into two zones of disparate size: one hot, bright, and compact, and the other cold, da ...
Oscillating White Dwarf Stars Background on White Dwarfs
... temperatures of 100.000.000 K. 8Be is unstable and decays back into He in 2.6 × 10–16 secs, but in the stellar interior a small equilibrium of 8Be exists. The 8Be ground state has almost exactly the energy of two alpha particles. In the second step, 8Be + 4He has almost exactly the energy of an exci ...
... temperatures of 100.000.000 K. 8Be is unstable and decays back into He in 2.6 × 10–16 secs, but in the stellar interior a small equilibrium of 8Be exists. The 8Be ground state has almost exactly the energy of two alpha particles. In the second step, 8Be + 4He has almost exactly the energy of an exci ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... viewing so that you can see faint stars as well. Magnifying by two may help you work easily. Find Zoom up icon in the upper left of the Makali`i window; it has a picture of magnifier with a plus mark. Clicking once the icon makes the image size twice. But you can not see the whole area at a time, so ...
... viewing so that you can see faint stars as well. Magnifying by two may help you work easily. Find Zoom up icon in the upper left of the Makali`i window; it has a picture of magnifier with a plus mark. Clicking once the icon makes the image size twice. But you can not see the whole area at a time, so ...
Chapter 14 Neutron Stars and Black holes
... from objects. c. The angular change in a star's position when observed during a solar eclipse. d. The alternating Doppler effect due to two bodies whose orbital plane contains our line of sight. e. We are unable to tell whether an object is moving away from us or we are moving away from the object. ...
... from objects. c. The angular change in a star's position when observed during a solar eclipse. d. The alternating Doppler effect due to two bodies whose orbital plane contains our line of sight. e. We are unable to tell whether an object is moving away from us or we are moving away from the object. ...
Star-S_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... o If your students have already done the Scale Model Solar System Activity, discuss the usefulness of the scale factor. Ask your students what the advantage would be of modeling stars on the same scale. By using the same scale factor of 1:10 billion, the students will more easily be able to make com ...
... o If your students have already done the Scale Model Solar System Activity, discuss the usefulness of the scale factor. Ask your students what the advantage would be of modeling stars on the same scale. By using the same scale factor of 1:10 billion, the students will more easily be able to make com ...
Lecture9
... Many of these stars are radio pulsars which emit non-thermal power-law radiation in radio, optical, X-ray, and/or -rays – see Section III-1b (v). Some of them have thermal radiation from stellar surface superimposed to non-thermal magnetospheric radiation – see Fig. III-22. ...
... Many of these stars are radio pulsars which emit non-thermal power-law radiation in radio, optical, X-ray, and/or -rays – see Section III-1b (v). Some of them have thermal radiation from stellar surface superimposed to non-thermal magnetospheric radiation – see Fig. III-22. ...
Skynet
... After its Discovery. This Asteroid Passed within 75,000 km of Earth (5 Times Closer than the Moon) ...
... After its Discovery. This Asteroid Passed within 75,000 km of Earth (5 Times Closer than the Moon) ...
15.1 Introduction
... Spectroscopically, WR stars are spectacular in appearance: their optical and UV spectra are dominated by strong, broad emission lines instead of the narrow absorption lines that are typical of ‘normal’ stars (Figure 15.3). The emission lines are so strong that they were first noticed as early as 186 ...
... Spectroscopically, WR stars are spectacular in appearance: their optical and UV spectra are dominated by strong, broad emission lines instead of the narrow absorption lines that are typical of ‘normal’ stars (Figure 15.3). The emission lines are so strong that they were first noticed as early as 186 ...
Slide 1
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... from objects. c. The angular change in a star's position when observed during a solar eclipse. d. The alternating Doppler effect due to two bodies whose orbital plane contains our line of sight. e. We are unable to tell whether an object is moving away from us or we are moving away from the object. ...
... from objects. c. The angular change in a star's position when observed during a solar eclipse. d. The alternating Doppler effect due to two bodies whose orbital plane contains our line of sight. e. We are unable to tell whether an object is moving away from us or we are moving away from the object. ...
Project Descriptions - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be mistaken for stars. However, their close proximity to the Earth also makes their apparent motion ...
... smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be mistaken for stars. However, their close proximity to the Earth also makes their apparent motion ...
