Neurodegenerative Changes in the Motor Cortex and Cerebellum in Wistar... Following Acute Pneumococcal Meningitis
... cortex and cerebellar tissue were selected for study. Tissue pieces were dehydrated in the ascending grades of ethyl alcohol and then cleared with Xylene. The tissue was further embedded in paraffin wax. Coronal sections of motor cortex and sagittal sections of cerebellum were taken at 5µm thickness ...
... cortex and cerebellar tissue were selected for study. Tissue pieces were dehydrated in the ascending grades of ethyl alcohol and then cleared with Xylene. The tissue was further embedded in paraffin wax. Coronal sections of motor cortex and sagittal sections of cerebellum were taken at 5µm thickness ...
cortical input to the basal forebrain
... respond to a range of visual and auditory stimuli that have been reinforced. It has been proposed68 that cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain receive information on the expected availability of reinforcement through afferent inputs from the orbitofrontal cortex. Through their widespread cortic ...
... respond to a range of visual and auditory stimuli that have been reinforced. It has been proposed68 that cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain receive information on the expected availability of reinforcement through afferent inputs from the orbitofrontal cortex. Through their widespread cortic ...
The Effect of Ischemia on Biogenic Amine Concentrations in
... some physical or biochemical phenomenon must be responsible for the dysfunction. Because biogenic amines are both neurotransmitters and have potent vasoactive properties, for many years there has been considerable speculation about their influences on the development of injury to the CNS. 1 Many exp ...
... some physical or biochemical phenomenon must be responsible for the dysfunction. Because biogenic amines are both neurotransmitters and have potent vasoactive properties, for many years there has been considerable speculation about their influences on the development of injury to the CNS. 1 Many exp ...
31 Relating the Activity of Sensory Neurons to Perception
... Psychophysical experiments can be carefully designed to minimize the ambiguity inherent in perceptual reports, often in ways that can be generalized from human subjects to nonhuman subjects. Rather than asking a subject how fast something went, for example, one could probe their ability to judge spe ...
... Psychophysical experiments can be carefully designed to minimize the ambiguity inherent in perceptual reports, often in ways that can be generalized from human subjects to nonhuman subjects. Rather than asking a subject how fast something went, for example, one could probe their ability to judge spe ...
Volitional enhancement of firing synchrony and oscillation by
... small timescales such as the bin (2–4 ms) used for the operant conditioning in our study (Sakurai and Takahashi, 2013), whereas in the motor cortex synchrony could be best functional at longer timescales such as that of low gamma oscillations. This assumption is apparently supported by the result of ...
... small timescales such as the bin (2–4 ms) used for the operant conditioning in our study (Sakurai and Takahashi, 2013), whereas in the motor cortex synchrony could be best functional at longer timescales such as that of low gamma oscillations. This assumption is apparently supported by the result of ...
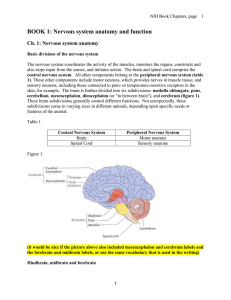
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... One type of monitoring approach is to use a microelectrode -- a small, microscopic probe typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The ...
... One type of monitoring approach is to use a microelectrode -- a small, microscopic probe typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The ...
PDF+Links
... brain. However, there is in fact no substantial evidence that neuronal loss appears on a large scale as a universal effect throughout the whole brain. It is estimated that, in the cortex, very few neurons become lost with age (Cragg 1975; Pakkenberg & Gundensen, 1997; Peters et al., 1998), and that ...
... brain. However, there is in fact no substantial evidence that neuronal loss appears on a large scale as a universal effect throughout the whole brain. It is estimated that, in the cortex, very few neurons become lost with age (Cragg 1975; Pakkenberg & Gundensen, 1997; Peters et al., 1998), and that ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
the distribution of the cells of origin of callosal projections in cat
... and Jones, 1971; Tusa and Palmer, 1980). This is unfortunate since, in behavioral experiments, Berlucchi et al. (1979) showed that the callosal connections of the cat’s suprasylvian cortex (including the lateral suprasylvian visual areas and area 21) make a significant contribution to the interhemis ...
... and Jones, 1971; Tusa and Palmer, 1980). This is unfortunate since, in behavioral experiments, Berlucchi et al. (1979) showed that the callosal connections of the cat’s suprasylvian cortex (including the lateral suprasylvian visual areas and area 21) make a significant contribution to the interhemis ...
