what is knowledge management?
... • Tacit (knowing how) & Explicit (knowing what) • Polanyi(1967) – continuum • Nonaka (1994) – neat conversion processes from one form to another: socialization, combination, externalization and internalization • All-encompassing but little revealing concept • Logical behaviourist perspective ...
... • Tacit (knowing how) & Explicit (knowing what) • Polanyi(1967) – continuum • Nonaka (1994) – neat conversion processes from one form to another: socialization, combination, externalization and internalization • All-encompassing but little revealing concept • Logical behaviourist perspective ...
Jean Piaget (1896
... but must be constructed and reconstructed by the learner Piaget asserted that for a child to know and construct knowledge of the world, the child must act on objects and it is this action which provides knowledge of those object The learner must be active; he is not a vessel to be filled with fa ...
... but must be constructed and reconstructed by the learner Piaget asserted that for a child to know and construct knowledge of the world, the child must act on objects and it is this action which provides knowledge of those object The learner must be active; he is not a vessel to be filled with fa ...
File - teacherver.com
... concept: refers to all cases of a particular class of objects, events, persons relationships, processes and ideas a unit of meaning that symbolizes or labels a segment reality breaks the complex world to identifiable ideas and elements forms jargons/vocabulary hypotheses: educated guess ...
... concept: refers to all cases of a particular class of objects, events, persons relationships, processes and ideas a unit of meaning that symbolizes or labels a segment reality breaks the complex world to identifiable ideas and elements forms jargons/vocabulary hypotheses: educated guess ...
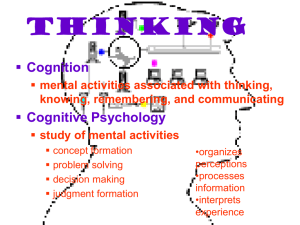
Thinking Cognition mental activities associated with thinking
... Peak-end rule; judge past experiences on how they were at peak (pleasant or unpleasant) and how they ended. All other information discarded, including pleasantness or unpleasantness, and how long experience lasted. This heuristic was first suggested by Daniel Kahneman ...
... Peak-end rule; judge past experiences on how they were at peak (pleasant or unpleasant) and how they ended. All other information discarded, including pleasantness or unpleasantness, and how long experience lasted. This heuristic was first suggested by Daniel Kahneman ...
Learning Theories
... • Kirschner, Sweller, and Clark suggest that novices be taught with direct methods of instruction like worked examples. Sweller (2006) discusses the worked-example effect as a alternative to problem-solving for novices. However practice with feedback is condoned and even encouraged by Sweller and hi ...
... • Kirschner, Sweller, and Clark suggest that novices be taught with direct methods of instruction like worked examples. Sweller (2006) discusses the worked-example effect as a alternative to problem-solving for novices. However practice with feedback is condoned and even encouraged by Sweller and hi ...
Cognitive Science - VideoLectures.NET
... • And many machine learning problems are defined in terms of human cognition (from object recognition, to machine translation) – Machine learning needs cognitive science (cf biomimetics) burrs ...
... • And many machine learning problems are defined in terms of human cognition (from object recognition, to machine translation) – Machine learning needs cognitive science (cf biomimetics) burrs ...
Language & Social Interaction
... Discourse formulation requires understanding & manipulating both linguistic information & the cognitive operations essential to the organisation of information “Social cognition encompasses wide ranging abilities including interpreting social cues, communication, interactions and social referencing ...
... Discourse formulation requires understanding & manipulating both linguistic information & the cognitive operations essential to the organisation of information “Social cognition encompasses wide ranging abilities including interpreting social cues, communication, interactions and social referencing ...
How Much AI Does a Cognitive Science Major Need to Know?
... to know about computation. But "computation" isn’t really a subject matter aside from the body of computational practice that has developed over the last half century. Theoretical approaches (such as Turing machines, formal semantics of programs, etc.) capture only part of the essence of computation ...
... to know about computation. But "computation" isn’t really a subject matter aside from the body of computational practice that has developed over the last half century. Theoretical approaches (such as Turing machines, formal semantics of programs, etc.) capture only part of the essence of computation ...
discintro
... candidate should be a robot that we can see is just one individual autonomous system like ourselves. That way we not only eliminate the possibility of collective play-acting, but we can also test the candidate’s full sensorimotor I/O capacity to confirm that it is indeed completely indistinguishable ...
... candidate should be a robot that we can see is just one individual autonomous system like ourselves. That way we not only eliminate the possibility of collective play-acting, but we can also test the candidate’s full sensorimotor I/O capacity to confirm that it is indeed completely indistinguishable ...
Distributed Cognition: Cognizing, Autonomy and the Turing Test
... candidate should be a robot that we can see is just one individual autonomous system like ourselves. That way we not only eliminate the possibility of collective play-acting, but we can also test the candidate’s full sensorimotor I/O capacity to confirm that it is indeed completely indistinguishable ...
... candidate should be a robot that we can see is just one individual autonomous system like ourselves. That way we not only eliminate the possibility of collective play-acting, but we can also test the candidate’s full sensorimotor I/O capacity to confirm that it is indeed completely indistinguishable ...
Autonomous Virtual Humans and Social Robots in Telepresence
... T. Mukai, S. Hirano, H. Nakashima, Y. Kato, Y. Sakaida, S. Guo, and S. Hosoe, “Development of a nursing-care assistant robot riba that can lift a human in its arms,” in 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5996– ...
... T. Mukai, S. Hirano, H. Nakashima, Y. Kato, Y. Sakaida, S. Guo, and S. Hosoe, “Development of a nursing-care assistant robot riba that can lift a human in its arms,” in 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5996– ...
