Unit 2―The Stars and Their Diurnal Motion
... The names of the stars: On any star map you might see a range of differences in how the star is named. Some have proper, but inconsistent, names. The North Star is also called Polaris but most stars in a constellation are assigned a Greek letter for a name according to the brightness, or magnitude ( ...
... The names of the stars: On any star map you might see a range of differences in how the star is named. Some have proper, but inconsistent, names. The North Star is also called Polaris but most stars in a constellation are assigned a Greek letter for a name according to the brightness, or magnitude ( ...
aaswinter06
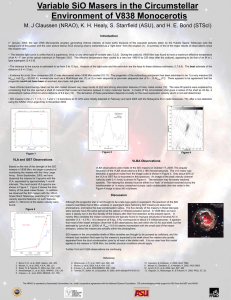
... • The detailed light curve is unlike that of a supernova, nova, or any other type of variable star (1,2,3). During the outburst, V838 Mon was found to have a maximum effective temperature of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~8 ...
... • The detailed light curve is unlike that of a supernova, nova, or any other type of variable star (1,2,3). During the outburst, V838 Mon was found to have a maximum effective temperature of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~8 ...
AST1001.ch1
... • Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. • Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. • Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
... • Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. • Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. • Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars
... What is the raw material for making stars and where did it come from? What forces of nature contribute to energy generation in stars? How and where did the chemical elements form? ? How long do stars live? How will our Sun die? How do massive stars explode? ? What are the remnants of such stellar ex ...
... What is the raw material for making stars and where did it come from? What forces of nature contribute to energy generation in stars? How and where did the chemical elements form? ? How long do stars live? How will our Sun die? How do massive stars explode? ? What are the remnants of such stellar ex ...
Glencoe Earth Science
... around Polaris. Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. The constellations appear to move, as shown in Figure 2, because Earth is in motion. The stars appear to complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 h as Earth rotates on its axis. One circumpolar constellation that’s e ...
... around Polaris. Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. The constellations appear to move, as shown in Figure 2, because Earth is in motion. The stars appear to complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 h as Earth rotates on its axis. One circumpolar constellation that’s e ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2/189) of a volume-limited (d < 25 pc) sample of K stars have lithium abundances and chromospheric activity suggesting ages possibly <100 Myr, with an additional 6% (11/189) pla ...
... by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2/189) of a volume-limited (d < 25 pc) sample of K stars have lithium abundances and chromospheric activity suggesting ages possibly <100 Myr, with an additional 6% (11/189) pla ...
Habitability of planets around Red Dwarf Stars
... Main sequence (MS) dwarfs of spectral class M (dM stars) comprise ∼70% of solar neighbourhood stars. At one end of the range are stars of about half a solar Mass (M ), with >6.0% solar luminosity (L ), and an effective photospheric temperature (Teff ) of )3,700 K. At the other are stars of about 0 ...
... Main sequence (MS) dwarfs of spectral class M (dM stars) comprise ∼70% of solar neighbourhood stars. At one end of the range are stars of about half a solar Mass (M ), with >6.0% solar luminosity (L ), and an effective photospheric temperature (Teff ) of )3,700 K. At the other are stars of about 0 ...
Ayres-Kepler-ASC
... Most late-type stars of near-solar color show long term variations in Ca II emission, many cyclic. Others, typically low RHK and often subgiants, are ‘flat activity’ (Radick et al. 1998) ...
... Most late-type stars of near-solar color show long term variations in Ca II emission, many cyclic. Others, typically low RHK and often subgiants, are ‘flat activity’ (Radick et al. 1998) ...
SDO | SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY HTTP://WWW.NASA
... solid, different regions rotate at different rates: about 24 Earth days at the equator & 30 days at the poles. ...
... solid, different regions rotate at different rates: about 24 Earth days at the equator & 30 days at the poles. ...
ppt
... actually much closer to 290 K Atmospheric greenhouse effect serves to keep the temperature higher (also a very tiny heating effect due to geothermal heat) ...
... actually much closer to 290 K Atmospheric greenhouse effect serves to keep the temperature higher (also a very tiny heating effect due to geothermal heat) ...
Which exoEarths should we search for life
... that may limit the habitability of planets in orbit around them. First, the low luminosity of these stars means that their HZs are very close to the star. Even for the most luminous M dwarfs, the HZ only stretches from around 0.2 to 0.4 AU. Exo-Earths located so close to their parent star will rapid ...
... that may limit the habitability of planets in orbit around them. First, the low luminosity of these stars means that their HZs are very close to the star. Even for the most luminous M dwarfs, the HZ only stretches from around 0.2 to 0.4 AU. Exo-Earths located so close to their parent star will rapid ...
γ The potential for intensity interferometry with -ray telescope arrays
... regions and young stellar clusters. The proximity of the comoving groups ensures that their members are bright and also makes these groups relatively sparse, making them unconfused targets, even given the large PSF of ∼ 30 . This sparseness is also the reason for incomplete group memberships, making ...
... regions and young stellar clusters. The proximity of the comoving groups ensures that their members are bright and also makes these groups relatively sparse, making them unconfused targets, even given the large PSF of ∼ 30 . This sparseness is also the reason for incomplete group memberships, making ...
Section 2
... The Light-Year Distances on Earth’s surface are often measured in kilometers. However, distances to the stars are so large that kilometers are not very practical units. Astronomers use a unit called the light-year to measure distances between the stars. In space, light travels at a speed of about 30 ...
... The Light-Year Distances on Earth’s surface are often measured in kilometers. However, distances to the stars are so large that kilometers are not very practical units. Astronomers use a unit called the light-year to measure distances between the stars. In space, light travels at a speed of about 30 ...
Warm-Up Monday, July 23, 2012
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.