Today: Oscilloscope and Faraday’s Law
... Using an Oscilloscope • You can measure the amplitude of a signal as well as the period and frequency. ...
... Using an Oscilloscope • You can measure the amplitude of a signal as well as the period and frequency. ...
SurveyMotors
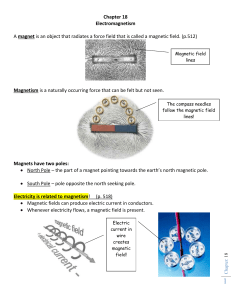
... In the early 1800’s, Michael Faraday notes that iron filings line up around a magnet to show “force field lines”. ...
... In the early 1800’s, Michael Faraday notes that iron filings line up around a magnet to show “force field lines”. ...
forcibly push - Cloudfront.net
... p436 1820 Hans Oersted showed that current affected a magnet. 1831 Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry made electricity from magnets. Made it possible to light up cities at night and ruined the sleep habits of the new era. It was simple…just rotate (move) a loop of wire in a magnetic field and electric ...
... p436 1820 Hans Oersted showed that current affected a magnet. 1831 Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry made electricity from magnets. Made it possible to light up cities at night and ruined the sleep habits of the new era. It was simple…just rotate (move) a loop of wire in a magnetic field and electric ...
Power Plants
... • You flip the switch, and the light comes on, . . . • But where does the power come from? • How does the power get into those power lines that bring it to your home? ...
... • You flip the switch, and the light comes on, . . . • But where does the power come from? • How does the power get into those power lines that bring it to your home? ...
File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
... Electric circuit - a continuous flow of electrical charges caused by the motion of electrons, expressed in amps Magnetic field - the area around a magnet in which magnetic forces act Magnetic force - the repelling or attraction of a magnetic Static electricity an object ...
... Electric circuit - a continuous flow of electrical charges caused by the motion of electrons, expressed in amps Magnetic field - the area around a magnet in which magnetic forces act Magnetic force - the repelling or attraction of a magnetic Static electricity an object ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... 17. When (resistance, current) is passed through a coil of wire with a piece of iron inside, an electromagnet is formed. 18. An electromagnet is a (permanent, temporary) magnet. 19. Adding more loops of wire to the coil (increases, decreases) the strength of an electromagnet. 20. More current flowin ...
... 17. When (resistance, current) is passed through a coil of wire with a piece of iron inside, an electromagnet is formed. 18. An electromagnet is a (permanent, temporary) magnet. 19. Adding more loops of wire to the coil (increases, decreases) the strength of an electromagnet. 20. More current flowin ...
UNIT 2 THE BODY
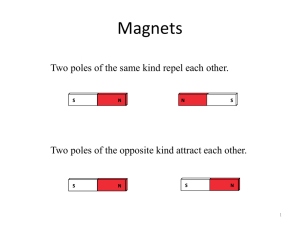
... MAGNETS HAVE TO POLES: NORTH AND SOUTH Opposite poles attract. Same poles repel LIKEWISE ELECTRICAL CHARGES ...
... MAGNETS HAVE TO POLES: NORTH AND SOUTH Opposite poles attract. Same poles repel LIKEWISE ELECTRICAL CHARGES ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.