Ionic Bonding www.AssignmentPoint.com Ionic bonding is a type of
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
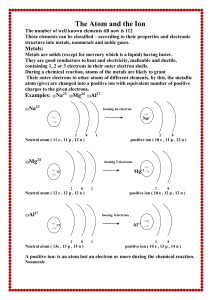
The Atom and the Ion
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... 1. The energy required to break the bond between two covalently bonded atoms. 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend ...
... 1. The energy required to break the bond between two covalently bonded atoms. 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend ...
Inroduction, Drude model
... CMP serves as a counterpoint to the ‘reductionism’. In the reductionist approach, complex systems are studied by breaking them down into smaller, fundamental units. This is exemplified by particle accelerator physics in which atoms are broken down into nucleons, which are further broken down into qu ...
... CMP serves as a counterpoint to the ‘reductionism’. In the reductionist approach, complex systems are studied by breaking them down into smaller, fundamental units. This is exemplified by particle accelerator physics in which atoms are broken down into nucleons, which are further broken down into qu ...
CHEMISTRY
... – The proportion of atoms are always fixed • Chemical formula shows the kind and proportion of atoms of each element that occurs in a particular compound ...
... – The proportion of atoms are always fixed • Chemical formula shows the kind and proportion of atoms of each element that occurs in a particular compound ...
Chapter 2
... stable When valence shell is not full, atoms tend to lose, gain, or share electrons ...
... stable When valence shell is not full, atoms tend to lose, gain, or share electrons ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... most compounds! ● EXAMPLE: 1 molecule of water, H2O, is the smallest unit of water possible; it consists of 2 hydrogen atoms & 1 oxygen atom bonded together. ...
... most compounds! ● EXAMPLE: 1 molecule of water, H2O, is the smallest unit of water possible; it consists of 2 hydrogen atoms & 1 oxygen atom bonded together. ...
Practice Exam 2 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Electronegativity is a measure of A. the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. C. the magnitude of the negative charge on an electron. E. the magnitude of the negative charge on a molecule. ...
... Electronegativity is a measure of A. the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. C. the magnitude of the negative charge on an electron. E. the magnitude of the negative charge on a molecule. ...
Chemistry Final Study Guide
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... Predicting properties using other elements data: Example: Predict the density of Aluminum given: Density: Ga = 5.9 g/cm3 & B = 2.3 g/cm3 ...
... Predicting properties using other elements data: Example: Predict the density of Aluminum given: Density: Ga = 5.9 g/cm3 & B = 2.3 g/cm3 ...
Unit 1 - Morgan Science
... ◦ Ability of an atom to attract an electron from another atom when in a compound. Noble gases are usually omitted since they don’t form compounds ...
... ◦ Ability of an atom to attract an electron from another atom when in a compound. Noble gases are usually omitted since they don’t form compounds ...
Section 3: Crystal Binding
... negatively charged free electrons in a metal serve as glue that holds positively charged ions together. The metallic bond is somewhat weaker than the ionic and covalent bond. For instance the melting temperature of metallic sodium is about 400o which is smaller than 1100o in NaCl and about 4000o in ...
... negatively charged free electrons in a metal serve as glue that holds positively charged ions together. The metallic bond is somewhat weaker than the ionic and covalent bond. For instance the melting temperature of metallic sodium is about 400o which is smaller than 1100o in NaCl and about 4000o in ...
C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... Nanoscience is the study of small particles that are between 1 and 100 nanometres in size 1 nanometre (1 nm) = 1 x 10-9 metres (0.000 000 001m or a billionth of a metre) Nanoparticles show different properties to the same materials in bulk and have a high surface area to volume ratio. This may lead ...
... Nanoscience is the study of small particles that are between 1 and 100 nanometres in size 1 nanometre (1 nm) = 1 x 10-9 metres (0.000 000 001m or a billionth of a metre) Nanoparticles show different properties to the same materials in bulk and have a high surface area to volume ratio. This may lead ...
Document
... Nanoscience is the study of small particles that are between 1 and 100 nanometres in size 1 nanometre (1 nm) = 1 x 10-9 metres (0.000 000 001m or a billionth of a metre) Nanoparticles show different properties to the same materials in bulk and have a high surface area to volume ratio. This may lead ...
... Nanoscience is the study of small particles that are between 1 and 100 nanometres in size 1 nanometre (1 nm) = 1 x 10-9 metres (0.000 000 001m or a billionth of a metre) Nanoparticles show different properties to the same materials in bulk and have a high surface area to volume ratio. This may lead ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... occurs between oppositely charged ions to hold them close together to become stable (like two magnets) • Ion: an atom that no longer has a neutral charge because it has lost or gained an electron • Typically between a metal & non-metal • Ex. Na+Cl- ...
... occurs between oppositely charged ions to hold them close together to become stable (like two magnets) • Ion: an atom that no longer has a neutral charge because it has lost or gained an electron • Typically between a metal & non-metal • Ex. Na+Cl- ...
chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... obtaining fully occupied outermost electron subshell. Depending on the starting point - in which direction the target is closer - they can ‘accept’ (acceptor) electrons from other atoms or ‘donate’ (donor) electrons to the bond (share them). • Additionally, bonding is also beneficial energetically – ...
... obtaining fully occupied outermost electron subshell. Depending on the starting point - in which direction the target is closer - they can ‘accept’ (acceptor) electrons from other atoms or ‘donate’ (donor) electrons to the bond (share them). • Additionally, bonding is also beneficial energetically – ...
atoms-chemical
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
2.1 Atoms and Bonds
... A chemical change occurs when compounds are formed Reactants are particles that are present before the reaction Products are particles that are present after the reaction Of the form: Reactant Products ◦ Ex: 2H2 + O2 2H2O ...
... A chemical change occurs when compounds are formed Reactants are particles that are present before the reaction Products are particles that are present after the reaction Of the form: Reactant Products ◦ Ex: 2H2 + O2 2H2O ...
Document
... Answer the following questions by circling the correct response on the answer sheet provided. (1 mark each) 16. The subatomic particle that has the smallest mass is the a.electron b.proton c. neutron d.nucleus 17. The atomic mass of barium is due to the number of a. neutrons and electrons in the nuc ...
... Answer the following questions by circling the correct response on the answer sheet provided. (1 mark each) 16. The subatomic particle that has the smallest mass is the a.electron b.proton c. neutron d.nucleus 17. The atomic mass of barium is due to the number of a. neutrons and electrons in the nuc ...
Ei otsikkoa
... Even higher oxidation states occur, but those are found in covalent bonds or the polyatomic ions: oxyanions. Examples: Cr2O72, MnO4 ...
... Even higher oxidation states occur, but those are found in covalent bonds or the polyatomic ions: oxyanions. Examples: Cr2O72, MnO4 ...