Biopsychology and Perception
... – MRI : magnetic fields from radio waves – PET : positron emission tomography, uses radioactive material, good for metabolic activity of the brain – CT : uses X-rays to look at soft tissue – SPECT : single proton emission computerized axial tomography, traces blood flow in the brain – SQUID : super ...
... – MRI : magnetic fields from radio waves – PET : positron emission tomography, uses radioactive material, good for metabolic activity of the brain – CT : uses X-rays to look at soft tissue – SPECT : single proton emission computerized axial tomography, traces blood flow in the brain – SQUID : super ...
Chapter 8
... Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about the same time as a neighbor child, whose parents did not use flashcards. Explain why Brianna's reading skills devel ...
... Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about the same time as a neighbor child, whose parents did not use flashcards. Explain why Brianna's reading skills devel ...
Studying the Brain
... Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature ...
... Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature ...
Frontal Lobe - Washington School Counselor Association
... • Fool brain into thinking that they are necessary for survival • Desire to repeat drug using behavior is strong ...
... • Fool brain into thinking that they are necessary for survival • Desire to repeat drug using behavior is strong ...
History and Methods
... for each other as far as learning is concerned. The Mass Action Principle: reduction in learning is proportional to the amount of tissue destroyed; the more complex the learning task, the more disruptive lesions are. ...
... for each other as far as learning is concerned. The Mass Action Principle: reduction in learning is proportional to the amount of tissue destroyed; the more complex the learning task, the more disruptive lesions are. ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 2:Hindbrain The
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
Nervous System - KidsHealth in the Classroom
... hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
... hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
http://catnet.adventist.ca/files/articles/pdf/oj_ID278.pdf
... Not long ago, I was involved in a course that helped me to understand the amazing intricacies of the human brain. Often referred to as “the last frontier,” the brain still includes mysteries that have yet to be unraveled. But during the past ten years we have begun to understand much more about its ...
... Not long ago, I was involved in a course that helped me to understand the amazing intricacies of the human brain. Often referred to as “the last frontier,” the brain still includes mysteries that have yet to be unraveled. But during the past ten years we have begun to understand much more about its ...
02_Neuroscience
... blood flow have been more active recently, so they must have been active in task ...
... blood flow have been more active recently, so they must have been active in task ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
Emerging Imaging Technologies and Their Application to Psychiatric
... concomitant abnormalities in synaptic pruning, which is known to take place throughout development. New diffusion-tensor imaging techniques in MRI, described by Makris et al. in this section, add the ability to track major fiber bundles in the white matter, which can give some insight into cortical ...
... concomitant abnormalities in synaptic pruning, which is known to take place throughout development. New diffusion-tensor imaging techniques in MRI, described by Makris et al. in this section, add the ability to track major fiber bundles in the white matter, which can give some insight into cortical ...
Chapter1
... Basic networks Random networks Feedforward network Competitive networks Point attractor networks ...
... Basic networks Random networks Feedforward network Competitive networks Point attractor networks ...
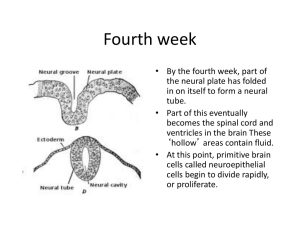
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
The use of Models - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... The strict-information processing approach to cognition was replaced with a broader, more inclusive approach now known as cognitive science. This approach described cognition as the coordinated, often parallel operation of mental processes within a multicomponent memory system. The approach is delib ...
... The strict-information processing approach to cognition was replaced with a broader, more inclusive approach now known as cognitive science. This approach described cognition as the coordinated, often parallel operation of mental processes within a multicomponent memory system. The approach is delib ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... Autism is a neurological disease that includes problems with communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. ...
... Autism is a neurological disease that includes problems with communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. ...
Chapter Six
... physiology in man and other species. Cognitive neuroscience studies the structures and processes underlying cognitive function. What are the neural mechanisms for pattern recognition, attention, memory, and problem solving? ...
... physiology in man and other species. Cognitive neuroscience studies the structures and processes underlying cognitive function. What are the neural mechanisms for pattern recognition, attention, memory, and problem solving? ...
Brain models: the next generation
... that one goal of cortical computation is to produce neural responses that are statistically independent. Similarly, Olshausen shows that if neural responses to natural movies are forced to be sparse and independent, the receptive fields that result resemble those found physiologically in V1. These t ...
... that one goal of cortical computation is to produce neural responses that are statistically independent. Similarly, Olshausen shows that if neural responses to natural movies are forced to be sparse and independent, the receptive fields that result resemble those found physiologically in V1. These t ...
Your Brain and What It Does
... These two halves are connected by long neuron branches called the corpus callosum which is relatively larger in women’s brains than in men’s. The cerebrum is positioned over and around most other brain structures, and its four lobes are specialized by function but are richly connected. The outer 3 m ...
... These two halves are connected by long neuron branches called the corpus callosum which is relatively larger in women’s brains than in men’s. The cerebrum is positioned over and around most other brain structures, and its four lobes are specialized by function but are richly connected. The outer 3 m ...
Central Nervous System
... “The Brain observatory at the University of California” • Jacopo Annese is looking for 1,000 brains. The director of the brain library is on a quest to collect, dissect, and digitize images of the human brain for the Digital Brain Library, which was launched with support from the National Science F ...
... “The Brain observatory at the University of California” • Jacopo Annese is looking for 1,000 brains. The director of the brain library is on a quest to collect, dissect, and digitize images of the human brain for the Digital Brain Library, which was launched with support from the National Science F ...
2000 NeuroCom BL
... few classes of subjects like head injured individuals (Bara, Tirassa, & Zettin, 1997), Alzheimer’s patients (Bara, Bucciarelli, & Geminiani, 1999), and normal and neuropsychologically abnormal children (Bara, Bosco, & Bucciarelli, 1999a, 1999b). Furthermore, our protocols have been more aimed at est ...
... few classes of subjects like head injured individuals (Bara, Tirassa, & Zettin, 1997), Alzheimer’s patients (Bara, Bucciarelli, & Geminiani, 1999), and normal and neuropsychologically abnormal children (Bara, Bosco, & Bucciarelli, 1999a, 1999b). Furthermore, our protocols have been more aimed at est ...
Nervous System
... Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cel ...
... Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cel ...
chapter 3 study guide
... The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The frontal lobe (primary motor cortex, mirror neurons, prefrontal cortex) ...
... The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The frontal lobe (primary motor cortex, mirror neurons, prefrontal cortex) ...
Understanding Teenagers
... (Peer Pressure) The need to be liked by their peers is paramount!!! Increase in emotional variability (high & low emotions) also can increase adolescents’ vulnerability. ...
... (Peer Pressure) The need to be liked by their peers is paramount!!! Increase in emotional variability (high & low emotions) also can increase adolescents’ vulnerability. ...
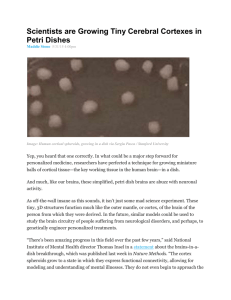
Scientists are Growing Tiny Cerebral Cortexes in Petri
... Yep, you heard that one correctly. In what could be a major step forward for personalized medicine, researchers have perfected a technique for growing miniature balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brain ...
... Yep, you heard that one correctly. In what could be a major step forward for personalized medicine, researchers have perfected a technique for growing miniature balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brain ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.