Orexin (Hypocretin)-Like Immunoreactivity in the Cat Hypothalamus
... which contained many small, clear, round vesicles with a few large, dense core vesicles, made asymmetrical synaptic contacts with OrA-ir dendrites, indicating that the activity of orexin neurons is under excitatory control. On the other hand, the terminals of OrA-ir neurons also made asymmetrical sy ...
... which contained many small, clear, round vesicles with a few large, dense core vesicles, made asymmetrical synaptic contacts with OrA-ir dendrites, indicating that the activity of orexin neurons is under excitatory control. On the other hand, the terminals of OrA-ir neurons also made asymmetrical sy ...
Discharge Rate of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata Neurons Is
... et al. 1978) and dyskinesia induced by dopaminergic hyperactivity in otherwise drug naive (normal) animals (Jenner 2000; Mones 1972; Pearce 1999). Although single-neuron electro-physiological recordings have been conducted in rodent models of dyskinesia without striatal dopamine depletion (Ruskin et ...
... et al. 1978) and dyskinesia induced by dopaminergic hyperactivity in otherwise drug naive (normal) animals (Jenner 2000; Mones 1972; Pearce 1999). Although single-neuron electro-physiological recordings have been conducted in rodent models of dyskinesia without striatal dopamine depletion (Ruskin et ...
Chapter 8: The Nervous System
... ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released into the synapse between adjacent neurons. These chemicals diffuse across the synapse and in ...
... ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released into the synapse between adjacent neurons. These chemicals diffuse across the synapse and in ...
Chapter 8: The Nervous System
... ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released into the synapse between adjacent neurons. These chemicals diffuse across the synapse and in ...
... ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released into the synapse between adjacent neurons. These chemicals diffuse across the synapse and in ...
Direction of action is represented in the ventral premotor cortex
... To generate a goal-directed movement, the brain must translate the location of a target, specified in an external coordinate frame, into a set of muscle activation patterns, specified in an intrinsic coordinate frame. Insight into the sensorimotor transformations involved in this process1,2 and how ...
... To generate a goal-directed movement, the brain must translate the location of a target, specified in an external coordinate frame, into a set of muscle activation patterns, specified in an intrinsic coordinate frame. Insight into the sensorimotor transformations involved in this process1,2 and how ...
Septins promote dendrite and axon development by negatively
... & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved. ...
... & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved. ...
Cerebral correlates of delta waves during non
... the thalamus. The discrepancy suggests that wakefulness data might indeed have played an important confounding effect in the identification of the cerebral correlates of delta waves. The present analysis shows, in non-sleep-deprived normal young adults, that rCBF in a set of brain areas is negativel ...
... the thalamus. The discrepancy suggests that wakefulness data might indeed have played an important confounding effect in the identification of the cerebral correlates of delta waves. The present analysis shows, in non-sleep-deprived normal young adults, that rCBF in a set of brain areas is negativel ...
Central mechanisms of osmosensation and systemic osmoregulation
... 15 minutes56. Osmoreceptors in these areas can therefore detect the osmotic strength of ingested materials and, through afferent connections to the CNS (FIG. 3), induce anticipatory responses that might buffer the potential impact of ingestion-related osmotic perturbations61. Indeed, water intake ca ...
... 15 minutes56. Osmoreceptors in these areas can therefore detect the osmotic strength of ingested materials and, through afferent connections to the CNS (FIG. 3), induce anticipatory responses that might buffer the potential impact of ingestion-related osmotic perturbations61. Indeed, water intake ca ...
Comparative analysis of the baseline spike activity of
... Comparison of measures of the baseline spike activity of fastigial nucleus neurons after exposure to vibration for 5 and 15 days showed that there were significant differences for the distribution of neurons in terms of interspike interval histogram modality and the distribution among mean discharge ...
... Comparison of measures of the baseline spike activity of fastigial nucleus neurons after exposure to vibration for 5 and 15 days showed that there were significant differences for the distribution of neurons in terms of interspike interval histogram modality and the distribution among mean discharge ...
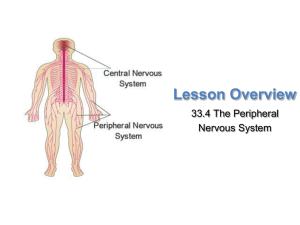
Autonomic Nervous System
... brain or spinal cord. Cranial nerves go through openings in the skull and stimulate regions of the head and neck. Spinal nerves stimulate the rest of the body. The cell bodies of cranial and spinal nerves are ...
... brain or spinal cord. Cranial nerves go through openings in the skull and stimulate regions of the head and neck. Spinal nerves stimulate the rest of the body. The cell bodies of cranial and spinal nerves are ...
Section 1: Anatomy of the sensorimotor system
... There is currently controversy over exactly how many cortical motor areas exist. This is further confounded by disagreement over what criteria should be used to define a motor area. Proposed criteria include requirements that a motor area has projections to spinal motor neurons and a full representa ...
... There is currently controversy over exactly how many cortical motor areas exist. This is further confounded by disagreement over what criteria should be used to define a motor area. Proposed criteria include requirements that a motor area has projections to spinal motor neurons and a full representa ...
