Guided Reading 15.1
... ____ Attracting force ____ Repelling force ____ Twisting force (torque) 12. In the diagram above, imagine that you flip magnet C so that its south pole is closer to the source magnet. Now describe the net force felt by magnet C. ...
... ____ Attracting force ____ Repelling force ____ Twisting force (torque) 12. In the diagram above, imagine that you flip magnet C so that its south pole is closer to the source magnet. Now describe the net force felt by magnet C. ...
Magnetism - MWMS HW Wiki
... Magnetism was discovered in Magnesia Greece (which is now Turkey) A mineral in rocks that is magnetic was discovered. This mineral was called magnetite. The name of these rocks are called lodestones. ...
... Magnetism was discovered in Magnesia Greece (which is now Turkey) A mineral in rocks that is magnetic was discovered. This mineral was called magnetite. The name of these rocks are called lodestones. ...
Magnetism - schoolphysics
... 8. Write down four uses of permanent magnets. 9. You have two bars of metal of equal sizes, one is iron and the other one is steel. (a) Which one would you use to make a permanent magnet? and (b) Why? 10. Two iron rods are placed side by side in a solenoid. Describe and explain what will happen if a ...
... 8. Write down four uses of permanent magnets. 9. You have two bars of metal of equal sizes, one is iron and the other one is steel. (a) Which one would you use to make a permanent magnet? and (b) Why? 10. Two iron rods are placed side by side in a solenoid. Describe and explain what will happen if a ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... Know that magnetism is the force of ________________ _____ __________________of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af ...
... Know that magnetism is the force of ________________ _____ __________________of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af ...
Magnetism 4 Electromagnets
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...
I happen to have discovered a direct relation
... For example, rocks from Magnesia in Asia Minor (town of Tekin in modern day Turkey), from which the term “magnet” is derived, became magnets by being heated inside the Earth and then cooled. ...
... For example, rocks from Magnesia in Asia Minor (town of Tekin in modern day Turkey), from which the term “magnet” is derived, became magnets by being heated inside the Earth and then cooled. ...
magnetism - Gyanpedia
... 2- Every magnet has two poles and it is present towards the end of the magnet. 3- The magnet has directive properties. 4- Like poles repel and unlike poles attract each other. 5- The property of magnetism is destroyed in a magnet by striking through hammer or by heating in a flame. 6- The two poles ...
... 2- Every magnet has two poles and it is present towards the end of the magnet. 3- The magnet has directive properties. 4- Like poles repel and unlike poles attract each other. 5- The property of magnetism is destroyed in a magnet by striking through hammer or by heating in a flame. 6- The two poles ...
Coverage - Smart Science
... Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between permanent and temporary magnets. Recognise the properties of a magnetic field and be ...
... Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between permanent and temporary magnets. Recognise the properties of a magnetic field and be ...
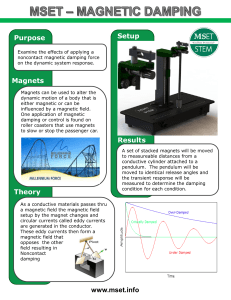
Purpose Magnets Theory Results www.mset.info Setup
... One application of magnetic damping or control is found on roller coasters that use magnets to slow or stop the passenger car. ...
... One application of magnetic damping or control is found on roller coasters that use magnets to slow or stop the passenger car. ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.