Doppler Effect
... 1. became higher and higher as the source approached and became lower and lower as the source receded 2. stayed at a constant high pitch as the source approached and then dropped to a constant lower pitch as the source receded 3. stayed at the same constant pitch throughout the motion 4. stayed at t ...
... 1. became higher and higher as the source approached and became lower and lower as the source receded 2. stayed at a constant high pitch as the source approached and then dropped to a constant lower pitch as the source receded 3. stayed at the same constant pitch throughout the motion 4. stayed at t ...
FREE Sample Here
... People from different cultures all see the same stars, but the asterisms and constellations are different. Technically, we would now all see the same constellations, because these have official definitions and borders; however, this designation might not be well accepted by people of various culture ...
... People from different cultures all see the same stars, but the asterisms and constellations are different. Technically, we would now all see the same constellations, because these have official definitions and borders; however, this designation might not be well accepted by people of various culture ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
December
... Fully one-third of the 1st magnitude stars visible in the sky (seven of twenty-one) are in the Winter Circle with Sirius, Procyon, Pollux - toss in 2nd magnitude Castor - Capella, Aldebaran, and Rigel on the periphery, and Betelgeuse located off-center. Although somewhat flattened, and thus more ell ...
... Fully one-third of the 1st magnitude stars visible in the sky (seven of twenty-one) are in the Winter Circle with Sirius, Procyon, Pollux - toss in 2nd magnitude Castor - Capella, Aldebaran, and Rigel on the periphery, and Betelgeuse located off-center. Although somewhat flattened, and thus more ell ...
Talk - Otterbein University
... • The more mass a galaxy has the brighter it is the faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
... • The more mass a galaxy has the brighter it is the faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... Milky Way is a typical disk galaxy (see Fig. 5). It consists a bulge and a thin disk. The disk is thin because it’s rotationally supported, like an audio CD. You also see black lanes in the galaxy, these are caused by dust obscuration. The diameter of our luminous Milky Way is about 30 kpc. The Sun ...
... Milky Way is a typical disk galaxy (see Fig. 5). It consists a bulge and a thin disk. The disk is thin because it’s rotationally supported, like an audio CD. You also see black lanes in the galaxy, these are caused by dust obscuration. The diameter of our luminous Milky Way is about 30 kpc. The Sun ...
BSA Astronomy Merit Badge
... Menkib (Xi Per) Atik (Omicron Per) Gorgonea Secunda (Pi Per) Gorgonea Tertia (Rho Per) Gorgonea Quarta (Omega Per) ...
... Menkib (Xi Per) Atik (Omicron Per) Gorgonea Secunda (Pi Per) Gorgonea Tertia (Rho Per) Gorgonea Quarta (Omega Per) ...
Document
... the universe with unprecedented clarity and sensitivity. • The picture clearly shows faint structure as small as 30 light-years across in a galaxy tens of millions of light-years away. The Earth and Beyond… GCSE Physics Notes LOJ ...
... the universe with unprecedented clarity and sensitivity. • The picture clearly shows faint structure as small as 30 light-years across in a galaxy tens of millions of light-years away. The Earth and Beyond… GCSE Physics Notes LOJ ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... 45. The prediction of the General Theory of Relativity that a mass bends spacetime and that other objects, including photons, move along the paths of shortest distance in the bent spacetime was confirmed by the observed shift in the positions of stars during a total solar eclipse. The person who did ...
... 45. The prediction of the General Theory of Relativity that a mass bends spacetime and that other objects, including photons, move along the paths of shortest distance in the bent spacetime was confirmed by the observed shift in the positions of stars during a total solar eclipse. The person who did ...
Lecture 30
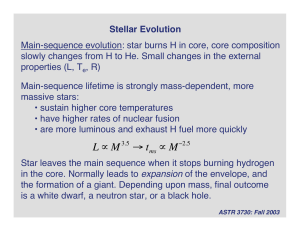
... Main-sequence lifetime is strongly mass-dependent, more massive stars: • sustain higher core temperatures • have higher rates of nuclear fusion • are more luminous and exhaust H fuel more quickly ...
... Main-sequence lifetime is strongly mass-dependent, more massive stars: • sustain higher core temperatures • have higher rates of nuclear fusion • are more luminous and exhaust H fuel more quickly ...
