Balancing chemical equations notes
... chemicals are combined together and what chemicals are made when a reaction occurs. The law of conservation of mass says that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, and this requires that all chemical reactions be balanced. Consider the following balanced equation: Cu (s) + 4 HNO3 (aq) Cu(NO ...
... chemicals are combined together and what chemicals are made when a reaction occurs. The law of conservation of mass says that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, and this requires that all chemical reactions be balanced. Consider the following balanced equation: Cu (s) + 4 HNO3 (aq) Cu(NO ...
Balanced Chemical Reaction Equations
... reacts with 5 molecules of oxygen to produce 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and 4 molecules of water. Or you could say, 1 mole of propane reacts with 5 moles of oxygen to produce 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water. (The scene closes as Dr. Dave rushes off to a faculty meeting, and the thr ...
... reacts with 5 molecules of oxygen to produce 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and 4 molecules of water. Or you could say, 1 mole of propane reacts with 5 moles of oxygen to produce 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water. (The scene closes as Dr. Dave rushes off to a faculty meeting, and the thr ...
Kinetics - Chemistry Geek
... The experimental rate law for the reaction between NO2 and CO to produce NO and CO2 is rate = k[NO2]2. The reaction is believed to occur via two steps: ...
... The experimental rate law for the reaction between NO2 and CO to produce NO and CO2 is rate = k[NO2]2. The reaction is believed to occur via two steps: ...
MIDDLE COLLEGE HIGH SCHOOL
... The rate of this reaction can be increased by (1) formation of a precipitate using 5.0 grams of powdered zinc instead of a (2) formation of a gas 5.0-gram strip of zinc because the powdered (3) effective collisions between reacting zinc has particles (1) lower kinetic energy (4) addition of a cataly ...
... The rate of this reaction can be increased by (1) formation of a precipitate using 5.0 grams of powdered zinc instead of a (2) formation of a gas 5.0-gram strip of zinc because the powdered (3) effective collisions between reacting zinc has particles (1) lower kinetic energy (4) addition of a cataly ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
... • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
Matter and Energy
... each element and is multiplied by each subscript to find the total number of atoms of each element and a total number of atoms in the molecule. ...
... each element and is multiplied by each subscript to find the total number of atoms of each element and a total number of atoms in the molecule. ...
hc1(8)notes
... reactants and products with appropriate symbols and formulas. • A formula equation represents the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas. • example: The formula equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ...
... reactants and products with appropriate symbols and formulas. • A formula equation represents the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas. • example: The formula equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ...
Mass-Mass Stoichiometry
... Barium Nitrate reacts with Sodium Sulfate to produce Barium Sulfate and Sodium Nitrate. If we react 12.0 grams of Barium Nitrate with 6.0 grams of Sodium Sulfate, A) what mass of Barium Sulfate will we be able to produce? B) Which reactant is the limiting reagent? C) How many grams of the excess rea ...
... Barium Nitrate reacts with Sodium Sulfate to produce Barium Sulfate and Sodium Nitrate. If we react 12.0 grams of Barium Nitrate with 6.0 grams of Sodium Sulfate, A) what mass of Barium Sulfate will we be able to produce? B) Which reactant is the limiting reagent? C) How many grams of the excess rea ...
CHEMISTRY A
... and hydrogen in the presence of copper, zinc oxide and alumina which act as a catalyst. This is a reversible reaction. CO(g) + 2H2(g) ...
... and hydrogen in the presence of copper, zinc oxide and alumina which act as a catalyst. This is a reversible reaction. CO(g) + 2H2(g) ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
decomposition - Chemical Minds
... 10) Some dry copper(II) hydroxide was heated in a test tube over a Bunsen burner. When a piece of blue cobalt chloride paper was held in the mouth of the test tube, the paper turned pink. Discuss what happened in the reaction in the test tube. Your answer should include any observations that would o ...
... 10) Some dry copper(II) hydroxide was heated in a test tube over a Bunsen burner. When a piece of blue cobalt chloride paper was held in the mouth of the test tube, the paper turned pink. Discuss what happened in the reaction in the test tube. Your answer should include any observations that would o ...
GC97F Pretest A - American Chemical Society
... This test is designed to be taken with an answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. All answers are to be marked on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test book ...
... This test is designed to be taken with an answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. All answers are to be marked on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test book ...
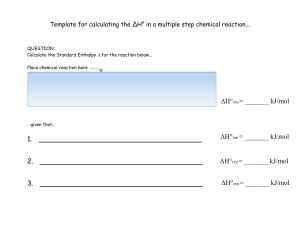
Template for calculating the ΔH° in a multiple step chemical reaction
... 20. _______________ systems can exchange energy and mass, whereas ________________ systems allow the transfer of energy (heat) but not mass. 21. What is the third type of system in Thermochemistry? __________________ 22. LIST three examples of an intensive property: 23. LIST three examples of an ext ...
... 20. _______________ systems can exchange energy and mass, whereas ________________ systems allow the transfer of energy (heat) but not mass. 21. What is the third type of system in Thermochemistry? __________________ 22. LIST three examples of an intensive property: 23. LIST three examples of an ext ...
THE GENERAL LAW OF CHEMICAL KINETICS, DOES IT EXIST?
... Imagine that hydrogen oxidation reaction is performed under steady-state or pseudo-steady-state conditions. It means that concentrations of intermediates are governed by gas concentrations. Do we know, how to present the reaction rate as a function of main reactant and product concentrations (hydrog ...
... Imagine that hydrogen oxidation reaction is performed under steady-state or pseudo-steady-state conditions. It means that concentrations of intermediates are governed by gas concentrations. Do we know, how to present the reaction rate as a function of main reactant and product concentrations (hydrog ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium Review Page 1
... Kinetics and Equilibrium Review 35. When AgNO3(aq) is mixed with NaCl(aq), a reaction occurs which tends to go to completion and not reach equilibrium because A) a gas is formed B) water is formed C) a weak acid is formed D) a precipitate is formed 36. The vapor pressure of a liquid at a given temp ...
... Kinetics and Equilibrium Review 35. When AgNO3(aq) is mixed with NaCl(aq), a reaction occurs which tends to go to completion and not reach equilibrium because A) a gas is formed B) water is formed C) a weak acid is formed D) a precipitate is formed 36. The vapor pressure of a liquid at a given temp ...
examples of chemical and physical reactions.
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
e c n i
... The activation energy is the energy needed by a system to initiate the reaction. It is the minimum energy needed for a specific chemical reaction to occur. Once achieved, the reaction continues until reactants are ...
... The activation energy is the energy needed by a system to initiate the reaction. It is the minimum energy needed for a specific chemical reaction to occur. Once achieved, the reaction continues until reactants are ...
CHM 101 THERMOCHEMISTRY DEFINITIONS ENERGY is the
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
... 0.1 mol of Ca reacts with 880 g water, 2.24 L of hydrogen gas forms (at STP). How would the amount of hydrogen produced change if the volume of water was decreased to 440 mL (440 g)? When two substances react to form products, the reactant which is used up is called the ____. ...
File
... D. Venting some CO2 gas from the flask 111. In a sealed bottle that is half full of water, equilibrium will be attained when water molecules A. Cease to evaporate B. Begin to condense C. Are equal in number for both the liquid and the gas phase D. Evaporate and condense at equal rates 112. At equili ...
... D. Venting some CO2 gas from the flask 111. In a sealed bottle that is half full of water, equilibrium will be attained when water molecules A. Cease to evaporate B. Begin to condense C. Are equal in number for both the liquid and the gas phase D. Evaporate and condense at equal rates 112. At equili ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.