Chemistry basics powerpoint Chapter 2
... atoms’ valence orbitals In a covalent bond, the s and p orbitals may hybridize, creating specific molecular shapes ...
... atoms’ valence orbitals In a covalent bond, the s and p orbitals may hybridize, creating specific molecular shapes ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... Graphite/diamond is the hardest natural substance known because all its bonds are strong/weak covalent bonds. Graphite/diamond is a very slippery substance because the bonds between/inside the layers of carbon atoms are weak/strong and easily broken so the layers can slide over each other easily. Me ...
... Graphite/diamond is the hardest natural substance known because all its bonds are strong/weak covalent bonds. Graphite/diamond is a very slippery substance because the bonds between/inside the layers of carbon atoms are weak/strong and easily broken so the layers can slide over each other easily. Me ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Differentiate between ionic and covalent using the chemical formulas. Describe the arrangement of ions in a crystal lattice. List and explain the physical properties of ionic compounds. Draw Lewis diagrams for molecular substances. Differentiate between single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Def ...
... Differentiate between ionic and covalent using the chemical formulas. Describe the arrangement of ions in a crystal lattice. List and explain the physical properties of ionic compounds. Draw Lewis diagrams for molecular substances. Differentiate between single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Def ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... 40. An ionic bond forms between what types of elements? A metal and a nonmetal An ionic bond is the attraction between positively charged metal cations and negatively charged anions. In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from the metal (cation) to the nonmetal (anion). What is the structure of ...
... 40. An ionic bond forms between what types of elements? A metal and a nonmetal An ionic bond is the attraction between positively charged metal cations and negatively charged anions. In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from the metal (cation) to the nonmetal (anion). What is the structure of ...
Electron
... • An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time • Each electron shell consists of a specific number of orbitals ...
... • An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time • Each electron shell consists of a specific number of orbitals ...
g - Porterville College Home
... naming of binary molecular compounds because they have similar formulas. Binary molecular compounds are named using the greek prefixes. Do not allow other instances of Greek or similar prefixes to confuse use in naming some of the oxyanions. For example, Cr2O72- is named dichromate. This has nothing ...
... naming of binary molecular compounds because they have similar formulas. Binary molecular compounds are named using the greek prefixes. Do not allow other instances of Greek or similar prefixes to confuse use in naming some of the oxyanions. For example, Cr2O72- is named dichromate. This has nothing ...
- Palisades School District
... If an element has several possible positive oxidation states, assume complete oxidation occurs during single replacement reactions and use the highest charge, but during composition reactions use the most stable oxidation state. ...
... If an element has several possible positive oxidation states, assume complete oxidation occurs during single replacement reactions and use the highest charge, but during composition reactions use the most stable oxidation state. ...
Question 1. Phosgene was used during the World War - IQ
... Consider half-cell A and B, draw an electrochemical cell with spontaneous reaction (write the global equation) and calculate the cell potential. Furthermore, you need to indicate: the flow of electrons, cathode and anode. (b) Metallic copper (Cu0) can be dissolved by HNO3(conc) and it is observed th ...
... Consider half-cell A and B, draw an electrochemical cell with spontaneous reaction (write the global equation) and calculate the cell potential. Furthermore, you need to indicate: the flow of electrons, cathode and anode. (b) Metallic copper (Cu0) can be dissolved by HNO3(conc) and it is observed th ...
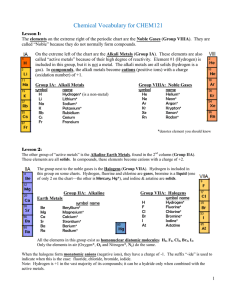
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Compounds may be divided into 2 general types: 1. Molecular (covalent) compounds are combinations of non-metals 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecul ...
... Compounds may be divided into 2 general types: 1. Molecular (covalent) compounds are combinations of non-metals 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecul ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...
Chapter 2
... • An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time • Each electron shell consists of a specific number of orbitals ...
... • An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time • Each electron shell consists of a specific number of orbitals ...
Transition-Metal Carbides. A Comparison of Bonding in Extended
... with carbon are also shown in this figure. Bonding with carbon is accomplished by orbitals of a,, symmetry (carbon s) and tl, symmetry (carbon p). There is only one alg orbital derived from the frontier set of Ru(CO)~,and it is occupied. On the other hand, there are two tl, sets, one occupied and on ...
... with carbon are also shown in this figure. Bonding with carbon is accomplished by orbitals of a,, symmetry (carbon s) and tl, symmetry (carbon p). There is only one alg orbital derived from the frontier set of Ru(CO)~,and it is occupied. On the other hand, there are two tl, sets, one occupied and on ...
Chapter 1 ELECTROMAGNETICS OF METALS
... with varying degrees of attenuation, depending on the details of the electronic band structure. Alkali metals such as sodium have an almost free-electron-like response and thus exhibit an ultraviolet transparency. For noble metals such as gold or silver on the other hand, transitions between electro ...
