An Assessment: Think Pair Share
... becomes much brighter because it is 1. moving closer to us. 2. losing its outer envelope. 3. fusing iron in its core. 4. increasing in size. ...
... becomes much brighter because it is 1. moving closer to us. 2. losing its outer envelope. 3. fusing iron in its core. 4. increasing in size. ...
Notes on Sun-Earth-Moon (pg. 119)
... Only stars with more than 40 times the mass of the Sun form black holes when they die. This happens after a supernova. 10. Describe what happens to an average star and a massive star when each runs out of fuel. Small and medium stars become white dwarfs and eventually black dwarfs. A giant star can ...
... Only stars with more than 40 times the mass of the Sun form black holes when they die. This happens after a supernova. 10. Describe what happens to an average star and a massive star when each runs out of fuel. Small and medium stars become white dwarfs and eventually black dwarfs. A giant star can ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 1. When observed from Earth on a clear night, the Milky Way Galaxy appears as a A. circular pattern of stars. B. elliptical pattern of stars. C. glowing band of light. D. random spotting of light. 2. How many times greater is Sun’s diameter than Earth’s diameter? A. 19 times B. 109 times C. 1109 tim ...
... 1. When observed from Earth on a clear night, the Milky Way Galaxy appears as a A. circular pattern of stars. B. elliptical pattern of stars. C. glowing band of light. D. random spotting of light. 2. How many times greater is Sun’s diameter than Earth’s diameter? A. 19 times B. 109 times C. 1109 tim ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
Stars
... – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared
... Multi-Epoch Star Formation? The Curious Case of Cluster 1806-20 Stephen Eikenberry University of Florida 11 April 2007 ...
... Multi-Epoch Star Formation? The Curious Case of Cluster 1806-20 Stephen Eikenberry University of Florida 11 April 2007 ...
18.1 NOTES How are stars formed? Objective: Describe how stars
... off heat and light. The Sun is only one of billions of stars that make up are galaxy, and there are billions of galaxies. Most stars appear to be white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how hot in temperature it is. Stars differ i ...
... off heat and light. The Sun is only one of billions of stars that make up are galaxy, and there are billions of galaxies. Most stars appear to be white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how hot in temperature it is. Stars differ i ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... infer the existence of black holes, use the example of two ice skaters holding hands and spinning in a circle. If one of the skaters were invisible, an observer could still infer that two skaters were present by observing the effect the invisible skater would have on the motion of the visible skater ...
... infer the existence of black holes, use the example of two ice skaters holding hands and spinning in a circle. If one of the skaters were invisible, an observer could still infer that two skaters were present by observing the effect the invisible skater would have on the motion of the visible skater ...
solar system formation and gal
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - A constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the Inte ...
... ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - A constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the Inte ...
Constellations 1
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
constellations[1]
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
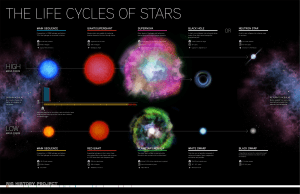
Life Cycles of Stars
... High-mass stars live for one million to tens of millions of years while low-mass stars, like our Sun, live for tens of millions to trillions of years. ...
... High-mass stars live for one million to tens of millions of years while low-mass stars, like our Sun, live for tens of millions to trillions of years. ...
Size Color and Temperature
... solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars in the sky, even though it is 522 light-years away. There are also stars much smaller than the Sun. Stars called w ...
... solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars in the sky, even though it is 522 light-years away. There are also stars much smaller than the Sun. Stars called w ...
HR Diagram Activity
... Materials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedure: 1. Review the star data chart below. Note that the sun, which is used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Using an “X” as a plot po ...
... Materials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedure: 1. Review the star data chart below. Note that the sun, which is used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Using an “X” as a plot po ...
Lund Observatory Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics
... Lund Observatory Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics LUND ...
... Lund Observatory Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics LUND ...
Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Hertzsprung
... even light cannot escape its gravity ...
... even light cannot escape its gravity ...
Dec 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
Introduction to Accretion Phenomena in Astrophysics
... each other, stars essentially evolve separately. • Semidetached binary stars: one of the components fills its Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the surface of the Roche lobe filling component (donor) is transferred to the other, accreting star. The mass transfer dominates the evolution of ...
... each other, stars essentially evolve separately. • Semidetached binary stars: one of the components fills its Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the surface of the Roche lobe filling component (donor) is transferred to the other, accreting star. The mass transfer dominates the evolution of ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.















![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)