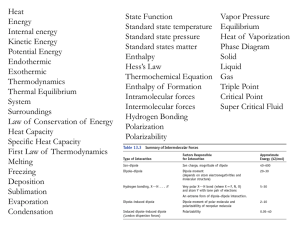
Nature of Molecules and Water
... partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water molecules • Each individual bond is weak • Cumulative effects are enormous • Responsible for many of water’s important physical ...
... partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water molecules • Each individual bond is weak • Cumulative effects are enormous • Responsible for many of water’s important physical ...
Atomic Theory Practice Test
... ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms results from the attraction between electrons and a. Lewis structures. c. van der Waals forces. b. ...
... ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms results from the attraction between electrons and a. Lewis structures. c. van der Waals forces. b. ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never __________ or destroyed. ...
... (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never __________ or destroyed. ...
File
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
Chapter 2
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
File
... shells that are either completely full or completely empty. • If we know the electron configuration of an atom we can usually work out how many electrons it must lose or gain to achieve a noble gas configuration. • This will tell us the charge on its ion. ...
... shells that are either completely full or completely empty. • If we know the electron configuration of an atom we can usually work out how many electrons it must lose or gain to achieve a noble gas configuration. • This will tell us the charge on its ion. ...
CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure
... • Form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons • Fills outer shell • Results in no net charge, no unpaired electrons • Strength of covalent bond depends on the number of shared electrons ...
... • Form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons • Fills outer shell • Results in no net charge, no unpaired electrons • Strength of covalent bond depends on the number of shared electrons ...
Final Exam Review Answers
... b. decreases from top to bottom within a group. c. remains constant within a period. d. decreases from left to right across a period. ...
... b. decreases from top to bottom within a group. c. remains constant within a period. d. decreases from left to right across a period. ...
2 - Castle High School
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...
Chapt9
... the H-Cl bond is described as "polar" and is said to have a "dipole" the entire HCl molecule is also polar as a result more complex molecules can be polar or nonpolar, depending on their 3-D shape (Later) ...
... the H-Cl bond is described as "polar" and is said to have a "dipole" the entire HCl molecule is also polar as a result more complex molecules can be polar or nonpolar, depending on their 3-D shape (Later) ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... Bases- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range for bases: ____________ True / False. Strong Acids and Strong Bases are both corrosive, which means they eat away at body tissue and dissolve other objects, and should always be ...
... Bases- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range for bases: ____________ True / False. Strong Acids and Strong Bases are both corrosive, which means they eat away at body tissue and dissolve other objects, and should always be ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron configurations of ions; atomic properties and periodic trends; periodic trends and chemical properties. 12. An electron microscope employs a beam of electrons to obtain an image of an object. What energy must ...
... atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron configurations of ions; atomic properties and periodic trends; periodic trends and chemical properties. 12. An electron microscope employs a beam of electrons to obtain an image of an object. What energy must ...
Document
... associated with that color; in this case Blue is 6. •Now 'read' the next color, here it is red so write down a '2' next to the six. (you should have '62' so far.) •Now read the third or 'multiplier' band and write down that number of zeros. •In this example it is two so we get '6200' or '6,200'. If ...
... associated with that color; in this case Blue is 6. •Now 'read' the next color, here it is red so write down a '2' next to the six. (you should have '62' so far.) •Now read the third or 'multiplier' band and write down that number of zeros. •In this example it is two so we get '6200' or '6,200'. If ...
All of these can affect the rate at which a
... 60. In many compounds, atoms of main-group elements form bonds so that the number of electrons in the outermost energy levels of each atom is A 10 B 8. C 6. D 2 61. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? A oct ...
... 60. In many compounds, atoms of main-group elements form bonds so that the number of electrons in the outermost energy levels of each atom is A 10 B 8. C 6. D 2 61. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? A oct ...
Unit 1, Lecture 1
... No more than one alpha (or spin up) and one beta (or spin down) electron can occupy a particular orbital at any time (also called Pauli Exclusion Principle) If degenerate orbitals are available, they will be singly occupied first, then doubly. ...
... No more than one alpha (or spin up) and one beta (or spin down) electron can occupy a particular orbital at any time (also called Pauli Exclusion Principle) If degenerate orbitals are available, they will be singly occupied first, then doubly. ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
... Point out that the more outer-shell electrons, the more electrons are delocalised and the stronger the attraction (e.g. m.pt. Al > Mg > Na). ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... 1. Metallic Bond 2. Covalent Bond 3. Ionic Bond ...
... 1. Metallic Bond 2. Covalent Bond 3. Ionic Bond ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
... atoms electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativities. This is seen in water (H2O). More electronegative atoms tend to pull electrons toward them creating a polar molecule. ...
... atoms electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativities. This is seen in water (H2O). More electronegative atoms tend to pull electrons toward them creating a polar molecule. ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...
... Nature of Atoms • Matter has mass and occupies space • All matter is composed of atoms • Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the nature of biological molecules ...