Main Sequence Star
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
11.1 Stars - St John Brebeuf
... Large high mass stars often explode as supernovas, spreading elements throughout the universe. ...
... Large high mass stars often explode as supernovas, spreading elements throughout the universe. ...
Chapter 29 Notes
... • Parallax is used to find the distance to stars • Constellations: Groups of stars in the same part of the sky • Clusters: groups of stars bound together by gravity • Binaries: two stars that orbit a common center of mass ...
... • Parallax is used to find the distance to stars • Constellations: Groups of stars in the same part of the sky • Clusters: groups of stars bound together by gravity • Binaries: two stars that orbit a common center of mass ...
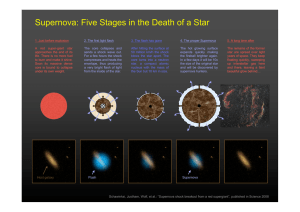
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
... The remains of the former star are spread over light years of space. They keep floating quickly, sweeping up interstellar gas here and there, leaving a faint beautiful glow behind… ...
... The remains of the former star are spread over light years of space. They keep floating quickly, sweeping up interstellar gas here and there, leaving a faint beautiful glow behind… ...
Solutions2
... d) Do you think you might be able to resolve its disk with the U of A telescope? Why or why not (show a calculation)? The U of A telescope has an aperture of 12 inches (0.33 m), and therefore an angular resolution (in V band, 550 nm) of θ = 1.22 ∗ (5.5 × 10−7 m/0.33m) = 2.0 × 10−6 radians, or 0.4”. ...
... d) Do you think you might be able to resolve its disk with the U of A telescope? Why or why not (show a calculation)? The U of A telescope has an aperture of 12 inches (0.33 m), and therefore an angular resolution (in V band, 550 nm) of θ = 1.22 ∗ (5.5 × 10−7 m/0.33m) = 2.0 × 10−6 radians, or 0.4”. ...
Supernova’s
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
Stars
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
lecture23
... All stars in a cluster are of about the same age. Clusters therefore are natural laboratory in which mass, rather than age, of stars is only significant variable. ...
... All stars in a cluster are of about the same age. Clusters therefore are natural laboratory in which mass, rather than age, of stars is only significant variable. ...
Practice Questions: This is a series of practice tests that you should
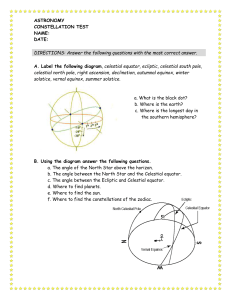
... 51. The term equinox is associated with a phenomenon that occurs in the months of a. September and March b. September and December c. March and June d. June and December 52. Draw and label the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... 51. The term equinox is associated with a phenomenon that occurs in the months of a. September and March b. September and December c. March and June d. June and December 52. Draw and label the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
Stellar Evolution Test Answers
... this a) the photon sphere b) the event horizon c) gravitational lensing d) the cosmological principle 2. Once you cross the ____________________, there is no going back…light can no longer escape. a) photon sphere b) event horizon c) singularity d) cosmological boundary 3. When we are able to observ ...
... this a) the photon sphere b) the event horizon c) gravitational lensing d) the cosmological principle 2. Once you cross the ____________________, there is no going back…light can no longer escape. a) photon sphere b) event horizon c) singularity d) cosmological boundary 3. When we are able to observ ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... BAA Variable Star Section. Good ongoing project for the 16”. Gamma Virginis. This interesting binary is best placed for observation from late evening through the early hours star. Now past periastron it should be possible to split visually with the 16” under good seeing conditions and worth trying w ...
... BAA Variable Star Section. Good ongoing project for the 16”. Gamma Virginis. This interesting binary is best placed for observation from late evening through the early hours star. Now past periastron it should be possible to split visually with the 16” under good seeing conditions and worth trying w ...
Quick Reference - Objects in the skies
... These are patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky. There are 88 standard constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) since 1922. The majority of these go back to the 48 constellations defined by Ptolemy in his Almag ...
... These are patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky. There are 88 standard constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) since 1922. The majority of these go back to the 48 constellations defined by Ptolemy in his Almag ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... 2) Why did the solar nebula heat up as it collapsed? A) Radiation from other nearby stars that had formed earlier heated the nebula. B) As the cloud shrank, its gravitational potential energy was converted to kinetic energy and then into thermal energy. C) Collisions among planetesimals generated fr ...
... 2) Why did the solar nebula heat up as it collapsed? A) Radiation from other nearby stars that had formed earlier heated the nebula. B) As the cloud shrank, its gravitational potential energy was converted to kinetic energy and then into thermal energy. C) Collisions among planetesimals generated fr ...
Apparent Magnitude
... Why do stars in the night sky appear considerably different in brightness? The distances to stars are not all the same. ...
... Why do stars in the night sky appear considerably different in brightness? The distances to stars are not all the same. ...
Distance to Stars
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
Light from stars part II
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • First encountered written down in Ptolemy’s Almagest (150 AD) • Thought to originate with Hipparchus (120 BC) • Stars classified by giving a number 1 - 6 • Brightest stars are class 1 • Dimmest stars visible to naked eye are class 6 • Class 1 is twi ...
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • First encountered written down in Ptolemy’s Almagest (150 AD) • Thought to originate with Hipparchus (120 BC) • Stars classified by giving a number 1 - 6 • Brightest stars are class 1 • Dimmest stars visible to naked eye are class 6 • Class 1 is twi ...
t2 images part 1
... If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began expanding outward. This point in time is called the “Big Bang” The Big Bang happened somewhere between 1016 Billion years ago ...
... If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began expanding outward. This point in time is called the “Big Bang” The Big Bang happened somewhere between 1016 Billion years ago ...
22 pm - Starmap
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects difficult. ...
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects difficult. ...
Life Cycle Of A Star
... that produces heat and light. There are many stars in our galaxy, and many more in others, but the star that is the most important and the one that we orbit around is called the Sun. The Sun produces heat and light for us and is also keeping all the planets in orbit. Stars aren’t just beautiful thin ...
... that produces heat and light. There are many stars in our galaxy, and many more in others, but the star that is the most important and the one that we orbit around is called the Sun. The Sun produces heat and light for us and is also keeping all the planets in orbit. Stars aren’t just beautiful thin ...
Astronomy Webquest _2 STARS
... Even though our sun is a fairly average star, because it is so close, it appears brighter on Earth than even the brightest objects in the universe. The brightness of a star as seen from earth is called its apparent magnitude. In order to learn more about a star, astronomers usually want to determine ...
... Even though our sun is a fairly average star, because it is so close, it appears brighter on Earth than even the brightest objects in the universe. The brightness of a star as seen from earth is called its apparent magnitude. In order to learn more about a star, astronomers usually want to determine ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.