Reward-Dependent Spatial Selectivity of Anticipatory Activity in
... The monkeys were trained to perform the memory-guided saccade task in two different reward conditions: all-directions-rewarded (ADR) condition and one-direction-rewarded (1DR) condition (Kawagoe et al. 1998) (Fig. 1). A task trial started with the onset of a central fixation point on which the monke ...
... The monkeys were trained to perform the memory-guided saccade task in two different reward conditions: all-directions-rewarded (ADR) condition and one-direction-rewarded (1DR) condition (Kawagoe et al. 1998) (Fig. 1). A task trial started with the onset of a central fixation point on which the monke ...
On the Role of the Pontine Brainstem in Vocal Pattern Generation: A
... positioned on the left side were mirrored to the right for better overview. Highlighted squares indicate the ventrolateral brainstem hoc tests with Bonferroni’s were conducted to shown enlarged in Figures 3, 6, and 9. AS, aquaeductus sylvii; BC, brachium conjunctivum; BP brachium pontis; Cb, cerebel ...
... positioned on the left side were mirrored to the right for better overview. Highlighted squares indicate the ventrolateral brainstem hoc tests with Bonferroni’s were conducted to shown enlarged in Figures 3, 6, and 9. AS, aquaeductus sylvii; BC, brachium conjunctivum; BP brachium pontis; Cb, cerebel ...
Conscious Modulation in Normal Sleep
... is quite different, more linear and fragmented, like an obsessive way of thinking. An interesting study shows us that some of this activity could be explained by the concept of modular cortex. They are anatomical and functional patches of active and inactive zones of brain cortex, when in slow wave ...
... is quite different, more linear and fragmented, like an obsessive way of thinking. An interesting study shows us that some of this activity could be explained by the concept of modular cortex. They are anatomical and functional patches of active and inactive zones of brain cortex, when in slow wave ...
Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... 3-7 kg) were used as subjects in this study. Seven animals were anesthetized with halothane, intubated, and artificially ventilated, 3 animals served as unoperated controls. To facilitate brain relaxation and minimize retraction pressure, mannitol(20%) was infused systemically over 30 min (2 gm/kg, ...
... 3-7 kg) were used as subjects in this study. Seven animals were anesthetized with halothane, intubated, and artificially ventilated, 3 animals served as unoperated controls. To facilitate brain relaxation and minimize retraction pressure, mannitol(20%) was infused systemically over 30 min (2 gm/kg, ...
Ultrastructural Characterization of Gerbil Olivocochlear Neurons
... also agree with the ones described in the gerbil LSO for LOC neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or ...
... also agree with the ones described in the gerbil LSO for LOC neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or ...
The Nervous System
... Fill in the blanks with: reflexes, saltatory conduction, neurotransmitter, or action potential. 1. A(n) _______________ is an all or none response. 2. _______________ occurs only in myelinated axons. 3. _______________ are rapid, involuntary responses. 4. The axon terminal has tiny vesicles filled w ...
... Fill in the blanks with: reflexes, saltatory conduction, neurotransmitter, or action potential. 1. A(n) _______________ is an all or none response. 2. _______________ occurs only in myelinated axons. 3. _______________ are rapid, involuntary responses. 4. The axon terminal has tiny vesicles filled w ...
The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders
... interneurons. Striatal interneurons can be subdivided by histochemical or immunohistochemical identification of which neurotransmitter or neuropeptide is contained within them. The best characterized subpopulations of striatal interneurons are cholinergic interneurons 11 and another group that conta ...
... interneurons. Striatal interneurons can be subdivided by histochemical or immunohistochemical identification of which neurotransmitter or neuropeptide is contained within them. The best characterized subpopulations of striatal interneurons are cholinergic interneurons 11 and another group that conta ...
multiple reward signals in the brain
... Figure 3 | Neuronal activity in primate striatum and orbitofrontal cortex related to the expectation of reward. a | Activity in a putamen neuron during a delayed go–no go task in which an initial cue instructs the monkey to produce or withhold a reaching movement following a trigger stimulus. The in ...
... Figure 3 | Neuronal activity in primate striatum and orbitofrontal cortex related to the expectation of reward. a | Activity in a putamen neuron during a delayed go–no go task in which an initial cue instructs the monkey to produce or withhold a reaching movement following a trigger stimulus. The in ...
