Synchrotron - The Bored of Studies Community
... Another early large synchrotron is the Cosmotron built at Brookhaven National Laboratory which reached 3.3 GeV in 1953. Currently, the highest energy synchrotron in the world is the Tevatron, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, in the United States. It accelerates protons and antiprotons t ...
... Another early large synchrotron is the Cosmotron built at Brookhaven National Laboratory which reached 3.3 GeV in 1953. Currently, the highest energy synchrotron in the world is the Tevatron, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, in the United States. It accelerates protons and antiprotons t ...
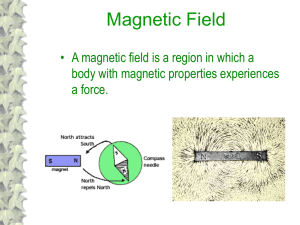
magnetic-properties
... induction of the magnetic material. This effect of retardation by material is called hysteresis. The magnetic field strength needed to bring the induced magnetization to zero is termed as coercivity, Hc. This must be applied anti-parallel to the original field. A further increase in the field in ...
... induction of the magnetic material. This effect of retardation by material is called hysteresis. The magnetic field strength needed to bring the induced magnetization to zero is termed as coercivity, Hc. This must be applied anti-parallel to the original field. A further increase in the field in ...
Susceptibility of Paramagnetic sample by using Quinck`s tube method
... and rinse it well with distilled water before starting and dry it with compressed air. Make several sets of measurements to ensure consistency; false readings can arise from liquid running down the tube or sticking to the sides. Carefully swab down the inside of the U- tube with a cotton bud, to ens ...
... and rinse it well with distilled water before starting and dry it with compressed air. Make several sets of measurements to ensure consistency; false readings can arise from liquid running down the tube or sticking to the sides. Carefully swab down the inside of the U- tube with a cotton bud, to ens ...
Maxwell`s equation
... “Ampere’s original law allows the calculation of the magnetic field B produced at a point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term ...
... “Ampere’s original law allows the calculation of the magnetic field B produced at a point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term ...
Magnetic field probe.indd
... You may see a small reading from the probe even when it is not next to a magnetic field. This is due both to local conditions and variations between data loggers. It is quite usual and can normally be ignored where trends of change and field strength are generally more important than accuracy. Some so ...
... You may see a small reading from the probe even when it is not next to a magnetic field. This is due both to local conditions and variations between data loggers. It is quite usual and can normally be ignored where trends of change and field strength are generally more important than accuracy. Some so ...
Downloand the Electromagnetism lesson
... contain a constant flow of electric charge. A magnetic field is generated anytime an electrical current flows through a conductor. Electromagnets are objects that produce a magnetic field only when an electric current passes through them. Electromagnets may be turned on or off, and made stronger by ...
... contain a constant flow of electric charge. A magnetic field is generated anytime an electrical current flows through a conductor. Electromagnets are objects that produce a magnetic field only when an electric current passes through them. Electromagnets may be turned on or off, and made stronger by ...
MAGNETISM and its practical applications - ardent
... The total amount of electromagnetic energy cannot change! Eddy currents (also called Foucault currents) are electric currents induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field in the conductor. Eddy currents will be generated wherever a conducting object experiences a change in the intensity or ...
... The total amount of electromagnetic energy cannot change! Eddy currents (also called Foucault currents) are electric currents induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field in the conductor. Eddy currents will be generated wherever a conducting object experiences a change in the intensity or ...
Magnetism - PearsonGreatPath
... will cancel each other out. 5) But, IF there is a strong magnetic field nearby when the metal is cooling, these domains will all align to the magnetic field creating a permanent magnet. ...
... will cancel each other out. 5) But, IF there is a strong magnetic field nearby when the metal is cooling, these domains will all align to the magnetic field creating a permanent magnet. ...
Steady electric currents. Magnetism. Generation of heat. Biot
... Using the elementary form (3) of Ohm’s law, we have shown that the energy generation per unit time in a conductor of resistance R through which flows a current I is W = RI 2 . ...
... Using the elementary form (3) of Ohm’s law, we have shown that the energy generation per unit time in a conductor of resistance R through which flows a current I is W = RI 2 . ...
CHAPTER 20 Induced Voltages and Inductance
... - Notice the B-field extends all the way around the inside of the iron. - A current in the secondary coil wire develops only momentarily when the switch is closed (indicated by the Galvanometer) and then returns to zero. - A current in the secondary coil also develops (in the opposite direction) mo ...
... - Notice the B-field extends all the way around the inside of the iron. - A current in the secondary coil wire develops only momentarily when the switch is closed (indicated by the Galvanometer) and then returns to zero. - A current in the secondary coil also develops (in the opposite direction) mo ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.