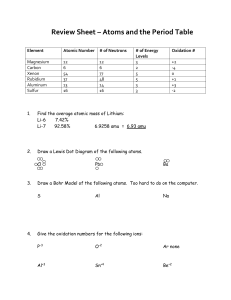
chapt02_lecture from text
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Ele ...
... charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Ele ...
Midterm Review Sample Content Questions
... 17. Which of the ions in problem 15 are anions? How would you recognize an anion? 18. What is the significance of Rutherford’s gold foil experimentation? 19. What is the significance of the Plum pudding model of the atom? 20. Bohr is known for the “planetary model” of the atom – what does this mean? ...
... 17. Which of the ions in problem 15 are anions? How would you recognize an anion? 18. What is the significance of Rutherford’s gold foil experimentation? 19. What is the significance of the Plum pudding model of the atom? 20. Bohr is known for the “planetary model” of the atom – what does this mean? ...
File
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to ...
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... 17. What are elements in the groups 3-12 called? ___________________________________ 18. Know what happens to the size of atoms as you move across a period or down a group. Know which member of the following pairs of particles is larger: Pd, Rb; Mg, Ba; Cs, Lu; Se, O. 19. Which of the following atom ...
... 17. What are elements in the groups 3-12 called? ___________________________________ 18. Know what happens to the size of atoms as you move across a period or down a group. Know which member of the following pairs of particles is larger: Pd, Rb; Mg, Ba; Cs, Lu; Se, O. 19. Which of the following atom ...
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS In solid substances electricity is
... as metals, semiconductors or insulators. In metals electrons are the only charge carriers and their concentration is very high because of the overlapping that takes place between the valence and the conduction band. In semiconductors however, this concentration depends on the energy gap between band ...
... as metals, semiconductors or insulators. In metals electrons are the only charge carriers and their concentration is very high because of the overlapping that takes place between the valence and the conduction band. In semiconductors however, this concentration depends on the energy gap between band ...
Table showing examples of Complex ions with their bond
... +2). Under certain circumstances a further electron may be lost form the 3d sub-level, to give the Fe3+ ion (O.S. of +3). Also ‘d’ electrons may be used for covalent bonding as in the ferrates (e.g. K 2+ FeO42— ), where oxidation state is +6. Mn, with the highest number of unpaired electrons shows w ...
... +2). Under certain circumstances a further electron may be lost form the 3d sub-level, to give the Fe3+ ion (O.S. of +3). Also ‘d’ electrons may be used for covalent bonding as in the ferrates (e.g. K 2+ FeO42— ), where oxidation state is +6. Mn, with the highest number of unpaired electrons shows w ...
video slide
... Happens between molecules a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
... Happens between molecules a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
Test 1 - UTC.edu
... 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's mass is equal to that of a proton plus an electron. D) An ...
... 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's mass is equal to that of a proton plus an electron. D) An ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... The formula for the hydronium ion is a. H+ b. H3O+ c. OH- d. HCa5(PO4)3 is held together by a. freely moving electrons b. hydrogen bonds between molecules c. shared electron pairs d. electrostatic attraction between ions What is the purpose of a catalysts a. it permits reactants to start at lower nr ...
... The formula for the hydronium ion is a. H+ b. H3O+ c. OH- d. HCa5(PO4)3 is held together by a. freely moving electrons b. hydrogen bonds between molecules c. shared electron pairs d. electrostatic attraction between ions What is the purpose of a catalysts a. it permits reactants to start at lower nr ...
www.theallpapers.com
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
oxidation number
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Quantum mechanical model (Werner Heisenberg): Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
... Quantum mechanical model (Werner Heisenberg): Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Quantum mechanical model (Werner Heisenberg): Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
... Quantum mechanical model (Werner Heisenberg): Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
inorganic-chemistry-gp-i-alkali-metals
... very accurate order are trend is irregular. Keeping this point in mind will help in resolving reactions with lithium compounds. Flame Test . ...
... very accurate order are trend is irregular. Keeping this point in mind will help in resolving reactions with lithium compounds. Flame Test . ...
Classification – 3 main groups
... Chemical Change- The substance has changed in color, or it fizzed, bubbled, created an odor, got warmer or colder ( temp. change caused by the chemical reaction ). The original substance is no longer there; frying an egg, any type of cooking, alka seltzer and water Physical Change- A noticeable chan ...
... Chemical Change- The substance has changed in color, or it fizzed, bubbled, created an odor, got warmer or colder ( temp. change caused by the chemical reaction ). The original substance is no longer there; frying an egg, any type of cooking, alka seltzer and water Physical Change- A noticeable chan ...
Review Sheet Filled Out
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 21. Which of the following always indicates that a chemical reaction has taken place? a. production of a gas b. absorption of heat c. change in colour d. appearance of a new substance ...
... 21. Which of the following always indicates that a chemical reaction has taken place? a. production of a gas b. absorption of heat c. change in colour d. appearance of a new substance ...
Document
... site, by a dopant with either extra or less electrons. In general, “metallic” dopants will substitute on the “metal” sites and “non-metallic” dopants will substitute on non-metal sites. For the case where the dopant is between the two elements in the compound, substitution can be amphoteric (i.e. on ...
... site, by a dopant with either extra or less electrons. In general, “metallic” dopants will substitute on the “metal” sites and “non-metallic” dopants will substitute on non-metal sites. For the case where the dopant is between the two elements in the compound, substitution can be amphoteric (i.e. on ...
Chemistry MSL Practical Style Review 1. What is the nuclear
... 10. What type of bonding is associated with compounds that have the following characteristics: •high melting points •conduct electricity in the molten state •solutions conduct electricity •normally crystalline solids at room temperature. A B C D ...
... 10. What type of bonding is associated with compounds that have the following characteristics: •high melting points •conduct electricity in the molten state •solutions conduct electricity •normally crystalline solids at room temperature. A B C D ...
PPT
... the interaction energy is estimated to be about 10 MHz. The frequency of the coupling is qubit state-dependent (because (er) is state-dependent). This forms the basis of the quantum logic gates like the CNOT gate. However, it is strongly distance-dependent. Thus, interactions are limited to nearest ...
... the interaction energy is estimated to be about 10 MHz. The frequency of the coupling is qubit state-dependent (because (er) is state-dependent). This forms the basis of the quantum logic gates like the CNOT gate. However, it is strongly distance-dependent. Thus, interactions are limited to nearest ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... Covalent compound – a compound formed between two or more non-metals with bonds that are formed by sharing electrons. Metallic compound – a compound formed between metals with bonds that consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. ...
... Covalent compound – a compound formed between two or more non-metals with bonds that are formed by sharing electrons. Metallic compound – a compound formed between metals with bonds that consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. ...