Hindbrain noradrenergic A2 neurons: diverse roles in autonomic
... medullary, pontine, diencephalic, and telencephalic brain regions that underlie these diverse processes. Direct projections from the cortex, limbic forebrain, and hypothalamus to the region of the A2 cell group provide a route through which emotional and cognitive events can modulate visceral respon ...
... medullary, pontine, diencephalic, and telencephalic brain regions that underlie these diverse processes. Direct projections from the cortex, limbic forebrain, and hypothalamus to the region of the A2 cell group provide a route through which emotional and cognitive events can modulate visceral respon ...
Maruska & Tricas 2011
... Cell size was determined from digital images of somata photographed at 400× and cell profile area was calculated with Sigma Scan Pro 5.0 (SPSS, Inc.). For each fish, 5–10 GnRH2 and GnRH3 cells were measured. Fewer than 10 cells were measured only when b10 cells were present, which only occurred in the ...
... Cell size was determined from digital images of somata photographed at 400× and cell profile area was calculated with Sigma Scan Pro 5.0 (SPSS, Inc.). For each fish, 5–10 GnRH2 and GnRH3 cells were measured. Fewer than 10 cells were measured only when b10 cells were present, which only occurred in the ...
Vesicular glutamate transporter 3
... for cholera toxin B subunit (CTb) as primary antibodies (Table 1). All antibodies have been characterized previously. Anti-serotonin serum was developed in rabbit using serotonin creatinine sulfate complex conjugated to bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the immunogen. The antibody stains serotonin-conta ...
... for cholera toxin B subunit (CTb) as primary antibodies (Table 1). All antibodies have been characterized previously. Anti-serotonin serum was developed in rabbit using serotonin creatinine sulfate complex conjugated to bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the immunogen. The antibody stains serotonin-conta ...
The habenular nuclei - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... The LHb establishes descending connectivity with numerous monoaminergic nuclei in the mid- and hindbrain. A major projection, especially from the medial LHb, innervates the median and dorsal raphe; LHb activity inhibits the raphe (Wang & Aghajanian 1977), probably as a result of activation of GABAer ...
... The LHb establishes descending connectivity with numerous monoaminergic nuclei in the mid- and hindbrain. A major projection, especially from the medial LHb, innervates the median and dorsal raphe; LHb activity inhibits the raphe (Wang & Aghajanian 1977), probably as a result of activation of GABAer ...
The Retrotrapezoid Nucleus and Central Chemoreception
... RTN neurons have numerous structural and physiological characteristics that are consistent with a central chemoreceptor role. RTN neurons are located at the VMS, their sensitivity to pH is high and independent of the activity of the rest of the respiratory network. RTN neurons release an excitatory ...
... RTN neurons have numerous structural and physiological characteristics that are consistent with a central chemoreceptor role. RTN neurons are located at the VMS, their sensitivity to pH is high and independent of the activity of the rest of the respiratory network. RTN neurons release an excitatory ...
Neuronal Regulation Implements Efficient Synaptic Pruning
... a near optimal strategy, maximizing memory capacity in the sparse connectivity levels observed in the brain. A fundamental requirement of central nervous system development is that the system should continuously function, while undergoing major structural and functional developmental changes. It has ...
... a near optimal strategy, maximizing memory capacity in the sparse connectivity levels observed in the brain. A fundamental requirement of central nervous system development is that the system should continuously function, while undergoing major structural and functional developmental changes. It has ...
Cortical projections to the nucleus of the optic tract and dorsal
... of the world on the retina to compensate for self-motion and movement of the visual world. There is accumulating evidence that the neuronal basis for these eye movements is distributed over visual cortical areas in addition to distinct pretectal and brainstem nuclei from where the visual information ...
... of the world on the retina to compensate for self-motion and movement of the visual world. There is accumulating evidence that the neuronal basis for these eye movements is distributed over visual cortical areas in addition to distinct pretectal and brainstem nuclei from where the visual information ...
Vasopressin Receptors of the Vasopressor (V,)
... In order to determinethe type of receptor which mediatesthe effects of vasopressinin the nucleus of the solitary tract, the efficiency of this peptide in evoking a neuronal excitation was comparedwith that of oxytocin and of various synthetic structural analogshaving selective oxytocic, vasopressor, ...
... In order to determinethe type of receptor which mediatesthe effects of vasopressinin the nucleus of the solitary tract, the efficiency of this peptide in evoking a neuronal excitation was comparedwith that of oxytocin and of various synthetic structural analogshaving selective oxytocic, vasopressor, ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.