Magnetism - Howard Elementary School
... repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic poles are north or south. One main difference is that magnetic poles cannot be iso ...
... repel and opposites attract, and the force between is inversely proportional to the distance between them. This means that closer is stronger, and further is weaker. Electric charges are positive or negative, magnetic poles are north or south. One main difference is that magnetic poles cannot be iso ...
Notes-1: Magnetic Fields
... especially if its ________________ is much greater than its _____________. However the magnetic field inside the solenoid is ________________ and _________________________. ...
... especially if its ________________ is much greater than its _____________. However the magnetic field inside the solenoid is ________________ and _________________________. ...
the step-by-step instructions
... copper or nickel. Twenty-pence coins are made of an alloy of copper and nickel, and will not work in this activity. ...
... copper or nickel. Twenty-pence coins are made of an alloy of copper and nickel, and will not work in this activity. ...
Energy and Electromagnetism Name: Investigation 3: The Force of
... Other things to know for written responses: 1. Be prepared to explain how to create and electromagnet. Tell what supplies you need and how to put them together. 2. Be prepared to explain why a magnet can form a chain and can pick up a series of iron/steel objects. This is induced magnetism. Key thin ...
... Other things to know for written responses: 1. Be prepared to explain how to create and electromagnet. Tell what supplies you need and how to put them together. 2. Be prepared to explain why a magnet can form a chain and can pick up a series of iron/steel objects. This is induced magnetism. Key thin ...
Magnets - mrzimmerman.org
... • The ancient Greeks knew that the lodestone or magnetite attracted iron towards it. It is known that the Vikings used a lodestone to navigate. Later at the end of the twelfth century Europeans were using this simple compass to aid navigation. ...
... • The ancient Greeks knew that the lodestone or magnetite attracted iron towards it. It is known that the Vikings used a lodestone to navigate. Later at the end of the twelfth century Europeans were using this simple compass to aid navigation. ...
Jeopardy - Pleasant Valley School District
... A device that changes motion into electrical energy ...
... A device that changes motion into electrical energy ...
File
... where it has enough power to attract things is called its magnetic field. The farther away from the magnet an item is, the weaker the magnetic field is. When it is weak, it is less likely an object will become attracted to the magnet. Magnets can be either permanent or temporary. A permanent magnet st ...
... where it has enough power to attract things is called its magnetic field. The farther away from the magnet an item is, the weaker the magnetic field is. When it is weak, it is less likely an object will become attracted to the magnet. Magnets can be either permanent or temporary. A permanent magnet st ...
By Erik,Brianna,michael,wyatt
... as the Earth's magnetosphere. That region contains a mix of electrically charged particles, and electric and magnetic rather than gravity determine its structure. We call it the Earth's atmosphere. ...
... as the Earth's magnetosphere. That region contains a mix of electrically charged particles, and electric and magnetic rather than gravity determine its structure. We call it the Earth's atmosphere. ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms
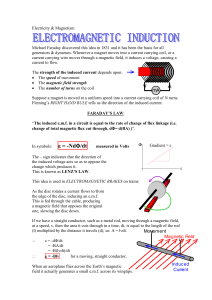
... Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms Solenoid|A long, helically wound coil of insulated wire. Magnetic domain|A group of atoms whose magnetic fields are aligned in the same direction. Magnetic field|A region in which a magnetic force can be detected. Electromagnetic induction|The process of crea ...
... Magnetism and Electromagnetism Key Terms Solenoid|A long, helically wound coil of insulated wire. Magnetic domain|A group of atoms whose magnetic fields are aligned in the same direction. Magnetic field|A region in which a magnetic force can be detected. Electromagnetic induction|The process of crea ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.























