Final Study Guide (Semester 2) Answer Key
... ***The first thing you should do when solving this is look at the common ion chart and write down all the ions. It’s much easier than looking them up again for each question. a. Write the balanced molecular equation. Include phase symbols. Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3 (aq) Switch the c ...
... ***The first thing you should do when solving this is look at the common ion chart and write down all the ions. It’s much easier than looking them up again for each question. a. Write the balanced molecular equation. Include phase symbols. Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3 (aq) Switch the c ...
Prospective Chemistry Teachers` Conceptions of Chemical
... this second group of studies is called chemical kinetics. The inter-relationship of chemical thermodynamics and chemical kinetics is an issue of some interest and complexity. However, for chemical reactions that are readily amendable to kinetic study, the reactant and product species are usually all ...
... this second group of studies is called chemical kinetics. The inter-relationship of chemical thermodynamics and chemical kinetics is an issue of some interest and complexity. However, for chemical reactions that are readily amendable to kinetic study, the reactant and product species are usually all ...
Research on Hydrogenation of FAME to Fatty Alcohols
... velocity increased. Compared with 0.15~0.4h-1 space velocity which calculated according to tradition process of hydrogenolysis of fatty acid methyl ester, supercritical reaction technology was taken, but there was 90% solvent remaining in reaction materials. When the space velocity of mixture made o ...
... velocity increased. Compared with 0.15~0.4h-1 space velocity which calculated according to tradition process of hydrogenolysis of fatty acid methyl ester, supercritical reaction technology was taken, but there was 90% solvent remaining in reaction materials. When the space velocity of mixture made o ...
Stoichiometry - Norbraten
... - be sure to maintain the coefficient ratio in the balanced equation. 1. Sodium sulfate reacts with carbon to form sodium sulfide and carbon dioxide. How many moles of carbon are needed to completely react with 5.15 moles of sodium sulfate? 2. Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to form nitric acid a ...
... - be sure to maintain the coefficient ratio in the balanced equation. 1. Sodium sulfate reacts with carbon to form sodium sulfide and carbon dioxide. How many moles of carbon are needed to completely react with 5.15 moles of sodium sulfate? 2. Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to form nitric acid a ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions: An Introduction
... • Shorthand way of describing a reaction • Provides information about the reaction: – Formulas of reactants and products – States of reactants and products – Relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required – Can be used to determine weights of reactants used and of products that ...
... • Shorthand way of describing a reaction • Provides information about the reaction: – Formulas of reactants and products – States of reactants and products – Relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required – Can be used to determine weights of reactants used and of products that ...
Chemistry - Pearson School
... 20.5 Free Energy and Redox Reactions Relationship of free energy (∆G) to cell potential, Faraday’s constant, predicting the direction of the reaction 20.7 Batteries and Fuel Cells Electrical energy from batteries, lead-acid, alkaline, nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal-hydride, lithium-ion, hydrogen fuel ...
... 20.5 Free Energy and Redox Reactions Relationship of free energy (∆G) to cell potential, Faraday’s constant, predicting the direction of the reaction 20.7 Batteries and Fuel Cells Electrical energy from batteries, lead-acid, alkaline, nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal-hydride, lithium-ion, hydrogen fuel ...
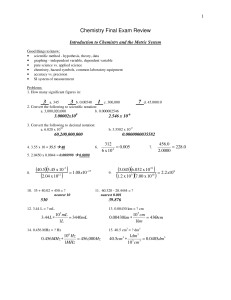
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... 6. What is the relative rate of helium (He) gas vs. chlorine (Cl2) gas? Which one diffuses faster? ...
... 6. What is the relative rate of helium (He) gas vs. chlorine (Cl2) gas? Which one diffuses faster? ...
Chemistry Unit Summaries - Oak Park Unified School District
... Molar mass (MM) is the sum of atomic masses in the chemical The electronic structure of an atom describes the energies formula. For example, the mass of one H2O molecule is 18.0 u, and arrangement of electrons around the atom. Much of what is so the molar mass of H2O is 18.0 g. known about the elect ...
... Molar mass (MM) is the sum of atomic masses in the chemical The electronic structure of an atom describes the energies formula. For example, the mass of one H2O molecule is 18.0 u, and arrangement of electrons around the atom. Much of what is so the molar mass of H2O is 18.0 g. known about the elect ...
Ch 17 Equilibrium Notes
... CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM • The state where the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with them. • All reactions are reversible. • Forward and reverse rates are equal at equilibrium. • Any chemical reaction carried out in a close vessel reaches equilibrium. • On the molecular level ...
... CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM • The state where the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with them. • All reactions are reversible. • Forward and reverse rates are equal at equilibrium. • Any chemical reaction carried out in a close vessel reaches equilibrium. • On the molecular level ...
Chemistry
... Batteries: types-difference, examples, Leclanche cell (dry cell) and Lead acid battery–anode, cathode, electrolyte, reactions at anode and cathode (diagram not required), Fuel cell – definition – examples, H2-O2 fuel cell – schematic diagram, anode, cathode, electrolyte, reactions at anode and catho ...
... Batteries: types-difference, examples, Leclanche cell (dry cell) and Lead acid battery–anode, cathode, electrolyte, reactions at anode and cathode (diagram not required), Fuel cell – definition – examples, H2-O2 fuel cell – schematic diagram, anode, cathode, electrolyte, reactions at anode and catho ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Homework Booklet Unit 1 Feb14
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
- Catalyst
... Step 1) Write the half-reactions for the chemical equation. Step 2) For each reaction, balance the atoms other than O and H. Step 3) Add H2O to balance O, then H+ to balance H. Step 4) Balance the charge by adding electrons. The net charge of the reactants should equal the net charge of the products ...
... Step 1) Write the half-reactions for the chemical equation. Step 2) For each reaction, balance the atoms other than O and H. Step 3) Add H2O to balance O, then H+ to balance H. Step 4) Balance the charge by adding electrons. The net charge of the reactants should equal the net charge of the products ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.