Week 9 Concept Summary - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... below), while their upper layers will gently puff away. The large nebulae formed by the escaping gas is called a planetary nebula, though it has nothing to do with planets. The exposed core is very hot, but very small, a white dwarf. They slowly cool off, emitting blackbody radiation, but generating ...
... below), while their upper layers will gently puff away. The large nebulae formed by the escaping gas is called a planetary nebula, though it has nothing to do with planets. The exposed core is very hot, but very small, a white dwarf. They slowly cool off, emitting blackbody radiation, but generating ...
Lecture 17: General Relativity and Black Holes
... c. light will be redshifted pulling away from a star d. the speed of light can not be exceeding e. none of these ...
... c. light will be redshifted pulling away from a star d. the speed of light can not be exceeding e. none of these ...
answers2004_05_BC - Particle Physics and Particle Astrophysics
... its days in the spectacular fashion adopted by Sanduleak −69 202. What will the Sun eventually evolve into? Sun is not massive enough to fuse elements heavier than helium (core never gets that hot), therefore it will not form an iron core (it is also not a close binary, so it will not produce a Ty ...
... its days in the spectacular fashion adopted by Sanduleak −69 202. What will the Sun eventually evolve into? Sun is not massive enough to fuse elements heavier than helium (core never gets that hot), therefore it will not form an iron core (it is also not a close binary, so it will not produce a Ty ...
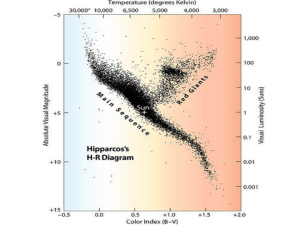
Stars, Stellar classification, H
... hydrogenburning stars reside on the main sequence of the H-R ...
... hydrogenburning stars reside on the main sequence of the H-R ...
notes
... light from another. Astronomers are have found other stars with planets around them. They are able to tell that these stars have planets because of how the planet effects the star. Only large planets have been detected so far (half the mass of Jupiter). A small planet would be difficult to detect be ...
... light from another. Astronomers are have found other stars with planets around them. They are able to tell that these stars have planets because of how the planet effects the star. Only large planets have been detected so far (half the mass of Jupiter). A small planet would be difficult to detect be ...
Unit 8 Chapter 30
... from Earth or 32.6 Light years away (10 parsecs). Our sun would be a 4.8, average star, Rigel has an Absolute Magnitude of -6.4 which makes it appear brighter than most stars. Remember, all stars are not the same distance away, therefore, a faint star may really be very bright if it were closer. ...
... from Earth or 32.6 Light years away (10 parsecs). Our sun would be a 4.8, average star, Rigel has an Absolute Magnitude of -6.4 which makes it appear brighter than most stars. Remember, all stars are not the same distance away, therefore, a faint star may really be very bright if it were closer. ...
ppt
... How can we test theories of star evolution? • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of ma ...
... How can we test theories of star evolution? • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of ma ...
ASTRONOMY 12 Problem Set 4 – Due March 10, 2016 1) After
... 2) Big and bright as a supernova is, it still radiates like a blackbody with an effective temperature not much hotter than the solar photosphere. A value of 5500 K is typical for a Type IIp supernova. But the supernova has an enormous radius, ∼ 3 × 1015 cm (i.e., 200 AU). Assuming these values for t ...
... 2) Big and bright as a supernova is, it still radiates like a blackbody with an effective temperature not much hotter than the solar photosphere. A value of 5500 K is typical for a Type IIp supernova. But the supernova has an enormous radius, ∼ 3 × 1015 cm (i.e., 200 AU). Assuming these values for t ...
Ch 28 Outline
... → particles of gas and dust move closer together due to gravity → become DENSER → temperature INCREASES → begins to glow (protostars). As contraction continues, protostars become HOTTER and BRIGHTER → nuclear fusion begins and the STAR IS BORN. Death of a Star Like the Sun These stars remain about t ...
