Chapter 8
... precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. ...
... precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. ...
Final "I Can Statements" Answer Key
... Two allotropes of the same element have different molecular structures and therefore have different _physical___ and ___chemical_____ properties. ...
... Two allotropes of the same element have different molecular structures and therefore have different _physical___ and ___chemical_____ properties. ...
Zumdahl`s Chap. 4 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Use moles divided by Final Volume to get concentration of leftovers. ...
... Use moles divided by Final Volume to get concentration of leftovers. ...
NYS Regents Chemistry
... ground state – giving off the absorbed energy in the form of light. The amount of energy in the released light (wavelength) depends on how many energy levels the electron jumps back, how many other electrons are around and also the charge of the nucleus. Every element has a different number of elect ...
... ground state – giving off the absorbed energy in the form of light. The amount of energy in the released light (wavelength) depends on how many energy levels the electron jumps back, how many other electrons are around and also the charge of the nucleus. Every element has a different number of elect ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
Semiconductor/Electrolyte Interface
... • Chemical reactions preceding or following the electron transfer. • homogeneous processes (e.g., protonation or dimerization) • heterogeneous ones (e.g., catalytic decomposition) on the electrode surface. • Other surface reactions, • adsorption, • desorption, • crystallization (electrodeposition). ...
... • Chemical reactions preceding or following the electron transfer. • homogeneous processes (e.g., protonation or dimerization) • heterogeneous ones (e.g., catalytic decomposition) on the electrode surface. • Other surface reactions, • adsorption, • desorption, • crystallization (electrodeposition). ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element sodium? a. Ar b. Cs c. Ca d. Mg Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element selenium? a. Fe b. K c. P d. O Which of the following elements will have similar physical an ...
... Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element sodium? a. Ar b. Cs c. Ca d. Mg Which of the following elements has the same number of valence electrons as the element selenium? a. Fe b. K c. P d. O Which of the following elements will have similar physical an ...
1 • Introduction The Scientific Method (1 of 20) 1
... 2•Stoichiometry: Chemical Arithmetic Writing Formula Equations Things To Remember (11 of 24) ...
... 2•Stoichiometry: Chemical Arithmetic Writing Formula Equations Things To Remember (11 of 24) ...
Document
... Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? (A) It is spontaneous and requires an electric current. (B) It is spontaneous and produces an electric current. (C) It is non-spontaneous and requires an electric current. (D) It is non-spontaneous and produces ...
... Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? (A) It is spontaneous and requires an electric current. (B) It is spontaneous and produces an electric current. (C) It is non-spontaneous and requires an electric current. (D) It is non-spontaneous and produces ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... If a crystal of sodium chloride was hit firmly with a hammer, it would shatter. Again, care is needed—safety glasses must be worn. ...
... If a crystal of sodium chloride was hit firmly with a hammer, it would shatter. Again, care is needed—safety glasses must be worn. ...
Notebook - Science
... proton, present in all atomic nuclei except ordinary hydrogen electron: stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, acts as the primary carrier of electricity in solids element: distinguished by its atomic number, the number of protons in the nuclei of its atoms Chemistry: Matte ...
... proton, present in all atomic nuclei except ordinary hydrogen electron: stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, acts as the primary carrier of electricity in solids element: distinguished by its atomic number, the number of protons in the nuclei of its atoms Chemistry: Matte ...
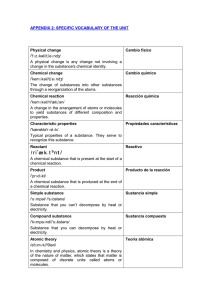
specific vocabulary of the unit
... Substance that you can decompose by heat or electricity. Atomic theory Teoría atómica /ə'tɒmɪk//'θiəri/ In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms or molecules. ...
... Substance that you can decompose by heat or electricity. Atomic theory Teoría atómica /ə'tɒmɪk//'θiəri/ In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms or molecules. ...
CHAPTER 2 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2.1 Chemical Elements
... 1. C; Hydrogen bonds do not hold heat energy, rather they require heat energy to be broken. They are strong enough to maintain the integrity of the DNA molecule. 2. D; Hydrogen bonds are readily broken and reformed, an ideal combination for the location between nucleic acids of the DNA strand. 3. A; ...
