The Parsec
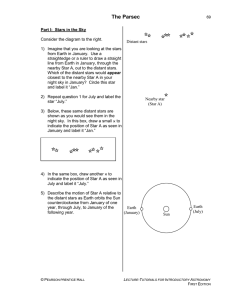
... by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the star. Since even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles ...
... by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the star. Since even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles ...
Stars
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
Star Classification
... Why are the stars in Orion’s Belt different colors? The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter, so they named it Orion after their mythical hunter. The line of three stars at the center is "Orion’s Belt." The many different colors of stars reflect the star’s temperature. The ...
... Why are the stars in Orion’s Belt different colors? The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter, so they named it Orion after their mythical hunter. The line of three stars at the center is "Orion’s Belt." The many different colors of stars reflect the star’s temperature. The ...
Key Stage 2: Teacher`s Pack
... pulsar spins on its axis 30 times a second. What is its rotational period? Period = 1 / frequency = 1/30 = 0.033 seconds 9. This shows one way of finding exoplanets. The amount of light from the star is being measured by a camera (in the red circle) and being displayed on screen. Explain how exoplan ...
... pulsar spins on its axis 30 times a second. What is its rotational period? Period = 1 / frequency = 1/30 = 0.033 seconds 9. This shows one way of finding exoplanets. The amount of light from the star is being measured by a camera (in the red circle) and being displayed on screen. Explain how exoplan ...
More on Cluster HR diagrams - University of Texas Astronomy
... pressure and shock waves from pulsations driving matter away—see Discovery 20-2, p. 564.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years); see Fig. 20.9. These bloated envelopes are not very stable! Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more or less sp ...
... pressure and shock waves from pulsations driving matter away—see Discovery 20-2, p. 564.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years); see Fig. 20.9. These bloated envelopes are not very stable! Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more or less sp ...
Test 1 - Brock physics
... (c) the radius of the region around a neutron star within which X-ray bursts occur. (d) the radius of the region around a black hole within which not even light can escape. 35. Neutron stars with masses greater than about 3 solar masses do not exist because neutron degeneracy pressure is not strong ...
... (c) the radius of the region around a neutron star within which X-ray bursts occur. (d) the radius of the region around a black hole within which not even light can escape. 35. Neutron stars with masses greater than about 3 solar masses do not exist because neutron degeneracy pressure is not strong ...
Laboratory Title
... depending on their initial starting mass. In the core of the red giant/supergiant, nuclear fusion will continue by converting the helium atoms into carbon. The amount of mass a star has determines which of the following life cycle paths it takes from here. A Red Giant low mass star moves on to………….. ...
... depending on their initial starting mass. In the core of the red giant/supergiant, nuclear fusion will continue by converting the helium atoms into carbon. The amount of mass a star has determines which of the following life cycle paths it takes from here. A Red Giant low mass star moves on to………….. ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... reversed filled triangle is WR 20b. The white dotted lines indicate a low-density “blister” next to the stellar cluster. One scenario suggests that cosmic rays are accelerated in the edges of the blister and propagate through the entire region, producing TeV gamma rays when they interact with ambien ...
... reversed filled triangle is WR 20b. The white dotted lines indicate a low-density “blister” next to the stellar cluster. One scenario suggests that cosmic rays are accelerated in the edges of the blister and propagate through the entire region, producing TeV gamma rays when they interact with ambien ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the center of the galax ...
... Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the center of the galax ...
A Star is
... • Small quantities of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are also found in stars, but stars are primarily composed of…. • HYDROGEN and HELIUM ...
... • Small quantities of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are also found in stars, but stars are primarily composed of…. • HYDROGEN and HELIUM ...
Phys133 Sample MidTerm #2 Covers Chs.10
... 4) What happens when a star exhausts its core hydrogen supply? A) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter. B) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness. C) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer. D) It contr ...
... 4) What happens when a star exhausts its core hydrogen supply? A) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter. B) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness. C) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer. D) It contr ...
H-R Diagram
... To identify the characteristics of a star from data in the diagram To classify a star by its position in the diagram To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature ...
... To identify the characteristics of a star from data in the diagram To classify a star by its position in the diagram To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature ...
Great Astronomers of the 20th Century
... Discovery of pulsars Evidence for dark matter The structure and evolution of galaxies Search for life in the universe ...
... Discovery of pulsars Evidence for dark matter The structure and evolution of galaxies Search for life in the universe ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... telescope has discovered the smallest planet known to orbit an ordinary star (the only smaller known orbit neutron stars). The planet, Kepler-37b, is smaller than Mercury, but slightly larger than our Moon. The discovery was made by a collaboration between Kepler scientists and asteroseismologists, ...
... telescope has discovered the smallest planet known to orbit an ordinary star (the only smaller known orbit neutron stars). The planet, Kepler-37b, is smaller than Mercury, but slightly larger than our Moon. The discovery was made by a collaboration between Kepler scientists and asteroseismologists, ...
Slide 1
... Low mass stars have lifetimes comparable to the Age of the Universe High mass stars have very short lifetimes, and disappear quickly! ...
... Low mass stars have lifetimes comparable to the Age of the Universe High mass stars have very short lifetimes, and disappear quickly! ...
Full Press Release - The Open University
... the image have swept out the gas and dust to the periphery of the nebula, creating a hollow shell-like structure. The gas that has been swept out creates the bright filament-like structures seen in the surrounding regions. The dust in the gas is heated by the intense light coming from both the mass ...
... the image have swept out the gas and dust to the periphery of the nebula, creating a hollow shell-like structure. The gas that has been swept out creates the bright filament-like structures seen in the surrounding regions. The dust in the gas is heated by the intense light coming from both the mass ...
What are yellow stars?
... • Arcturus is the brightest star in the Constellation of Boötes. • Arcturus is the 4th Brightest stars. • Arcturus is visible from both hemispheres in the sky. ...
... • Arcturus is the brightest star in the Constellation of Boötes. • Arcturus is the 4th Brightest stars. • Arcturus is visible from both hemispheres in the sky. ...
Review of "Man`s Place in Nature" by Alfred Russel Wallace
... The writer then proceeds to discuss in elaborate, fascinating and easily intelligible detail the distribution of the stars in space, the knowledge of their movements and nally the position in the universe of the solar system. His conclusions are: “The results so far reached by astronomers as the dir ...
... The writer then proceeds to discuss in elaborate, fascinating and easily intelligible detail the distribution of the stars in space, the knowledge of their movements and nally the position in the universe of the solar system. His conclusions are: “The results so far reached by astronomers as the dir ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.























