PH607lec10
... formation event a few million years ago. The existence of these relatively young (though evolved) stars there was of a surprise to experts, who would have expected the tidal forces from the central black-hole to prevent their formation. They are much too young to have migrated far, but it seems even ...
... formation event a few million years ago. The existence of these relatively young (though evolved) stars there was of a surprise to experts, who would have expected the tidal forces from the central black-hole to prevent their formation. They are much too young to have migrated far, but it seems even ...
Chapter 2 Test Review Vocabulary • axis – an imaginary line
... Why does the moon’s shape look different on different nights? As the moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of its bright side can be seen. Stars Why does the sun look larger than the other stars you can see? The sun looks larger than other stars you can see because it is so much clos ...
... Why does the moon’s shape look different on different nights? As the moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of its bright side can be seen. Stars Why does the sun look larger than the other stars you can see? The sun looks larger than other stars you can see because it is so much clos ...
6 March 2013 Exoplanets and Where to Find Them Professor
... The Galaxy is continually evolving and changing, albeit on the astronomical timescale of millions of years. Within the disc, the spiral arms show where diffuse hydrogen gas clouds have been compressed by density waves, triggering the process of gravitational collapse that leads to the formation of s ...
... The Galaxy is continually evolving and changing, albeit on the astronomical timescale of millions of years. Within the disc, the spiral arms show where diffuse hydrogen gas clouds have been compressed by density waves, triggering the process of gravitational collapse that leads to the formation of s ...
Clusters of galaxies
... ESO Distant Cluster Survey Identification, deep photometry and spectroscopy of 10 clusters around z ~ 0.5 and 10 around z ~ 0.8 Spectroscopy is FORS2 (R ~ 1200) Science goals are build up of stellar populations with redshift (plus weak lensing). ...
... ESO Distant Cluster Survey Identification, deep photometry and spectroscopy of 10 clusters around z ~ 0.5 and 10 around z ~ 0.8 Spectroscopy is FORS2 (R ~ 1200) Science goals are build up of stellar populations with redshift (plus weak lensing). ...
TheSky6 Review - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... star/object/location, either click on the object or Find it (see #7 above) and then use the centering icon object. ...
... star/object/location, either click on the object or Find it (see #7 above) and then use the centering icon object. ...
Collapse of an unstable Neutron Star to a Black Hole
... star merger process a new supramassive or hypermassive neutron star is formed, which could be stable for longer times or collapse almost immediately to a black hole. During this process a short gamma ray burst is emitted, releasing in less than one second the energy emitted by our Galaxy over one ye ...
... star merger process a new supramassive or hypermassive neutron star is formed, which could be stable for longer times or collapse almost immediately to a black hole. During this process a short gamma ray burst is emitted, releasing in less than one second the energy emitted by our Galaxy over one ye ...
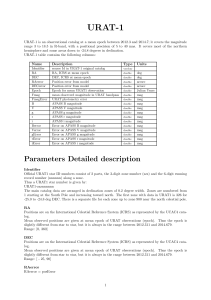
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... slightly different from star to star, but it is always in the range between 2012.311 and 2014.679. Range: [0, 360] DEC Positions are on the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) as represented by the UCAC4 catalog. Mean observed positions are given at mean epoch of URAT observations (epoch ...
... slightly different from star to star, but it is always in the range between 2012.311 and 2014.679. Range: [0, 360] DEC Positions are on the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) as represented by the UCAC4 catalog. Mean observed positions are given at mean epoch of URAT observations (epoch ...
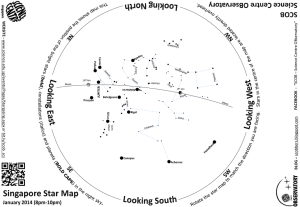
Star Map - Science Centre
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
A generic relation between baryonic and radiative energy densities
... with self-gravitation (Bowers & Deeming 1984). This is the way primordial astrophysical clouds remain quasi-stable for millions of years; by generating their own pressure, temperature and luminosity by slow gravitational contraction. The originally cold primordial clouds become hot enough to be visi ...
... with self-gravitation (Bowers & Deeming 1984). This is the way primordial astrophysical clouds remain quasi-stable for millions of years; by generating their own pressure, temperature and luminosity by slow gravitational contraction. The originally cold primordial clouds become hot enough to be visi ...
S1-4-05 - Seasonal Constelallations - Lesson
... There were many different learner difficulties highlighted in Rosalind Drivers book about learner difficulties in science. The first difficulty was the concept of how children understand light. Some students thought we could see objects because light “hits them”, and some thought that light hits an ...
... There were many different learner difficulties highlighted in Rosalind Drivers book about learner difficulties in science. The first difficulty was the concept of how children understand light. Some students thought we could see objects because light “hits them”, and some thought that light hits an ...
A Tale of Two (Solar) Telescopes: something old, something
... bottom-most rungs of Drake’s Ladder, where sadly the sexiness is low, but on positive side the knowledge content was though to be high; even so, a few surprises still were to be found… ...
... bottom-most rungs of Drake’s Ladder, where sadly the sexiness is low, but on positive side the knowledge content was though to be high; even so, a few surprises still were to be found… ...
3P15.pdf
... High resolution spectra of 10 UV Cet type flare stars have been analysed in this work. Age, line profiles, rotation and flux-flux relationships have been studied and the results have been compared with the ones obtained by López-Santiago et al (2004a, b) for a sample of 144 stars, with spectral type ...
... High resolution spectra of 10 UV Cet type flare stars have been analysed in this work. Age, line profiles, rotation and flux-flux relationships have been studied and the results have been compared with the ones obtained by López-Santiago et al (2004a, b) for a sample of 144 stars, with spectral type ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet Open the HR Diagram Explorer. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the capabilities of the HertzsprungRussell Diagram Explorer through experimentation. An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active ...
... HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet Open the HR Diagram Explorer. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the capabilities of the HertzsprungRussell Diagram Explorer through experimentation. An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... • significant fraction of red sequence are disks, particularly at low masses • red disks are more bulge-dominated than higher z star-forming disks • a key intermediate phase in the transition to present day spheroidals Bundy et al 0912.1077 ...
... • significant fraction of red sequence are disks, particularly at low masses • red disks are more bulge-dominated than higher z star-forming disks • a key intermediate phase in the transition to present day spheroidals Bundy et al 0912.1077 ...
Wrongway Planets_Do Gymnastics
... hot Jupiters. (Exoplanet is short f or "extra-solar planet," which is a planet outside the solar system.) Astronomers would like to find a small, rocky planet not too far from or too close to its star — one that looks a lot like Earth. These types of planets are most likely to host life as we know i ...
... hot Jupiters. (Exoplanet is short f or "extra-solar planet," which is a planet outside the solar system.) Astronomers would like to find a small, rocky planet not too far from or too close to its star — one that looks a lot like Earth. These types of planets are most likely to host life as we know i ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 1 to Chapter 9
... of energy given off by a star can be quite different from the brightness as it appears from Earth. This energy output is referred to as the star’s LUMINOSITY and this is closely related to the star’s ABSOLUTE VISUAL MAGNITUDE which indicates how bright the star would be if it were located at a refe ...
... of energy given off by a star can be quite different from the brightness as it appears from Earth. This energy output is referred to as the star’s LUMINOSITY and this is closely related to the star’s ABSOLUTE VISUAL MAGNITUDE which indicates how bright the star would be if it were located at a refe ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.