Which of the following is a vector quantity?
... electrical power, such as a battery or electrical outlet. B. The energy comes from the heat being absorbed by the coil as it turns. C. The energy comes from an external agent, which is doing mechanical work on the coil. D. The energy comes from chemical reactions within the coil. E. The energy comes ...
... electrical power, such as a battery or electrical outlet. B. The energy comes from the heat being absorbed by the coil as it turns. C. The energy comes from an external agent, which is doing mechanical work on the coil. D. The energy comes from chemical reactions within the coil. E. The energy comes ...
The Physics of MRI Scans
... Most of the human body is made up of water molecules, which consist of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The MRI machine does not see the oxygen molecule, only the Hydrogens. At the center of each hydrogen atom, there is an even smaller particle called a proton. Protons are like tiny magnets and are very s ...
... Most of the human body is made up of water molecules, which consist of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The MRI machine does not see the oxygen molecule, only the Hydrogens. At the center of each hydrogen atom, there is an even smaller particle called a proton. Protons are like tiny magnets and are very s ...
Electromagnetism ()
... Magnetomotive Force, U (Ampere-turn) Magnetic Field Strength, H (Ampere/meter) Magnetic constant, μο (Henry/meter) (or magnetic permeability) ...
... Magnetomotive Force, U (Ampere-turn) Magnetic Field Strength, H (Ampere/meter) Magnetic constant, μο (Henry/meter) (or magnetic permeability) ...
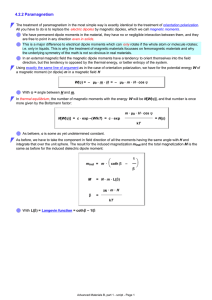
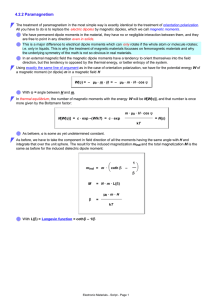
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
Faraday Disk
... heating of a platinum wire by the electric current from a voltaic pile. He had planned to demonstrate both the heating of the wire and to also to carry out some general demonstrations of magnetism, for which he had provided a compass needle mounted on a wooden stand. While performing the wire heatin ...
... heating of a platinum wire by the electric current from a voltaic pile. He had planned to demonstrate both the heating of the wire and to also to carry out some general demonstrations of magnetism, for which he had provided a compass needle mounted on a wooden stand. While performing the wire heatin ...
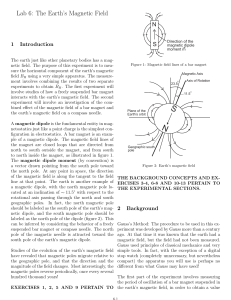
Understanding electric and magnetic fields
... Electric fields are created by voltage (the flow of power). Magnetic fields (the force of power being discharged while electricity is moved) are created by alternating current. To illustrate, an electric field will be present around a lamp that is plugged in but not turned on. A magnetic field will ...
... Electric fields are created by voltage (the flow of power). Magnetic fields (the force of power being discharged while electricity is moved) are created by alternating current. To illustrate, an electric field will be present around a lamp that is plugged in but not turned on. A magnetic field will ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.