Chemistry Lesson Plans #12
... different orientations in space (x, y &z) o d orbitals are more like two sets of dumbbells at right angles to each other o f orbitals are too complex to visualize The p and d orbitals taper as they approach the nucleus, indicating areas where electrons have a low probability of existing. Where these ...
... different orientations in space (x, y &z) o d orbitals are more like two sets of dumbbells at right angles to each other o f orbitals are too complex to visualize The p and d orbitals taper as they approach the nucleus, indicating areas where electrons have a low probability of existing. Where these ...
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
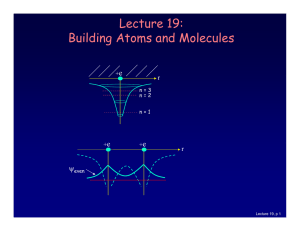
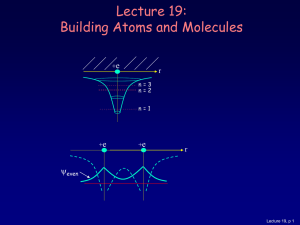
... Let’s consider what happens when there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels th ...
... Let’s consider what happens when there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels th ...
Electronic structure and spectroscopy
... In a cathode ray tube, independently of the material of the cathode, the same event can be observed: light spots (flashes) appear on the screen, i.e. a particles leave the cathode and fly against the plate. In an electric field, this particle deviates towards the positive pole, i.e. it must have a n ...
... In a cathode ray tube, independently of the material of the cathode, the same event can be observed: light spots (flashes) appear on the screen, i.e. a particles leave the cathode and fly against the plate. In an electric field, this particle deviates towards the positive pole, i.e. it must have a n ...
PPT
... Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
... Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 8. Use the mass number and atomic number to determine the element and its number of protons, electrons, and neutrons 9. Be able to determine the atomic number and mass number of an element when the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons is specified 10. How does mass number relate to number of p ...
... 8. Use the mass number and atomic number to determine the element and its number of protons, electrons, and neutrons 9. Be able to determine the atomic number and mass number of an element when the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons is specified 10. How does mass number relate to number of p ...
Why are the Co-based 115 compounds different?: The case study of
... Sign problems for the full magnetic Hamiltonian. Let's Include quantum fluctuations to the mean field solution. ...
... Sign problems for the full magnetic Hamiltonian. Let's Include quantum fluctuations to the mean field solution. ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 notes (10/20, PDF)
... _______________ __________________ Principle: any atomic orbital can contain at most ______ electrons but only if they have opposite __________. __________ is a quantum mechanical property that can be described as either ____________________ or ________________________________. _________ Rule: elect ...
... _______________ __________________ Principle: any atomic orbital can contain at most ______ electrons but only if they have opposite __________. __________ is a quantum mechanical property that can be described as either ____________________ or ________________________________. _________ Rule: elect ...
2 Chemical bonding is a genuinely quantum effect, which cannot be
... Chemical bonding is a genuinely quantum effect, which cannot be understood on the grounds of classical physics. However, the solution of the Schrödinger equation is numerically very expensive, and only small molecules can be treated quantum mechanically (up to ≈100 atoms). To be able to treat large ...
... Chemical bonding is a genuinely quantum effect, which cannot be understood on the grounds of classical physics. However, the solution of the Schrödinger equation is numerically very expensive, and only small molecules can be treated quantum mechanically (up to ≈100 atoms). To be able to treat large ...
presentation - WordPress.com
... The tendency of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity. Electronegativity difference affect bond type and explains which type of molecules formed; polar or non polar molecules. ...
... The tendency of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity. Electronegativity difference affect bond type and explains which type of molecules formed; polar or non polar molecules. ...
Chemistry XL-14A Nature of Light and the Atom
... Electron configuration – list of the electrons are in each orbital Pauli Exclusion Principle: • No more than 2 electrons in any orbital. • When 2 electrons do occupy one orbital, their spins are paired • 1 is spin up and 1 is spin down. • No 2 electrons in an atom can have the same set of 4 quantum ...
... Electron configuration – list of the electrons are in each orbital Pauli Exclusion Principle: • No more than 2 electrons in any orbital. • When 2 electrons do occupy one orbital, their spins are paired • 1 is spin up and 1 is spin down. • No 2 electrons in an atom can have the same set of 4 quantum ...
Exercised Review for Test
... B. Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line. 1. All the elements in a particular group of the periodic table have the same number of a. electrons. c. valence electrons. b. energy levels. d. protons. 2. What is the number of valence electrons in an atom of Al? a. 13 c ...
... B. Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line. 1. All the elements in a particular group of the periodic table have the same number of a. electrons. c. valence electrons. b. energy levels. d. protons. 2. What is the number of valence electrons in an atom of Al? a. 13 c ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.