... 1. C; Hydrogen bonds do not hold heat energy, rather they require heat energy to be broken. They are strong enough to maintain the integrity of the DNA molecule. 2. D; Hydrogen bonds are readily broken and reformed, an ideal combination for the location between nucleic acids of the DNA strand. 3. A; ...
File
... v) Alkaline Earth Metal: the Alkaline Earth Metals is the common name for the Group II elements. The Alkaline Earth Metals include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, barium and radium. w) Noble Gas: the Noble Gases is the common name for the Group VIII elements. The Noble gas elements have a full outer ...
... v) Alkaline Earth Metal: the Alkaline Earth Metals is the common name for the Group II elements. The Alkaline Earth Metals include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, barium and radium. w) Noble Gas: the Noble Gases is the common name for the Group VIII elements. The Noble gas elements have a full outer ...
File - Mc Guckin Science
... o) Electron Configuration: a way of showing where the electrons are found in an atom. Includes the number of electrons found in each quantum level of the atom, arranged in order from lowest to highest energy. p) Orbital: a region in three-dimensional space around the nucleus of an atom where there i ...
... o) Electron Configuration: a way of showing where the electrons are found in an atom. Includes the number of electrons found in each quantum level of the atom, arranged in order from lowest to highest energy. p) Orbital: a region in three-dimensional space around the nucleus of an atom where there i ...
FE Exam review for Chemistry
... As temperature increases: solid liquid gas As pressure increases: gas liquid solid How do they differ in terms of: Solids > liquids > gases • density (abundance) Gas > liquid > solids • energy / movement • shape & compressibility Only gases can be compressed. Solids have definite shapes, but ...
... As temperature increases: solid liquid gas As pressure increases: gas liquid solid How do they differ in terms of: Solids > liquids > gases • density (abundance) Gas > liquid > solids • energy / movement • shape & compressibility Only gases can be compressed. Solids have definite shapes, but ...
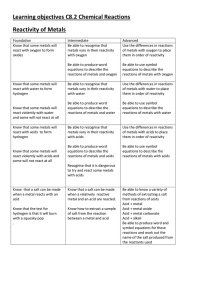
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... are more reactive than others and this allows us to place the metals in order of reactivity Understand that the reactivity of a metal affects what it’s uses are ...
... are more reactive than others and this allows us to place the metals in order of reactivity Understand that the reactivity of a metal affects what it’s uses are ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... do not have the ‘noble gas’ structures (SO3, SF6, XeF4, AlCl3, and possibly - depending upon how the formalism is applied - B2H6). On its own, this approach has little to say about why H2O is so much more stable than H2O2, for example - as both can be shown to ‘have’ (or perhaps better, mimic?) nobl ...
... do not have the ‘noble gas’ structures (SO3, SF6, XeF4, AlCl3, and possibly - depending upon how the formalism is applied - B2H6). On its own, this approach has little to say about why H2O is so much more stable than H2O2, for example - as both can be shown to ‘have’ (or perhaps better, mimic?) nobl ...
Exam Review
... 22. The formation of bonds between atoms depends on __. a) the electron configurations of the atoms involved c) both of the preceding factors b) the attraction the atoms have for electrons d) neither of the preceding factors 23. The particle that results when two or more atoms form covalent bonds is ...
... 22. The formation of bonds between atoms depends on __. a) the electron configurations of the atoms involved c) both of the preceding factors b) the attraction the atoms have for electrons d) neither of the preceding factors 23. The particle that results when two or more atoms form covalent bonds is ...
Question 2
... Predict if a precipitation reaction will occur in each of the following cases. If it does, write the full, balanced equation AND the net ionic equation (including state symbols) to show the formation of the precipitate. If there is no reaction, say so, and indicate why. (9) a) CuSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ...
... Predict if a precipitation reaction will occur in each of the following cases. If it does, write the full, balanced equation AND the net ionic equation (including state symbols) to show the formation of the precipitate. If there is no reaction, say so, and indicate why. (9) a) CuSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure and Properties
... 3.2-2. Shielding and Effective Nuclear Charge Core electrons shield valence electrons better than do other valence electrons. The nuclear charge experienced by an electron affects the size and energy of its orbitals, so it is an important factor in determining the properties of the valence electrons ...
... 3.2-2. Shielding and Effective Nuclear Charge Core electrons shield valence electrons better than do other valence electrons. The nuclear charge experienced by an electron affects the size and energy of its orbitals, so it is an important factor in determining the properties of the valence electrons ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...