Methods of Studying The Nervous System - U
... photographic plate; any part of the object that absorbs X-rays differently than does the surrounding medium will be distinguishable ...
... photographic plate; any part of the object that absorbs X-rays differently than does the surrounding medium will be distinguishable ...
The History of the EEG
... • Fast Fourier Transform seperates spontaneous EEG signal to component frequencies and amplitudes • Restriction: high frequency resolution demands long (in the range of seconds) analysis windows ...
... • Fast Fourier Transform seperates spontaneous EEG signal to component frequencies and amplitudes • Restriction: high frequency resolution demands long (in the range of seconds) analysis windows ...
Ciccarelli 2: The Biological Perspective
... (thousandths of a second). At first the cell is resting; it then reaches threshold and an action potential is triggered. After a brief hyperpolarization period, the cell returns to its resting potential. ...
... (thousandths of a second). At first the cell is resting; it then reaches threshold and an action potential is triggered. After a brief hyperpolarization period, the cell returns to its resting potential. ...
Heterogeneity of the Population of Command Neurons in the Lamprey
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
kbook or W NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
... Can we use what we know to control someone else’s brain? How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcrani ...
... Can we use what we know to control someone else’s brain? How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcrani ...
Nitric Oxide Synthase Protein and mRNA Are
... of NOS in rat brain is species specific or might be generalized, we have mapped NOS immunoreactivity throughout monkey brain. In all regions examined, the cell and fiber groups stained are the same as in rat (data not shown). In certain areas of monkey brain we havecompared NOS and NADPH diaphorase ...
... of NOS in rat brain is species specific or might be generalized, we have mapped NOS immunoreactivity throughout monkey brain. In all regions examined, the cell and fiber groups stained are the same as in rat (data not shown). In certain areas of monkey brain we havecompared NOS and NADPH diaphorase ...
Low Quality
... oxygen-carrying substance, called heme, in red blood cells. Genes for molecules that help remodel neural connections are also revved up in sleep. Studies in mice, rats, fruit flies and white-crowned sparrows have found similar patterns of gene activity, Pack and colleagues noted in a review in the F ...
... oxygen-carrying substance, called heme, in red blood cells. Genes for molecules that help remodel neural connections are also revved up in sleep. Studies in mice, rats, fruit flies and white-crowned sparrows have found similar patterns of gene activity, Pack and colleagues noted in a review in the F ...
Descartes` Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain
... recent investigations of his modern counterparts and review perti nent findings from neuropsychological research in humans and animals. Further, I propose that human reason depends on several brain systems, working in concert across many levels of neuronal organization, rather than on a single brai ...
... recent investigations of his modern counterparts and review perti nent findings from neuropsychological research in humans and animals. Further, I propose that human reason depends on several brain systems, working in concert across many levels of neuronal organization, rather than on a single brai ...
slides
... disorders caused by dmg to the brain early on • spinal cord injury – fractures or displacements of the vertebrae can result in injury to the spinal cord ...
... disorders caused by dmg to the brain early on • spinal cord injury – fractures or displacements of the vertebrae can result in injury to the spinal cord ...
Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Inputs to `AIP`
... the extensive interconnections between AIP and PMv, we sought to examine whether these two cortical areas received inputs from common sources. PMv is the target of output from both the dentate and the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi) (Hoover and Strick, 1993; Dum and Strick, 2002). Whil ...
... the extensive interconnections between AIP and PMv, we sought to examine whether these two cortical areas received inputs from common sources. PMv is the target of output from both the dentate and the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi) (Hoover and Strick, 1993; Dum and Strick, 2002). Whil ...
Optogenetic Brain Interfaces
... The work of R. Pashaie was supported in part by the University of Wisconsin research growth initiative; grants 101X172, 101X213, and 101X254. The work of P. Anikeeva was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF, MRSEC DMR-0819762, and NSF CAREER CBET-1253890) and by the Defense Advanced Res ...
... The work of R. Pashaie was supported in part by the University of Wisconsin research growth initiative; grants 101X172, 101X213, and 101X254. The work of P. Anikeeva was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF, MRSEC DMR-0819762, and NSF CAREER CBET-1253890) and by the Defense Advanced Res ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Neurons have one behavior property in common with muscles: Irritability – the ability to respond to a stimulus. • However, neurons have an aspect of irritability that muscles DO NOT have: converting stimuli into nerve impulses. • Nerve impulse = a tiny electrical charge that transmits information ...
... • Neurons have one behavior property in common with muscles: Irritability – the ability to respond to a stimulus. • However, neurons have an aspect of irritability that muscles DO NOT have: converting stimuli into nerve impulses. • Nerve impulse = a tiny electrical charge that transmits information ...
Spontaneous Spike Activity of Spinoreticular Tract Neurons During
... Abstract: Sleep mentation studies infer that pain sensation in humans may be reduced during active REM sleep. However, to provide a mechanistic explanation for this phenomenon, few, if any neurophysiological studies have been performed at the lumbar level from neurons comprising classical pain pathw ...
... Abstract: Sleep mentation studies infer that pain sensation in humans may be reduced during active REM sleep. However, to provide a mechanistic explanation for this phenomenon, few, if any neurophysiological studies have been performed at the lumbar level from neurons comprising classical pain pathw ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.