Planetary Nebula
... thinking on this nebula’s formation focused around the central star itself. But the motions of the gas are also being observed and a recent study suggest that some of the structures observed are caused by the interaction of central star wind and radiation with preplanetary nebula debris: planets, mo ...
... thinking on this nebula’s formation focused around the central star itself. But the motions of the gas are also being observed and a recent study suggest that some of the structures observed are caused by the interaction of central star wind and radiation with preplanetary nebula debris: planets, mo ...
File - We All Love Science
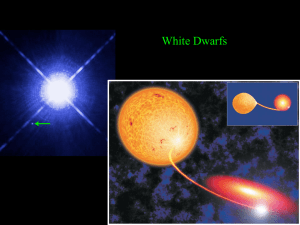
... White Dwarfs? • After ejection of planetary nebula shell, the core is what’s left. That’s our white dwarf • Mainly C and O2, trace H and He on crust • Cools rapidly (by universal standards) • Eventually dies out, like an ember in a fire • Becomes so dark referred to as a black dwarf ...
... White Dwarfs? • After ejection of planetary nebula shell, the core is what’s left. That’s our white dwarf • Mainly C and O2, trace H and He on crust • Cools rapidly (by universal standards) • Eventually dies out, like an ember in a fire • Becomes so dark referred to as a black dwarf ...
Stellar Evolution 1
... Theory: Energy source gravitational PE. Star evolves by contracting from giant to MS & then down MS from larger to smaller ...
... Theory: Energy source gravitational PE. Star evolves by contracting from giant to MS & then down MS from larger to smaller ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... Spectroscopy is the study of “what kinds” of light we see from an object. It is a measure of the quantity of each color of light (or more specifically, the amount of each wavelength of light). It is a powerful tool in astronomy. In fact, most of what we know in astronomy is a result of spectroscopy: ...
... Spectroscopy is the study of “what kinds” of light we see from an object. It is a measure of the quantity of each color of light (or more specifically, the amount of each wavelength of light). It is a powerful tool in astronomy. In fact, most of what we know in astronomy is a result of spectroscopy: ...
Chapter 12 Star Stuff How do stars form?
... The relationship between apparent brightness and luminosity depends on distance: ...
... The relationship between apparent brightness and luminosity depends on distance: ...
Document
... • Blue and UV continuum increase by several magnitudes in seconds (unlike the Sun, where the contrast to the photospheric background is less) • Typically a black body of 8,000 –10,000K • The source of the white light is still unknown • Strong,broad emission lines in the UV and optical – Balmer, Ca I ...
... • Blue and UV continuum increase by several magnitudes in seconds (unlike the Sun, where the contrast to the photospheric background is less) • Typically a black body of 8,000 –10,000K • The source of the white light is still unknown • Strong,broad emission lines in the UV and optical – Balmer, Ca I ...
November - Hawaiian Astronomical Society
... “lace like.” Unlike most open clusters, NGC 7789 is a rich cluster, which is best observed with higher powers. Jane notes that at 200x there is a noticeable dark spot in the center of the cluster. I found that even at 300x the cluster only looks more interesting. M11, the “Wild Duck” cluster reacts ...
... “lace like.” Unlike most open clusters, NGC 7789 is a rich cluster, which is best observed with higher powers. Jane notes that at 200x there is a noticeable dark spot in the center of the cluster. I found that even at 300x the cluster only looks more interesting. M11, the “Wild Duck” cluster reacts ...
THE MONTHLY SKY GUIDE, SIXTH EDITION
... magnitude, and so on. The faintest objects that can be detected by telescopes on Earth are about magnitude 25. ...
... magnitude, and so on. The faintest objects that can be detected by telescopes on Earth are about magnitude 25. ...
Pictures in the Sky Teacher`s Guide
... Have your students color the planets on page 7 as described below. You may have to read the descriptions to your students, then see if they can figure out which planet is which and color it. The Sun: The Sun is not a planet but a star. It seems bigger, brighter, and hotter than the stars we see at n ...
... Have your students color the planets on page 7 as described below. You may have to read the descriptions to your students, then see if they can figure out which planet is which and color it. The Sun: The Sun is not a planet but a star. It seems bigger, brighter, and hotter than the stars we see at n ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.