Past Present Future
... • In relation to the described dynamics of views we witness the shift from the ideas of strict localization of functions to the concepts of dynamic localization and distributed system. However, often this transfer is nothing but declarations. Dynamic localization is again substituted by the reviving ...
... • In relation to the described dynamics of views we witness the shift from the ideas of strict localization of functions to the concepts of dynamic localization and distributed system. However, often this transfer is nothing but declarations. Dynamic localization is again substituted by the reviving ...
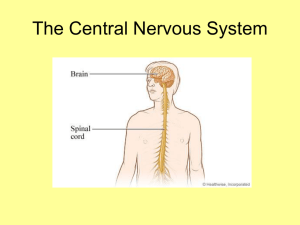
Unit 2: The body and the Brain
... 13. What connects this division? 14. What happens if this connection is disrupted? 15. Defend the argument that supports the concept of brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization). What factors could you identify to oppose the existence of hemispheric specialization? ...
... 13. What connects this division? 14. What happens if this connection is disrupted? 15. Defend the argument that supports the concept of brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization). What factors could you identify to oppose the existence of hemispheric specialization? ...
Methods to Study the Brain
... PET PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... PET PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
Methods to Study the Brain - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... PET PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... PET PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
Cognitive Function
... antioxidant which strengthens memory and stimulates nerve growth. B VITAMINS – Folate, Vitamin B6 and B12 are important in methylation processes. Deficiencies in one of these vitamins can raise homocysteine levels which is linked to increased Alzheimer’s risk. Vitamin B1 protects against mitochondri ...
... antioxidant which strengthens memory and stimulates nerve growth. B VITAMINS – Folate, Vitamin B6 and B12 are important in methylation processes. Deficiencies in one of these vitamins can raise homocysteine levels which is linked to increased Alzheimer’s risk. Vitamin B1 protects against mitochondri ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 3. Your brain is an energy hog. It occupies 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an ...
... 3. Your brain is an energy hog. It occupies 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an ...
Information Processing and Other Models of Human Learning
... Education 173 Cognition and Learning in Educational Settings ...
... Education 173 Cognition and Learning in Educational Settings ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
Ch.02
... several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
... several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
... • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
Possible Solutions from the Cognitive Neuroscience of Emotion
... Most of the past Cognitive Neuroscience researches on emotion focused on the attempt to find specific brain regions implementing discrete basic emotions: “The various classes of emotion are mediated by ...
... Most of the past Cognitive Neuroscience researches on emotion focused on the attempt to find specific brain regions implementing discrete basic emotions: “The various classes of emotion are mediated by ...
MUE 482 Julio Contreras Philosophy of Music Education I strongly
... Also, playing an instrument engages practically every area of the brain, especially the auditory, visual, and motor cortexes. By performing an instrument, students can strengthen those brain functions allowing them to apply that strength to other activities. Music also leads to higher levels of exec ...
... Also, playing an instrument engages practically every area of the brain, especially the auditory, visual, and motor cortexes. By performing an instrument, students can strengthen those brain functions allowing them to apply that strength to other activities. Music also leads to higher levels of exec ...
Barry Jacobs presentation
... computer? Do computers think? Do they have free will, consciousness, and emotion? • Could we build a machine with the same physicochemical components of our brain that would have a mind? Why not? ...
... computer? Do computers think? Do they have free will, consciousness, and emotion? • Could we build a machine with the same physicochemical components of our brain that would have a mind? Why not? ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is dedicated to specific purposes. Frontal lobe: contains areas that ...
... brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is dedicated to specific purposes. Frontal lobe: contains areas that ...
The Brain and Learning Summary Review
... selections quickly explain several major concepts for educational neuroscience that will be found in later chapters. The second part addresses “brain-‐based education.” This concept is focused on the idea ...
... selections quickly explain several major concepts for educational neuroscience that will be found in later chapters. The second part addresses “brain-‐based education.” This concept is focused on the idea ...
What is Neuroscience?
... ie. Brain, spinal cord and all nerves of the body We study it from all aspects – the tiny (eg. DNA/genes)….. ….. to the large (eg. thought, consciousness) ...
... ie. Brain, spinal cord and all nerves of the body We study it from all aspects – the tiny (eg. DNA/genes)….. ….. to the large (eg. thought, consciousness) ...
University of Split Danica Škara, PhD e
... nervous system and is a highly complex organ. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times as large as the brain of a typical mammal. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive functions such as self-control, planning, reas ...
... nervous system and is a highly complex organ. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times as large as the brain of a typical mammal. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive functions such as self-control, planning, reas ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.