Comparative Psychology
... "While one of those who were assisting me touched lightly, and by chance, the point of his scalpel to the internal crural nerves of the frog, suddenly all the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
... "While one of those who were assisting me touched lightly, and by chance, the point of his scalpel to the internal crural nerves of the frog, suddenly all the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
Cognitive and Brain Sciences Minor Checklist
... CD 195. Developmental Disorders in language and reading CD 243 Reading, Dyslexia, and the Brain ED/ML/GER 114. linguistic approaches to second language acquisition ...
... CD 195. Developmental Disorders in language and reading CD 243 Reading, Dyslexia, and the Brain ED/ML/GER 114. linguistic approaches to second language acquisition ...
The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
... Frontal Lobe Frontal lobe has to do with decision making, thinking, personality. Phineas Gage was a railroad working in 1848 that had a spike go through his brain. He could think and had memories, but his personality was total different. ...
... Frontal Lobe Frontal lobe has to do with decision making, thinking, personality. Phineas Gage was a railroad working in 1848 that had a spike go through his brain. He could think and had memories, but his personality was total different. ...
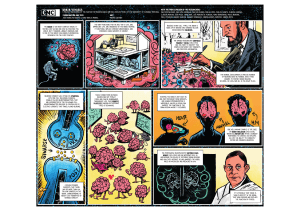
here - CNC
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
Cognitive Neuroscience - U
... – Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) – Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
... – Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) – Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
Chapter 2 – Biology of the Mind
... limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association areas aphasia Broca’s area Wernicke’s area plasticity neurogenesis corpus callosum split brain Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience ...
... limbic system amygdala hypothalamus cerebral glial cells (glia) frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex sensory cortex association areas aphasia Broca’s area Wernicke’s area plasticity neurogenesis corpus callosum split brain Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... The Forebrain › Cerebral Cortex Lobes of the Brain › The Limbic System Structures ...
... The Forebrain › Cerebral Cortex Lobes of the Brain › The Limbic System Structures ...
Chapter 2
... • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language ...
... • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... represented by a dispropor3onally greater number of place cells than non-‐rewarded loca3ons. Spa3al coding was also highly dynamic, for on each day the neural representa3on of this environment involved a uni ...
... represented by a dispropor3onally greater number of place cells than non-‐rewarded loca3ons. Spa3al coding was also highly dynamic, for on each day the neural representa3on of this environment involved a uni ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_01/i_01_cr/i_01_cr_ana/i_01_cr_ana.html ...
... http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_01/i_01_cr/i_01_cr_ana/i_01_cr_ana.html ...
Chapter 3 – early studies of the central nervous system
... The accidental damage to Phineas Gage provided empirical evidence to show that Flouren’s findings with animals apply to humans too. After the accident, Gage became fitful, irreverent, profane, impatient of restraint or advice conflicting with his desires, obstinate, unable to plan or make decisions ...
... The accidental damage to Phineas Gage provided empirical evidence to show that Flouren’s findings with animals apply to humans too. After the accident, Gage became fitful, irreverent, profane, impatient of restraint or advice conflicting with his desires, obstinate, unable to plan or make decisions ...
The Review
... 5. What are the lobes of the brain? What is each lobe responsible for? 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrai ...
... 5. What are the lobes of the brain? What is each lobe responsible for? 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrai ...
brain09.3
... such data and using them to answer the question of how neural coding actually takes place. The analytical method developed by the Hebrew University researchers should be able to provide an indication, for example, of how many neurons encode a given stimulus such as reactions to a face or a movement ...
... such data and using them to answer the question of how neural coding actually takes place. The analytical method developed by the Hebrew University researchers should be able to provide an indication, for example, of how many neurons encode a given stimulus such as reactions to a face or a movement ...
Cognitive
... • Cognitive Science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of mind and its processes. It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works (wiki). • It si complex of study, which have an aim to answer old epistemological question by the empiral way. Mostly answer about nature of cognition ...
... • Cognitive Science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of mind and its processes. It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works (wiki). • It si complex of study, which have an aim to answer old epistemological question by the empiral way. Mostly answer about nature of cognition ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.