Quoting Glen Rein Ph
... zero (Seiki, 1990). It has been proposed that bucking of the EM fields in the mobius confirguation causes curvature of local space/time thereby acting as a gateway for bringing a higher dimensional energy into our 3D world(Johnson, 1992). The term non-Hertzian will be used here to refer to this nove ...
... zero (Seiki, 1990). It has been proposed that bucking of the EM fields in the mobius confirguation causes curvature of local space/time thereby acting as a gateway for bringing a higher dimensional energy into our 3D world(Johnson, 1992). The term non-Hertzian will be used here to refer to this nove ...
Magic of Magnets Teacher Plans - Spartanburg School District 2
... of the program. At the completion of the program, there is a short quiz. The narrator will read the questions which are displayed on the screen. Students can use Blackline Master 2 to record their answers. Answers to the questions are provided in the Answer Key section of this instructor's guide. • ...
... of the program. At the completion of the program, there is a short quiz. The narrator will read the questions which are displayed on the screen. Students can use Blackline Master 2 to record their answers. Answers to the questions are provided in the Answer Key section of this instructor's guide. • ...
Motors, Controllers, and Regenerative Braking
... Read hall effect sensors, determine location Get desired speed from user Set the next phase to occur to match that speed Extra tasks Limit acceleration Monitor temperature Regenerative Braking ...
... Read hall effect sensors, determine location Get desired speed from user Set the next phase to occur to match that speed Extra tasks Limit acceleration Monitor temperature Regenerative Braking ...
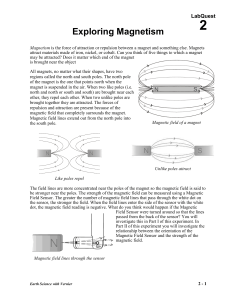
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... 4. Zero the Magnetic Field Sensor. This reduces the effect of the surrounding environment on the magnetic field reading. a. Move all magnets far away from the Magnetic Field Sensor. b. When the readings on the screen stabilize, choose Zero from the Sensors menu. When the process is complete, the rea ...
... 4. Zero the Magnetic Field Sensor. This reduces the effect of the surrounding environment on the magnetic field reading. a. Move all magnets far away from the Magnetic Field Sensor. b. When the readings on the screen stabilize, choose Zero from the Sensors menu. When the process is complete, the rea ...
magnetism - Earth and Environmental Sciences
... Immediately upon closing the switch, Faraday noticed a brief flicker of current in the secondary coil, but none thereafter. As the magnetic field was being established in the iron ring (i.e., when the field lines were moving), a current was induced in the secondary coil. However, once the magnetic f ...
... Immediately upon closing the switch, Faraday noticed a brief flicker of current in the secondary coil, but none thereafter. As the magnetic field was being established in the iron ring (i.e., when the field lines were moving), a current was induced in the secondary coil. However, once the magnetic f ...
presentation source
... - OR the or the amount of magnetic field lines surrounded by the wire has to change • Direction of the current given by Lenz’s law: The induced current always produces a magnetic field to oppose the change! ...
... - OR the or the amount of magnetic field lines surrounded by the wire has to change • Direction of the current given by Lenz’s law: The induced current always produces a magnetic field to oppose the change! ...
Draft - NYU Steinhardt
... Electric current flows only when it can follow a closed path called a closed circuit. The circuit in the picture has three parts. First, the battery pushes electrons through the path. Second, the bulb lights up when current passes through it. Third, a wire connects the battery to the bulb. A wire al ...
... Electric current flows only when it can follow a closed path called a closed circuit. The circuit in the picture has three parts. First, the battery pushes electrons through the path. Second, the bulb lights up when current passes through it. Third, a wire connects the battery to the bulb. A wire al ...
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
... Like poles of magnets repel each other while unlike poles of magnets attract each other. Similar to other effects; electric current also produces magnetic effect. The magnetic effect of electric current is known as electromagnetic effect. It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current ...
... Like poles of magnets repel each other while unlike poles of magnets attract each other. Similar to other effects; electric current also produces magnetic effect. The magnetic effect of electric current is known as electromagnetic effect. It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current ...
Course Title
... Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and activities Final Exam ...
... Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and activities Final Exam ...
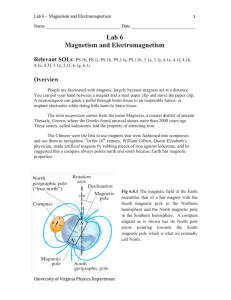
Lab 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Galileo
... poles obey the inverse-square law, and his results were confirmed by Charles Coulomb. The subjects of magnetism and electricity developed almost independently of each other until 1820, when a Danish physicist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered, in a classroom demonstration, that an electric cur ...
... poles obey the inverse-square law, and his results were confirmed by Charles Coulomb. The subjects of magnetism and electricity developed almost independently of each other until 1820, when a Danish physicist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered, in a classroom demonstration, that an electric cur ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.