... with varying degrees of attenuation, depending on the details of the electronic band structure. Alkali metals such as sodium have an almost free-electron-like response and thus exhibit an ultraviolet transparency. For noble metals such as gold or silver on the other hand, transitions between electro ...
as a PDF
... The mathematics of the theory of Table 1.1 therefore accounts for the variations in both I3 and in the stability of alkaline earth-like dihalides. There remains the question of a physical explanation. The most important irregularity is the very large downward break after the half-filled shell, and t ...
... The mathematics of the theory of Table 1.1 therefore accounts for the variations in both I3 and in the stability of alkaline earth-like dihalides. There remains the question of a physical explanation. The most important irregularity is the very large downward break after the half-filled shell, and t ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... Many/strong covalent bonds need to be broken If any other element mentioned other than C, CE = 0 Ignore the no of covalent bonds around the C if mentioned The first 3 marks could be scored with a labelled diagram. Need to label or state covalent bonds within the layers. Covalent or ionic or metallic ...
... Many/strong covalent bonds need to be broken If any other element mentioned other than C, CE = 0 Ignore the no of covalent bonds around the C if mentioned The first 3 marks could be scored with a labelled diagram. Need to label or state covalent bonds within the layers. Covalent or ionic or metallic ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...
... The distribution of the elements in the Earth’s layers was controlled by their chemical affinity for one of the three phases. Elements with low or high electronegativity tended to congregate in the silicate phase as ionic compounds. These included active metals and nonmetals. ...
Document
... Carrying out the titration 1. A pipette-filler is added to the volumetric pipette. 2. Some of the solution is drawn into the pipette. The pipette is tilted and rotated so that all the surfaces are rinsed in the solution. 3. The rinsing solution is then discarded. 4. The solution is drawn into the pi ...
... Carrying out the titration 1. A pipette-filler is added to the volumetric pipette. 2. Some of the solution is drawn into the pipette. The pipette is tilted and rotated so that all the surfaces are rinsed in the solution. 3. The rinsing solution is then discarded. 4. The solution is drawn into the pi ...
Group 1: The Alkali Metals
... their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are characterized as being extremely soft and silvery in color. They also have low boiling and melting points and are less dense than most elements. Li, Na, and K float on water because of their low densities. All of ...
... their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are characterized as being extremely soft and silvery in color. They also have low boiling and melting points and are less dense than most elements. Li, Na, and K float on water because of their low densities. All of ...
File
... for the first 3 energy levels, the maximum number of electrons that can be present are 2, 8 and 8 in order of increasing energy (increasing distance from nucleus) a lower energy level is filled with electrons to its maximum before the next level is started. the electrons in the highest (outerm ...
... for the first 3 energy levels, the maximum number of electrons that can be present are 2, 8 and 8 in order of increasing energy (increasing distance from nucleus) a lower energy level is filled with electrons to its maximum before the next level is started. the electrons in the highest (outerm ...
CHEM 20 FINAL EXAM: STUDY HEADINGS Jan 2012
... molecular bonds: sigma and pi bonds; delocalized pi bonds in benzene, C6H6 determining and indicating direction of dipole within a covalent bond predicting the polarity of molecules from dipole moments and molecular geometry intermolecular forces: van der waals, hydrogen bonding, dispersion forces, ...
... molecular bonds: sigma and pi bonds; delocalized pi bonds in benzene, C6H6 determining and indicating direction of dipole within a covalent bond predicting the polarity of molecules from dipole moments and molecular geometry intermolecular forces: van der waals, hydrogen bonding, dispersion forces, ...
Day 13 Main Group Pt 1
... There are important differences between hydrogen and the alkali metals within the +1 oxidation state. The alkali metals utilize the +1 oxidation state in all of their common ionic salts and thus exhibit ionic character. Hydrogen in the +1 oxidation state is generally covalent. For example, hydrogen ...
... There are important differences between hydrogen and the alkali metals within the +1 oxidation state. The alkali metals utilize the +1 oxidation state in all of their common ionic salts and thus exhibit ionic character. Hydrogen in the +1 oxidation state is generally covalent. For example, hydrogen ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... A. They are made up of individual molecules A.They are made of ions arranged in a crystal lattice B. The bonding forces in they are very weak D. The bonding forces in them are very strong 15. Which property of ionic substance leads scientists to infer that ionic substance can break down into mobile, ...
... A. They are made up of individual molecules A.They are made of ions arranged in a crystal lattice B. The bonding forces in they are very weak D. The bonding forces in them are very strong 15. Which property of ionic substance leads scientists to infer that ionic substance can break down into mobile, ...
Honors Chemistry Final Review
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...
Language of chemistry
... All matter in the universe exists in any of four different states. They are: 1. Solid state 2. Liquid state 3. Gaseous state 4. Plasma state ...
... All matter in the universe exists in any of four different states. They are: 1. Solid state 2. Liquid state 3. Gaseous state 4. Plasma state ...
Lecture 6 - TCD Chemistry
... t1u ligands in one axis contribute – With opposite phase – one nodal plane – Interaction with p orbitals 3 ...
... t1u ligands in one axis contribute – With opposite phase – one nodal plane – Interaction with p orbitals 3 ...