Star Life Guided Notes
... Core ________ at 1/4 the speed of light & takes about 1/10 of a second Collapse of the core to about 100 km across Outer layers “bounce” of the solid core Releases 100x the energy of our sun produces in it’s lifetime -- in 1/10 of a ...
... Core ________ at 1/4 the speed of light & takes about 1/10 of a second Collapse of the core to about 100 km across Outer layers “bounce” of the solid core Releases 100x the energy of our sun produces in it’s lifetime -- in 1/10 of a ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
Star Life Cycles WS
... 5. A red giant is (hotter, cooler) due the (contraction, expansion) of gases in the outer layer. 6. At the end of its life, a low mass star (1.4 SM) shrinks to become a ______________. 7. At the end, a very MASSIVE star will follow sequence: a. white dwarf, planetary nebula, neutron star b. red gian ...
... 5. A red giant is (hotter, cooler) due the (contraction, expansion) of gases in the outer layer. 6. At the end of its life, a low mass star (1.4 SM) shrinks to become a ______________. 7. At the end, a very MASSIVE star will follow sequence: a. white dwarf, planetary nebula, neutron star b. red gian ...
July - astra
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
Document
... Concept Test • We can see X-rays from black holes because? a. X-rays are more energetic than visible light and so can escape from the event horizon. b. X-rays can pass through ordinary matter showing us things we can’t normally see. c. Light given off by objects as they enter the event horizon are ...
... Concept Test • We can see X-rays from black holes because? a. X-rays are more energetic than visible light and so can escape from the event horizon. b. X-rays can pass through ordinary matter showing us things we can’t normally see. c. Light given off by objects as they enter the event horizon are ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Deadly from neutrinos within 30 light years. • Atmosphere, weather, ruined. • Major extinction. • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowin ...
... • Deadly from neutrinos within 30 light years. • Atmosphere, weather, ruined. • Major extinction. • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowin ...
The Life of a Star
... between planets and stars. 13.3: Rotation vs. Revolution, How does this relate to the Earth’s days, years, seasons. 13.4: Constellations – know how to locate on a star map. 14.7: Composition of the Sun, Parts of the Sun, How the Sun’s energy is made. *14.10: 5 key characteristics of the Sun: Colour, ...
... between planets and stars. 13.3: Rotation vs. Revolution, How does this relate to the Earth’s days, years, seasons. 13.4: Constellations – know how to locate on a star map. 14.7: Composition of the Sun, Parts of the Sun, How the Sun’s energy is made. *14.10: 5 key characteristics of the Sun: Colour, ...
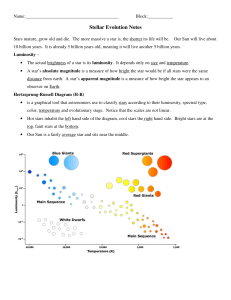
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Nov 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
Due: January 15, 2014 Name
... a massive star's iron core and which leaves a neutron star or a black hole. Furthermore, not all neutron stars are pulsars because the radiation beam of a spinning neutron star might not point toward the Earth. Not all pulsars are found within supernova remnants because the supernova blast can “kick ...
... a massive star's iron core and which leaves a neutron star or a black hole. Furthermore, not all neutron stars are pulsars because the radiation beam of a spinning neutron star might not point toward the Earth. Not all pulsars are found within supernova remnants because the supernova blast can “kick ...
Star Classification
... Star Classification The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, ...
... Star Classification The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, ...
20.1 Notes
... own gravity and rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the stars outer layers from the core. This huge, bright explosion is called a Type II _________________________. If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very den ...
... own gravity and rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the stars outer layers from the core. This huge, bright explosion is called a Type II _________________________. If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very den ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
The Brightness of Stars
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... way to feed large sources of energy and mass into the interstellar medium. • So, everything we are made of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
... way to feed large sources of energy and mass into the interstellar medium. • So, everything we are made of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... Triggering the Formation of the Solar System --- New data from meteorites indicates that formation of the Solar System was triggered by a supernova. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous ev ...
... Triggering the Formation of the Solar System --- New data from meteorites indicates that formation of the Solar System was triggered by a supernova. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous ev ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.