PowerPoint - University of Virginia, Department of Computer Science
... pattern matching for humans • But what patterns do we see? • What rules do we use to evaluate perceived patterns? ...
... pattern matching for humans • But what patterns do we see? • What rules do we use to evaluate perceived patterns? ...
Kenneth D Forbus - (QRG), Northwestern University
... Professor Forbus is a fellow of the AAAI, ACM, and the Cognitive Science Society. He was the founding head of the Artificial Intelligence group at the Beckman Institute, University of Illinois before taking up a post at Northwestern University, where he is the Walter P. Murphy Professor of Computer ...
... Professor Forbus is a fellow of the AAAI, ACM, and the Cognitive Science Society. He was the founding head of the Artificial Intelligence group at the Beckman Institute, University of Illinois before taking up a post at Northwestern University, where he is the Walter P. Murphy Professor of Computer ...
INTRODUCTION TO SOCIAL COGNITION AND BEHAVIOR Assoc
... The course aims at delineating the basic aspects of social cognition: how perceivers of the social world go about attaining understanding of self and others, moving beyond their naive lay theories about how people operate. It concentrates on the methods used, the research being done and the implemen ...
... The course aims at delineating the basic aspects of social cognition: how perceivers of the social world go about attaining understanding of self and others, moving beyond their naive lay theories about how people operate. It concentrates on the methods used, the research being done and the implemen ...
Chapter 04-06
... •More brain resources dedicated to processing •E.g. musicians’ cortical representation of hands ...
... •More brain resources dedicated to processing •E.g. musicians’ cortical representation of hands ...
Corinne Stevens
... findings revealed differentiated customs and beliefs shaping children, therefore presenting a variety of different childhoods globally. Some beliefs emerged from nativist standpoints, such as children being deemed as vulnerable and weak dependents, lacking awareness and knowledge, whereas children b ...
... findings revealed differentiated customs and beliefs shaping children, therefore presenting a variety of different childhoods globally. Some beliefs emerged from nativist standpoints, such as children being deemed as vulnerable and weak dependents, lacking awareness and knowledge, whereas children b ...
What is immediate perception? The Buddhist answer
... Does it mean that we really apprehend svalakshana at the moment of perception? Taking into account that all of our own cognitive devices – images, conceptions, words, etc. – are products of mental construction, how could we say that immediate perception of particulars or of their aspects is a cognit ...
... Does it mean that we really apprehend svalakshana at the moment of perception? Taking into account that all of our own cognitive devices – images, conceptions, words, etc. – are products of mental construction, how could we say that immediate perception of particulars or of their aspects is a cognit ...
Extremes meet each other: Artificial General Intelligence
... the human cognition is the second most important factor determining all human knowledge. 1.2. Brief history of achieving the main goal of cognitive sciences The goal of cognitive sciences, especially its most progressive Artificial Intelligence’s part is to model a human cognition in a computable w ...
... the human cognition is the second most important factor determining all human knowledge. 1.2. Brief history of achieving the main goal of cognitive sciences The goal of cognitive sciences, especially its most progressive Artificial Intelligence’s part is to model a human cognition in a computable w ...
Embodied Action as a ‘Helping Hand’ in Social Interaction
... transformation of information through different media at a more general level, rather than the particular role of the body in these processes. This means, despite the emphasis on interactions between agents and their material as well as social surroundings, the DC approach offers not much on the emb ...
... transformation of information through different media at a more general level, rather than the particular role of the body in these processes. This means, despite the emphasis on interactions between agents and their material as well as social surroundings, the DC approach offers not much on the emb ...
Social Learning Theory
... Learning is the result of the thinking process which is influenced by environment ...
... Learning is the result of the thinking process which is influenced by environment ...
ijcai 2015 - Department of Intelligent Systems
... •The test investigates whether people can detect if they are talking to machines or humans. •The experiment is based on Alan Turing's question-andanswer game Can Machines Think? •No computer has passed the test before under these conditions, it is reported. ...
... •The test investigates whether people can detect if they are talking to machines or humans. •The experiment is based on Alan Turing's question-andanswer game Can Machines Think? •No computer has passed the test before under these conditions, it is reported. ...
Understanding Research Nils J. Nilsson, SRI International
... our imaginary system doesn’t really have to run on a computer we can strip it of the various ad hoc features of real systems so necessary for efficiency. Now maybe we can reorganize it a bit to give it a more coherent internal organization and to relate it more closely to existing well-understood AI ...
... our imaginary system doesn’t really have to run on a computer we can strip it of the various ad hoc features of real systems so necessary for efficiency. Now maybe we can reorganize it a bit to give it a more coherent internal organization and to relate it more closely to existing well-understood AI ...
CS440 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... used in AI. Deals with the questions of what to represent and how to represent it. How to structure knowledge? What is explicit, and what must be inferred? How to encode "rules" for inferencing so as to find information that is only implicitly known? How to deal with incomplete, inconsistent, and pr ...
... used in AI. Deals with the questions of what to represent and how to represent it. How to structure knowledge? What is explicit, and what must be inferred? How to encode "rules" for inferencing so as to find information that is only implicitly known? How to deal with incomplete, inconsistent, and pr ...
A PhD RESEARCH TOPIC PROPOSAL PRESENTED BY NWEKE
... this fact. As a result, the majority of existing AI architectures is incorrectly based on an (explicit or implicit) assumption of infinite or sufficient computational resources. Attention has not yet been recognized as a key cognitive process of AI systems and in particular not of artificial general ...
... this fact. As a result, the majority of existing AI architectures is incorrectly based on an (explicit or implicit) assumption of infinite or sufficient computational resources. Attention has not yet been recognized as a key cognitive process of AI systems and in particular not of artificial general ...