The Sky Tonight - Northern Stars Planetarium
... powerful magnetic storms on the Sun. When the energy from these storms reaches Earth, the energy is shielded from us by Earth's magnetic field; however, the energy does interact with the upper atmosphere near the north and south poles. This causes the air to glow, causing northern lights or Aurora B ...
... powerful magnetic storms on the Sun. When the energy from these storms reaches Earth, the energy is shielded from us by Earth's magnetic field; however, the energy does interact with the upper atmosphere near the north and south poles. This causes the air to glow, causing northern lights or Aurora B ...
SHELL H II REGIONS IN NGC 6334
... • They last between 2 and 10 million years. • But little is known about their formation, about their earliest stages. • It can be argued theoretically that the disks should start small and grow with time… ...
... • They last between 2 and 10 million years. • But little is known about their formation, about their earliest stages. • It can be argued theoretically that the disks should start small and grow with time… ...
Centimeter and Millimeter Observations of Very Young Binary Systems
... • They last between 2 and 10 million years. • But little is known about their formation, about their earliest stages. • It can be argued theoretically that the disks should start small and grow with time… ...
... • They last between 2 and 10 million years. • But little is known about their formation, about their earliest stages. • It can be argued theoretically that the disks should start small and grow with time… ...
second grade - Math/Science Nucleus
... We see objects in the night sky because they are either generating or reflecting light. While these objects also shine or reflect light during the day, we generally cannot see them because they are much dimmer than the bright light emitted by the nearby Sun. Most of the light we see at night comes f ...
... We see objects in the night sky because they are either generating or reflecting light. While these objects also shine or reflect light during the day, we generally cannot see them because they are much dimmer than the bright light emitted by the nearby Sun. Most of the light we see at night comes f ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
File
... A star's birth mass is the most important predictor of a star's luminosity. A star born with low mass will have a high luminosity; a star born with high mass will have a significantly lower luminosity. A star's birth mass is the most important predictor of a star's surface temperature. A star born ...
... A star's birth mass is the most important predictor of a star's luminosity. A star born with low mass will have a high luminosity; a star born with high mass will have a significantly lower luminosity. A star's birth mass is the most important predictor of a star's surface temperature. A star born ...
Geoscience Astronomy Formative on Stellar Evolution and
... the speed of light d. Many astronomers believe that black dwarfs a. are hotter than white dwarfs c. are more massive than white dwarfs b. are more dense than white dwarfs d. do not exist yet A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole ...
... the speed of light d. Many astronomers believe that black dwarfs a. are hotter than white dwarfs c. are more massive than white dwarfs b. are more dense than white dwarfs d. do not exist yet A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole ...
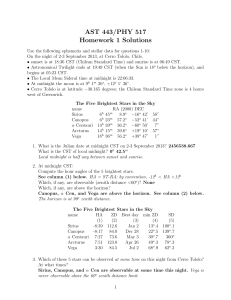
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Frantic Finish - Max-Planck
... diamond. In its interior, the first step is the formation of islands in which thermonuclear reactions occur. Silicon and nickel are formed. The ignition sources spread at subsonic speed (deflagration) and burn from the center of the star outward toward its surface. This causes instabilities, leading ...
... diamond. In its interior, the first step is the formation of islands in which thermonuclear reactions occur. Silicon and nickel are formed. The ignition sources spread at subsonic speed (deflagration) and burn from the center of the star outward toward its surface. This causes instabilities, leading ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... was shown. The first part was about large raging storms in the atmospheres of the gas giant planets. Some of these storms are the size of our planet Earth, with winds blowing at many hundreds of kilometers per hour. It also showed an interview with the Australian amateur astronomer who discovered an ...
... was shown. The first part was about large raging storms in the atmospheres of the gas giant planets. Some of these storms are the size of our planet Earth, with winds blowing at many hundreds of kilometers per hour. It also showed an interview with the Australian amateur astronomer who discovered an ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... are extremely luminous, blue and short-lived, while low-mass stars are long-lived, red and faint. Consequently, early-type galaxies are red and their brightness distributions are smooth because they are generated by enormous numbers of individually faint stars. Late-type galaxies, by contrast, are b ...
... are extremely luminous, blue and short-lived, while low-mass stars are long-lived, red and faint. Consequently, early-type galaxies are red and their brightness distributions are smooth because they are generated by enormous numbers of individually faint stars. Late-type galaxies, by contrast, are b ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.