... → particles of gas and dust move closer together due to gravity → become DENSER → temperature INCREASES → begins to glow (protostars). As contraction continues, protostars become HOTTER and BRIGHTER → nuclear fusion begins and the STAR IS BORN. Death of a Star Like the Sun These stars remain about t ...
Neutron Stars
... • Our atoms were once parts of stars that died more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
... • Our atoms were once parts of stars that died more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
test - Scioly.org
... 13. What are accretion disks also known as? 14. Name 5 ways to determine distance in space: Part IV: Math (3 pts each) You must show work in order to receive credit. Please use units, circle your answers, and round answers to 3 sig. figs. 1. Consider an object of .2 solar masses orbiting the Sun. Th ...
... 13. What are accretion disks also known as? 14. Name 5 ways to determine distance in space: Part IV: Math (3 pts each) You must show work in order to receive credit. Please use units, circle your answers, and round answers to 3 sig. figs. 1. Consider an object of .2 solar masses orbiting the Sun. Th ...
157a_midterm_2016
... Orbit radius 47 108 m emissivity 0.3 We are observing this system from a long distance, so we cannot resolve individual details. Plot the relative intensity that we would observe as a function of time (i.e. as a function of the planet position in its orbit) at a wavelength of 16 microns. Can we ...
... Orbit radius 47 108 m emissivity 0.3 We are observing this system from a long distance, so we cannot resolve individual details. Plot the relative intensity that we would observe as a function of time (i.e. as a function of the planet position in its orbit) at a wavelength of 16 microns. Can we ...
One way to measure distance
... Demonstration. Close one eye and hold your hand at arms length, pointing the tip of your index finger at me. Close one eye then open the other. What happens? ...
... Demonstration. Close one eye and hold your hand at arms length, pointing the tip of your index finger at me. Close one eye then open the other. What happens? ...
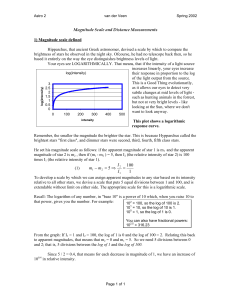
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... From the graph: If I1 = 1 and I2 = 100, the log of 1 is 0 and the log of 100 = 2. Relating this back to apparent magnitudes, that means that m2 = 0 and m1 = 5. So we need 5 divisions between 0 and 2; that is, 5 divisions between the log of 1 and the log of 100. Since 5 / 2 = 0.4, that means for each ...
... From the graph: If I1 = 1 and I2 = 100, the log of 1 is 0 and the log of 100 = 2. Relating this back to apparent magnitudes, that means that m2 = 0 and m1 = 5. So we need 5 divisions between 0 and 2; that is, 5 divisions between the log of 1 and the log of 100. Since 5 / 2 = 0.4, that means for each ...
RED GIANTS
... Missing the Main Sequence • If the protostar has a mass < 0.08 M: – It does not contain enough gravitational energy to reach a core temperature of 107 K – No fusion reactions occur – The star is stillborn! ...
... Missing the Main Sequence • If the protostar has a mass < 0.08 M: – It does not contain enough gravitational energy to reach a core temperature of 107 K – No fusion reactions occur – The star is stillborn! ...
star
... Giants are large bright stars that are smaller and fainter than supergiants. A white dwarf is the small dense remains of a low or medium-‐mass star. ...
... Giants are large bright stars that are smaller and fainter than supergiants. A white dwarf is the small dense remains of a low or medium-‐mass star. ...
Final Exam from 2005
... a. East, set in the West and revolve anti-clockwise around the South celestial pole. b. East, set in the West and revolve clockwise around the South celestial pole. c. West, set in the East and revolve clockwise around the South celestial pole. d. West, set in the East and revolve anti-clockwise aro ...
... a. East, set in the West and revolve anti-clockwise around the South celestial pole. b. East, set in the West and revolve clockwise around the South celestial pole. c. West, set in the East and revolve clockwise around the South celestial pole. d. West, set in the East and revolve anti-clockwise aro ...
Star Evolution
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.